Unveiling the Secrets of Weather: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Weather: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Weather: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Weather: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/isobarmap-56a9e0d25f9b58b7d0ffa3cf.gif)
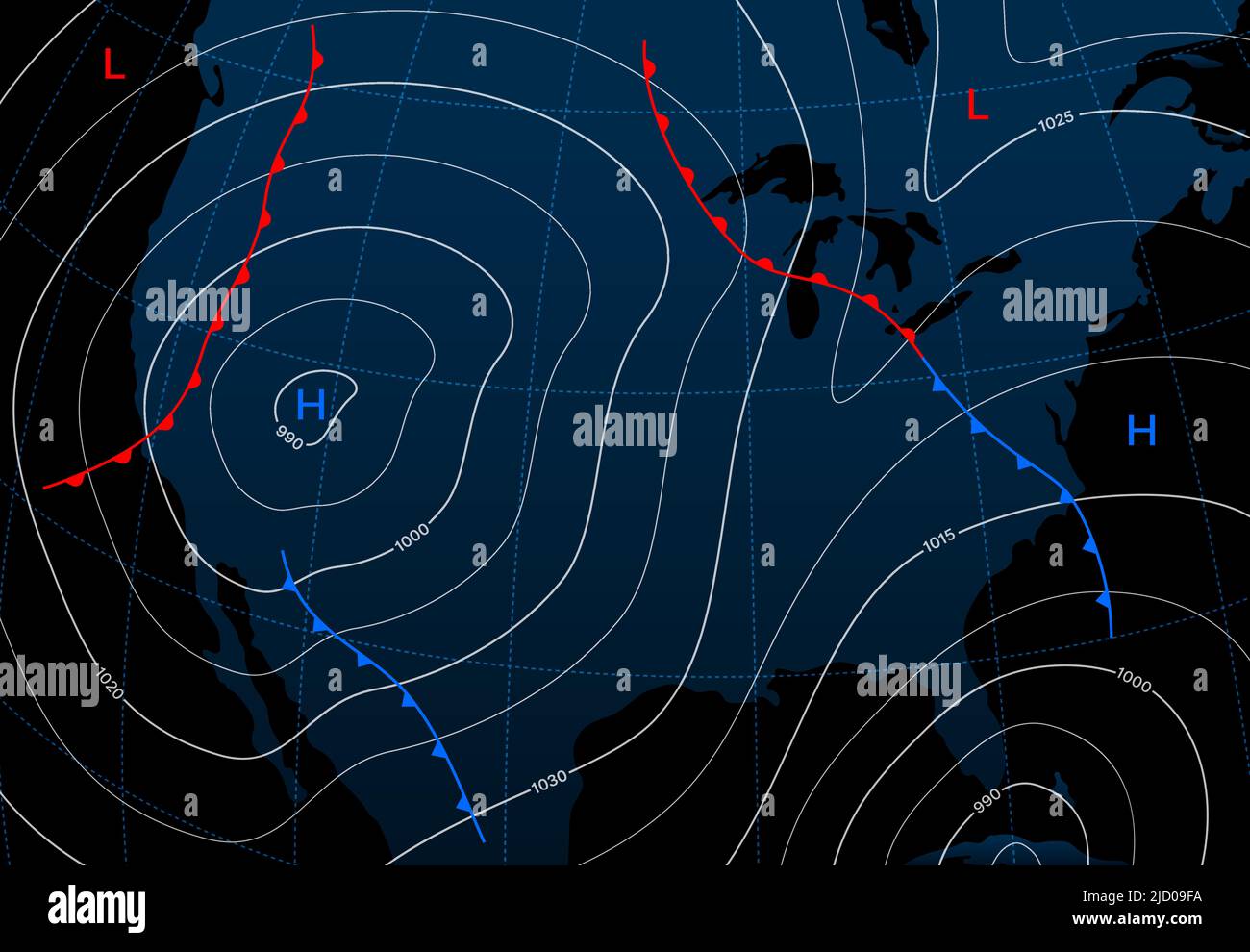
Weather maps, those colorful and intricate diagrams we often see in news reports, hold a wealth of information about the atmospheric conditions that shape our daily lives. One of the most fundamental elements of these maps, often represented by smooth, flowing lines, are isobars. These lines, seemingly simple at first glance, hold the key to understanding the dynamics of wind, pressure, and the potential for storms and other weather events.
Isobars are lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure, the weight of the air above a particular point, plays a crucial role in weather patterns. Areas of high pressure are typically associated with clear skies and calm conditions, while low-pressure areas are often linked to stormy weather and strong winds. Isobars, by visually representing these pressure gradients, provide a powerful tool for meteorologists and weather enthusiasts alike.
The Significance of Isobars:
Isobars are more than just lines on a map; they represent the invisible forces that drive weather patterns. The closer the isobars are to each other, the steeper the pressure gradient, indicating a greater difference in pressure over a short distance. This steep gradient creates stronger winds, as air rushes from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. Conversely, when isobars are spaced farther apart, the pressure gradient is gentler, resulting in weaker winds.
Interpreting Isobars: A Window into Weather Dynamics
Understanding the relationship between isobars and wind is crucial for interpreting weather maps. The direction of wind flow is determined by the pressure gradient, with wind moving perpendicular to the isobars.
-
High Pressure Systems: Isobars surrounding high-pressure areas are typically circular, with higher pressure in the center. Winds in these systems rotate clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. These systems are often associated with clear skies, calm conditions, and generally pleasant weather.
-
Low Pressure Systems: Isobars surrounding low-pressure areas also form circular patterns, but with lower pressure in the center. Winds in these systems rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. These systems are often associated with stormy weather, cloud formation, and precipitation.
Beyond Wind: Isobars and Weather Phenomena
Isobars provide valuable insights into other weather phenomena:
-
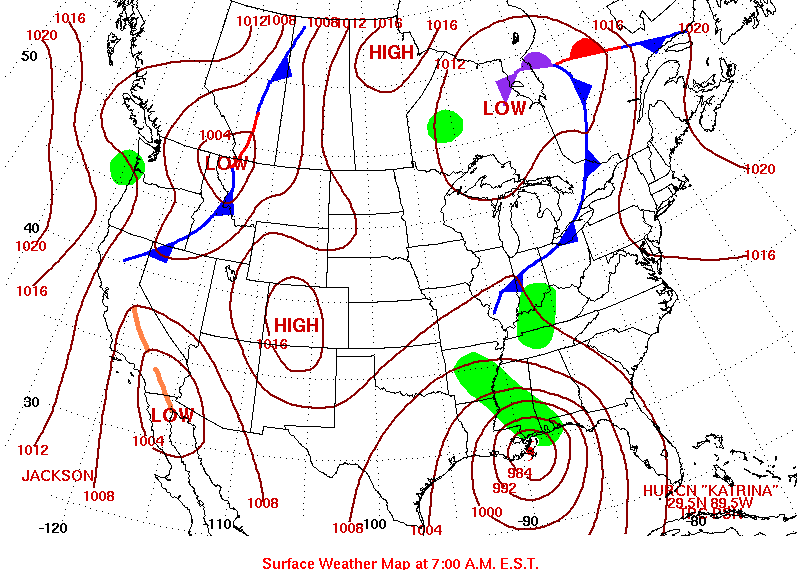
Frontal Systems: Isobars can help identify frontal boundaries, where contrasting air masses meet. These boundaries are often marked by a sharp change in pressure and can lead to significant weather changes, including precipitation, thunderstorms, and shifts in temperature.
-
Jet Streams: Isobars can also be used to track jet streams, fast-flowing air currents high in the atmosphere. These powerful winds play a significant role in steering weather systems and influencing temperature patterns.
-
Tropical Cyclones: Isobars are essential for tracking and predicting the path of tropical cyclones. The tightly packed isobars around the center of a cyclone indicate strong winds and potential for heavy rainfall and storm surges.
Utilizing Isobars for Informed Decisions
Isobars are vital tools for meteorologists, providing them with valuable data for forecasting weather patterns. By analyzing the spacing, shape, and movement of isobars, meteorologists can predict wind speeds, precipitation levels, and the potential for severe weather events. This information is crucial for issuing timely warnings and allowing people to prepare for potential hazards.
FAQs about Isobars on Weather Maps
Q: How are isobars drawn on weather maps?
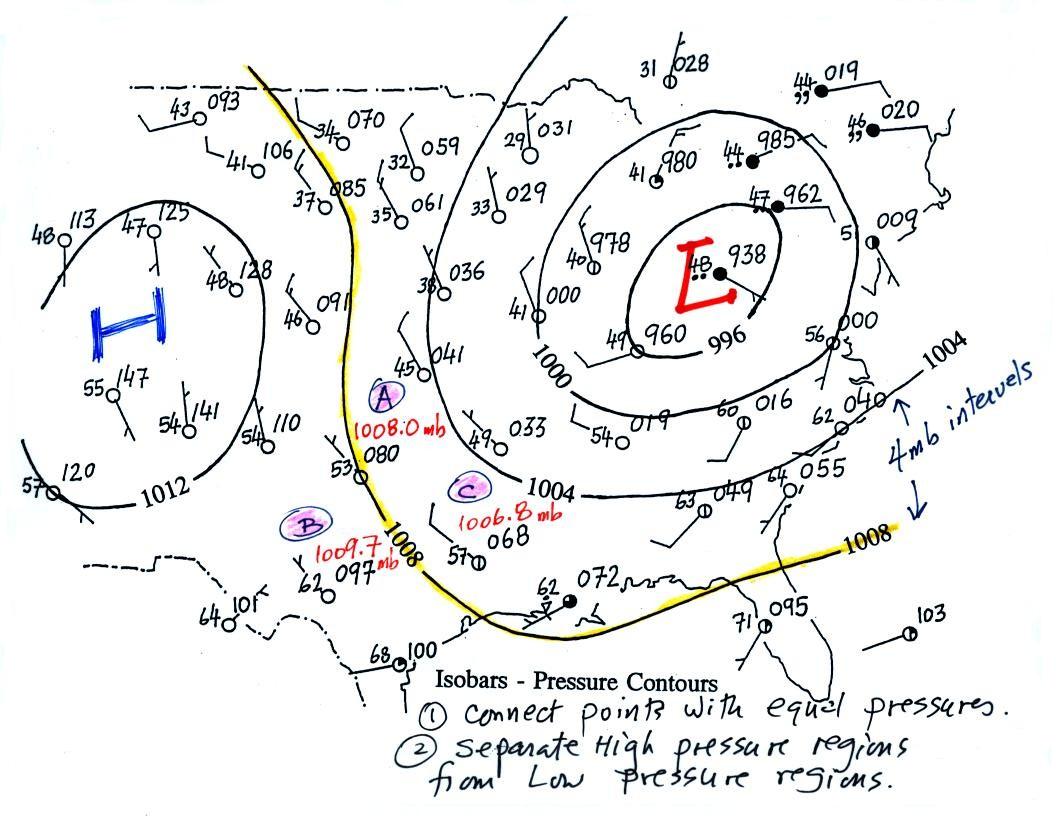
A: Isobars are drawn based on pressure readings taken at various weather stations across a region. These readings are then plotted on a map, and lines are drawn connecting points of equal pressure.
Q: What are the units used for measuring atmospheric pressure?
A: Atmospheric pressure is typically measured in millibars (mb) or hectopascals (hPa). These units are equivalent, with 1 hPa equal to 1 mb.
Q: Can isobars cross each other?
A: No, isobars cannot cross each other. This is because each isobar represents a specific pressure value, and two different pressure values cannot exist at the same location simultaneously.
Q: How do isobars help predict weather?
A: Isobars provide information about pressure gradients, which influence wind speed and direction. They also help identify areas of high and low pressure, indicating potential for clear or stormy weather.
Q: What are some limitations of using isobars for weather forecasting?
A: While isobars offer valuable insights, they are just one piece of the complex puzzle of weather forecasting. Other factors, such as temperature, humidity, and wind shear, also play a significant role in shaping weather patterns.
Tips for Reading Isobars on Weather Maps
-
Focus on the spacing: Closely spaced isobars indicate a steep pressure gradient and strong winds. Widely spaced isobars suggest a gentle pressure gradient and weaker winds.
-
Look for patterns: Circular patterns around high and low-pressure areas provide insights into wind direction and potential weather conditions.
-
Consider the context: Isobars are most useful when interpreted alongside other weather data, such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
Conclusion
Isobars are essential elements of weather maps, providing a visual representation of atmospheric pressure and its influence on wind patterns and weather phenomena. By understanding the relationship between isobars and pressure gradients, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of weather systems and make informed decisions about our daily lives. Whether it’s preparing for a storm, planning an outdoor activity, or simply understanding the forces shaping our environment, isobars offer a window into the intricate world of weather.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Pacific-Ocean_HLcenters-noaa-OPC-58b740303df78c060e196387.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Weather: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!