Unveiling the Power of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Statistics
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Statistics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Statistics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Statistics

The world is a tapestry woven with intricate patterns of human activity and natural phenomena. Understanding these patterns requires more than just looking at individual points of data; it demands a holistic view, a way to visualize and analyze information across space. This is where map statistics, the art and science of extracting meaningful insights from geographic data, comes into play.
The Essence of Map Statistics
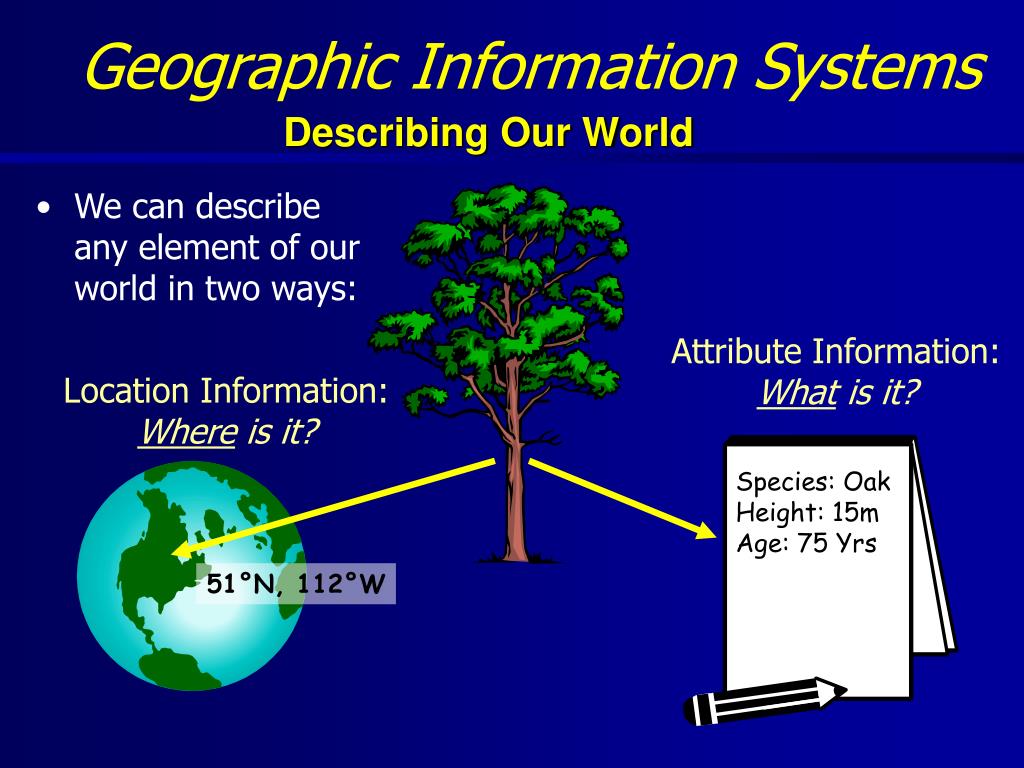
At its core, map statistics involves the application of statistical methods to spatial data. This data, often represented in the form of maps, can encompass a wide range of information, including population density, environmental conditions, economic indicators, crime rates, and disease outbreaks. By analyzing this data through a geographic lens, map statistics allows us to uncover spatial relationships, identify trends, and make informed decisions based on the distribution and interaction of phenomena across space.
The Building Blocks of Spatial Analysis
Map statistics relies on a foundation of spatial analysis techniques, each offering unique perspectives on geographic data. These techniques can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Descriptive Statistics: These techniques provide basic summaries of spatial data, such as the mean, median, and standard deviation of a variable across a geographic region. They help in understanding the general characteristics and distribution of data.
- Spatial Autocorrelation: This technique assesses the degree to which values at nearby locations are similar or dissimilar. It helps identify spatial patterns and understand how phenomena cluster or disperse across space.
- Spatial Regression: This technique explores the relationships between variables while accounting for their spatial location. It allows us to model how one variable influences another, considering the spatial context.
- Spatial Interpolation: This technique estimates values at unsampled locations based on data from known locations. It helps in creating continuous maps from scattered data points, providing a more complete picture of spatial patterns.
- Spatial Clustering: This technique identifies areas of high or low concentration of a particular phenomenon, revealing clusters of similar values within a geographic space.
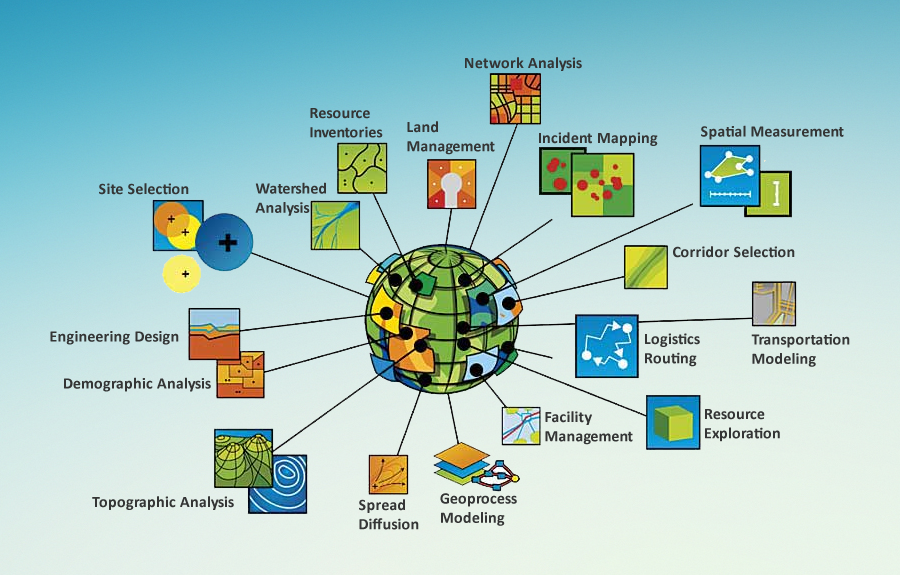
Applications Across Disciplines
The power of map statistics extends far beyond academic circles, finding practical applications in various fields:
- Urban Planning: Map statistics assists in understanding urban growth patterns, identifying areas of high population density, and optimizing infrastructure development.
- Environmental Management: Analyzing spatial patterns of pollution, deforestation, and climate change helps in developing effective conservation strategies and mitigating environmental risks.
- Public Health: Mapping disease outbreaks and identifying spatial patterns of health risks allows for targeted interventions and improved public health outcomes.
- Marketing and Business: Understanding customer demographics, market segmentation, and location-based consumer behavior helps businesses optimize marketing campaigns and target specific markets.
- Transportation Planning: Analyzing traffic patterns, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing transportation networks improves efficiency and reduces congestion.
Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of Map Statistics
The use of map statistics offers numerous benefits, making it an invaluable tool for decision-making and problem-solving across various sectors:
- Enhanced Data Visualization: Maps provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize data, making complex patterns and relationships easily understandable.
- Spatial Context Awareness: By considering the spatial context of data, map statistics helps in understanding the influence of location on various phenomena and their interactions.
- Improved Decision-Making: By revealing hidden trends and insights, map statistics empowers informed decision-making based on a comprehensive understanding of spatial patterns.
- Targeted Interventions: Identifying areas of high concentration or specific patterns allows for targeted interventions and resource allocation, maximizing efficiency and impact.
- Prediction and Forecasting: By analyzing historical spatial data, map statistics can help in predicting future trends and forecasting potential outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are some common software tools used for map statistics?
A: Popular software tools for map statistics include ArcGIS, QGIS, GeoDa, R with spatial packages, and Python with libraries like Geopandas and Shapely. These tools offer a range of functionalities for data visualization, spatial analysis, and map creation.
Q: How can I learn more about map statistics?
A: Numerous online resources, courses, and books are available to learn about map statistics. Universities also offer degree programs in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and spatial analysis, providing comprehensive training in this field.
Q: What are some examples of real-world applications of map statistics?
A: Map statistics has been used to map the spread of COVID-19, identify areas at risk of natural disasters, optimize delivery routes for logistics companies, and target public health interventions in areas with high disease prevalence.
Tips for Effective Map Statistics
- Define your research question clearly: Ensure your analysis focuses on a specific question and the relevant data.
- Choose appropriate data sources: Select data that is relevant, accurate, and spatially referenced.
- Understand the limitations of your data: Be aware of potential biases, errors, and missing data.
- Use appropriate statistical methods: Select methods that are suitable for the type of data and research question.
- Visualize your results effectively: Use maps and other visual representations to communicate your findings clearly.
- Interpret your findings thoughtfully: Draw conclusions based on the evidence and consider the implications of your results.
Conclusion
Map statistics, with its ability to analyze spatial data and reveal hidden patterns, has become an indispensable tool in various fields. By understanding spatial relationships and leveraging the power of geographic data, map statistics empowers informed decision-making, enhances problem-solving, and ultimately contributes to a more informed and sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve and data becomes increasingly abundant, the role of map statistics will only become more crucial in shaping our understanding of the world and guiding our actions.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Statistics. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!