Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Accumulation Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Accumulation Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Accumulation Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Accumulation Maps
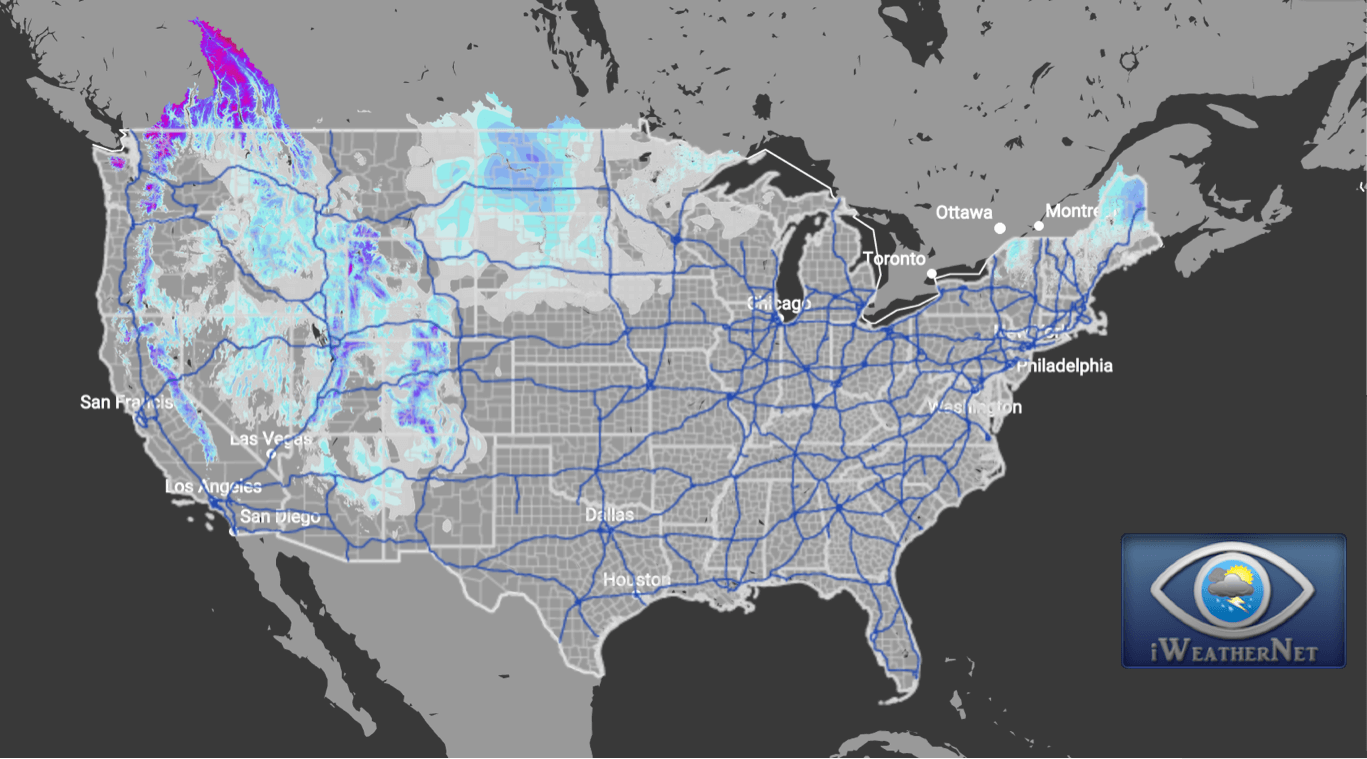
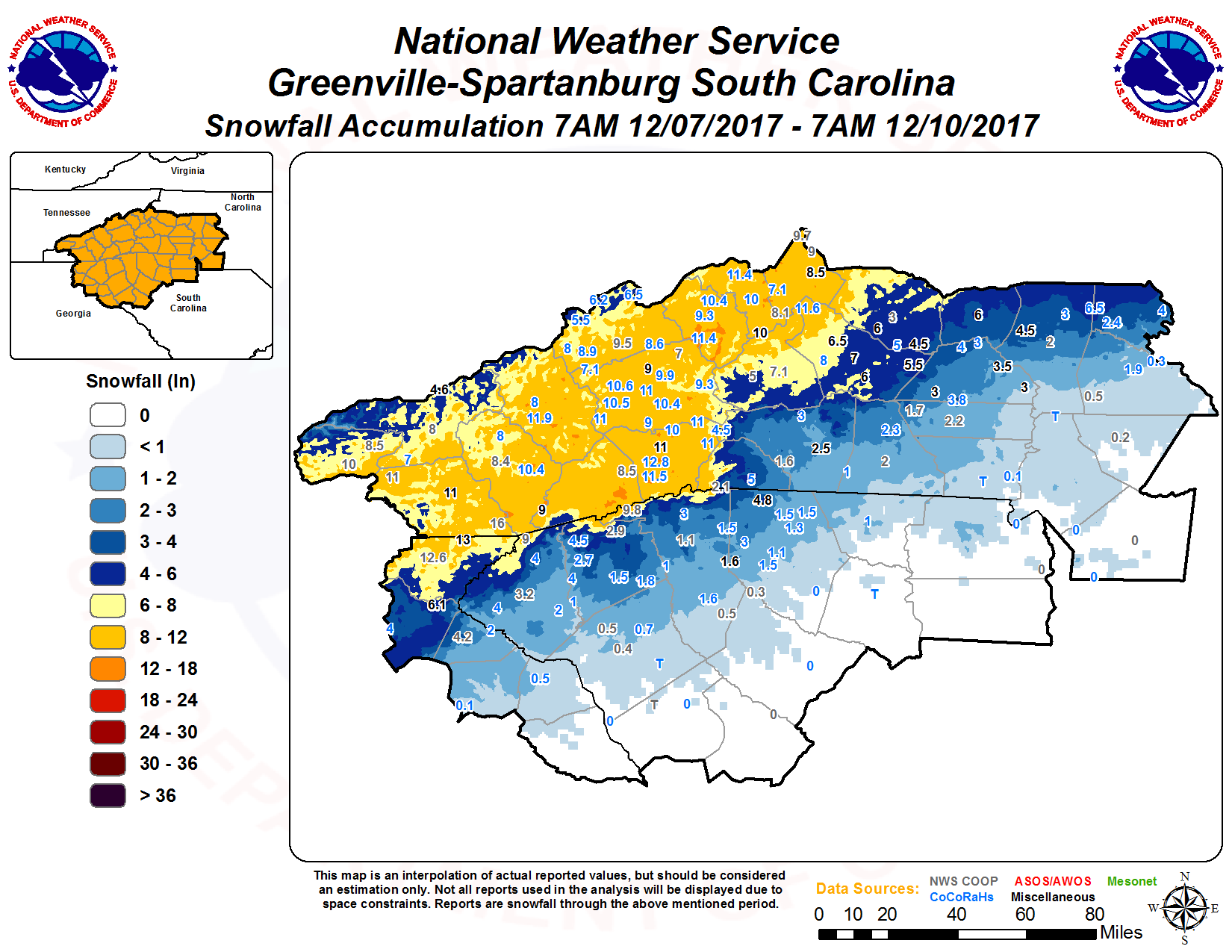
Snow, a seemingly simple element of nature, holds profound implications for our world. Its accumulation, distribution, and eventual melt play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems, influencing water resources, and impacting human activities. A current snow accumulation map, a visual representation of snow depth across a region, provides a powerful tool for understanding these intricate processes.
A Snapshot of Winter’s Legacy
Imagine a map, not of landforms or political boundaries, but of the white blanket that covers vast stretches of the Earth during winter. This is a current snow accumulation map. It paints a picture of snow depth, measured in inches or centimeters, across a specified area. This data, collected through satellite imagery, ground-based sensors, and weather station observations, offers a comprehensive view of the snowpack’s current state.
Beyond the Visual: Insights into the Snowpack
A current snow accumulation map is more than just a pretty picture; it’s a treasure trove of information. It reveals the spatial distribution of snow, highlighting areas of deep accumulation and regions where snow is scarce. This information is critical for various stakeholders:
- Hydrologists: Snowpack is a vital source of water for rivers and streams, especially in regions with arid climates. By analyzing snow accumulation maps, hydrologists can predict spring runoff, helping manage water resources and mitigate potential flooding.
- Water Resource Managers: Snow accumulation data informs decisions regarding water allocation, irrigation, and hydropower generation. Understanding snowpack dynamics allows for more effective management of these crucial resources.
- Ski Resorts: Snow accumulation maps are essential for ski resorts, providing insights into snow conditions and helping plan operations, including trail maintenance and snowmaking efforts.
- Transportation Agencies: Snow accumulation maps aid in planning snow removal efforts, ensuring safe road conditions and mitigating disruptions to transportation networks.
- Environmental Scientists: Snowpack plays a significant role in regulating ecosystems. Snow accumulation maps help monitor snowmelt timing, which influences plant growth, wildlife habitat, and overall ecosystem health.
- Climate Scientists: Snow accumulation data provides valuable insights into climate change impacts. Monitoring trends in snow depth and distribution over time reveals the influence of warming temperatures and altered precipitation patterns.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Symbols and Scales
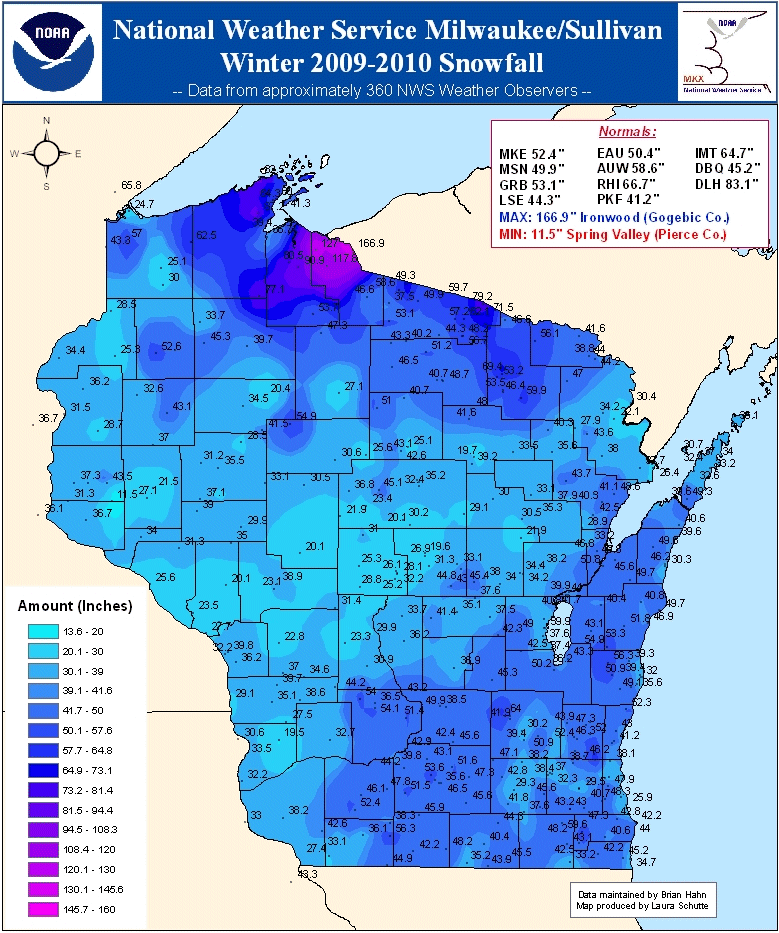
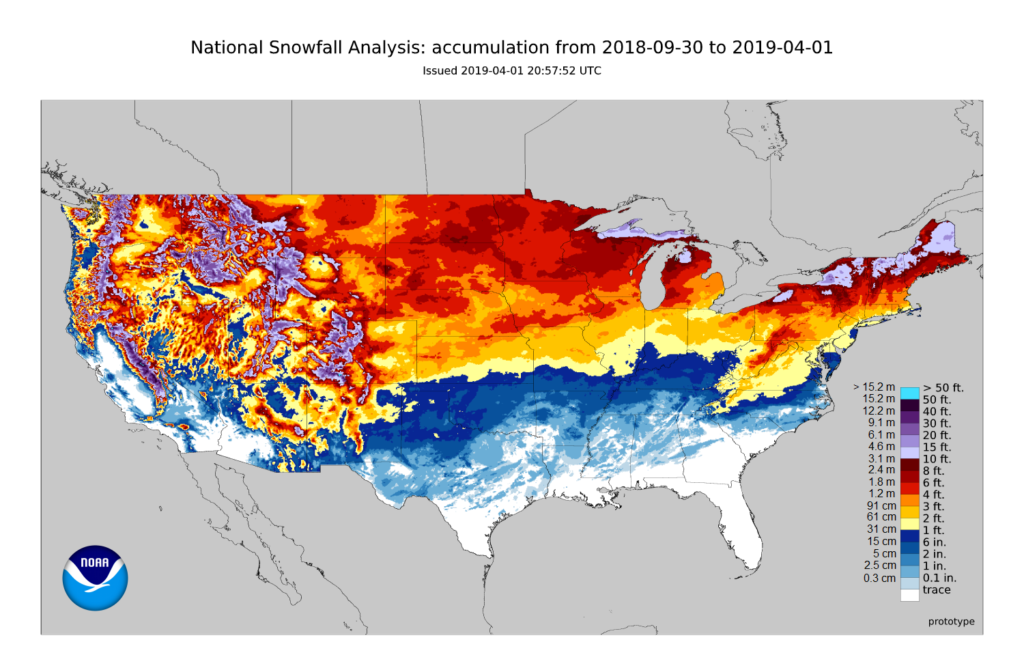
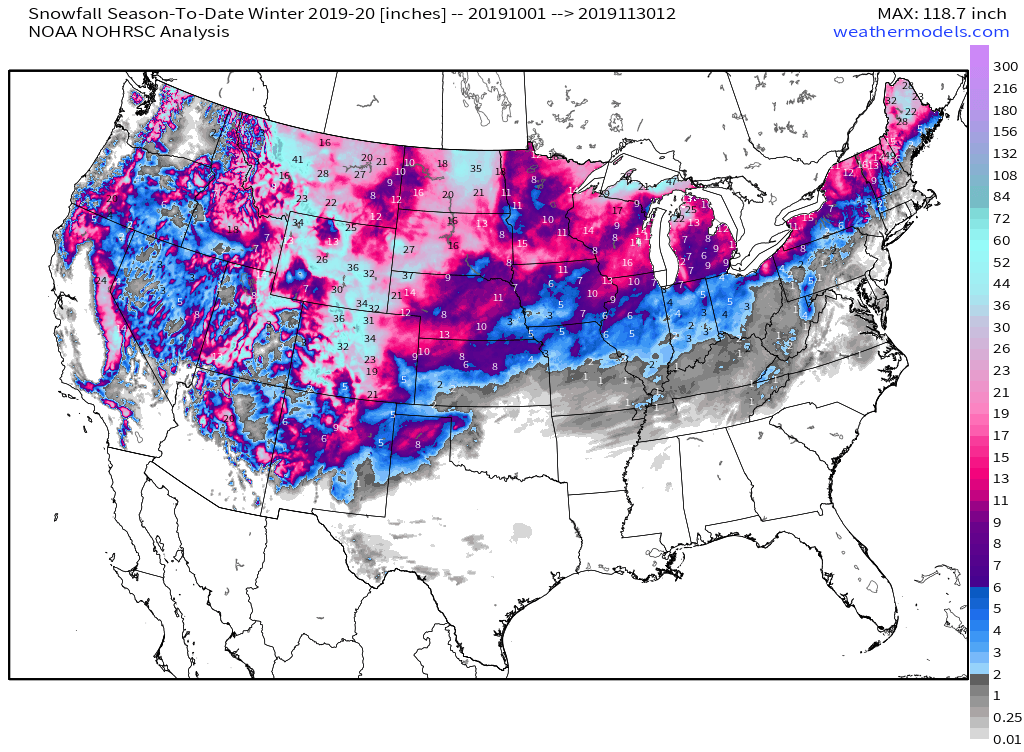
Current snow accumulation maps typically employ a color scheme to visually represent snow depth. Deeper snow is often depicted in darker shades, while lighter colors indicate less snow accumulation. The map’s legend clearly defines the color-depth relationship, ensuring accurate interpretation.
Additionally, the map may include contour lines, which connect points of equal snow depth, providing a more nuanced understanding of the snowpack’s topography. Scale bars and geographic coordinates help orient the map and pinpoint specific locations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Current Snow Accumulation Maps
Q: How often are snow accumulation maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates depends on the source of data and the specific application. Some maps are updated daily, while others may be updated weekly or even monthly.
Q: What is the accuracy of snow accumulation maps?
A: Accuracy varies depending on the data collection methods and the resolution of the map. Satellite imagery often provides a broader view, while ground-based sensors offer more localized, precise data.
Q: What are the limitations of current snow accumulation maps?
A: Snow accumulation maps provide a snapshot of the snowpack at a given time. They do not account for factors like snow density, which can significantly influence water content. Additionally, maps may not capture localized variations in snow depth due to terrain features and other factors.
Tips for Utilizing Current Snow Accumulation Maps
- Consider the source: Ensure the map is from a reputable source, such as a government agency or scientific organization.
- Pay attention to the date: The map reflects snow accumulation at a specific point in time. Be aware of the map’s date and potential changes in snow depth since then.
- Understand the scale: The map’s scale determines the level of detail it provides. A large-scale map may show detailed local variations, while a small-scale map provides a broader overview.
- Interpret the legend: Carefully review the map’s legend to understand the color scheme and the corresponding snow depths.
- Combine with other data: Integrating snow accumulation maps with other data sources, such as weather forecasts and historical snow records, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of snowpack dynamics.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Understanding Winter’s Impact
Current snow accumulation maps provide a valuable tool for understanding the distribution and dynamics of snowpack. This information is crucial for managing water resources, planning transportation infrastructure, and understanding the impacts of climate change. By leveraging these maps and integrating them with other data sources, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the vital role snow plays in shaping our world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Current Snow Accumulation Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!