Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Soil Survey Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Soil Survey Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Soil Survey Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Soil Survey Mapping
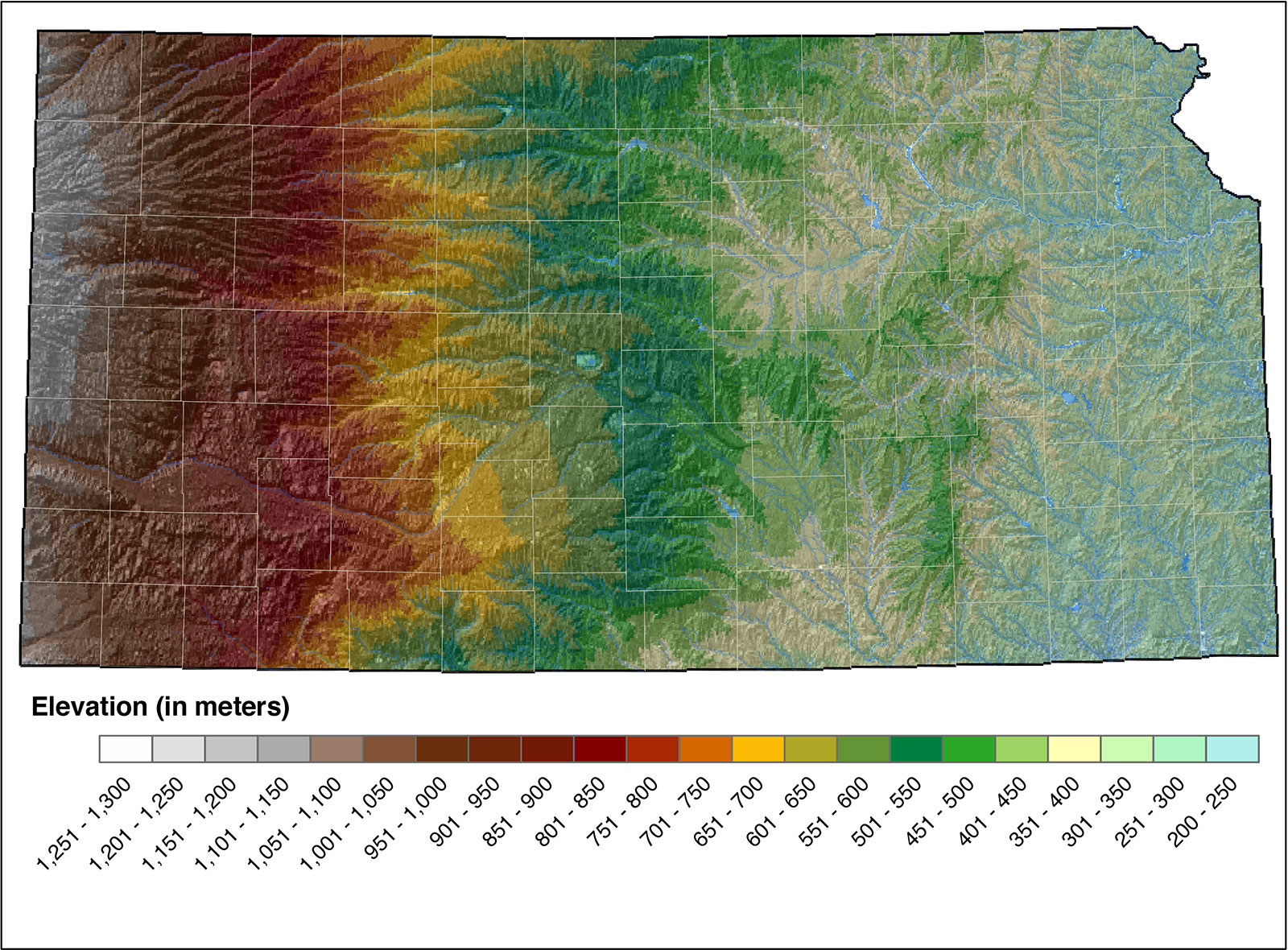
Soil, the foundation of life on Earth, is a complex and dynamic system. Its properties, distribution, and characteristics are crucial for understanding and managing land use, agricultural practices, and environmental sustainability. Soil survey mapping, a systematic process of investigating and documenting soil characteristics across a landscape, provides a vital framework for informed decision-making in these areas.
The Foundation of Understanding: The Soil Survey Process
Soil survey mapping involves a multi-faceted approach that integrates field observations, laboratory analysis, and advanced technologies. The process begins with the identification of specific soil characteristics, including:
- Soil Texture: The relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles, determining water holding capacity and drainage.
- Soil Structure: The arrangement of soil particles into aggregates, influencing aeration, root penetration, and water infiltration.
- Soil Depth: The vertical extent of the soil profile, affecting root development and nutrient availability.
- Soil pH: The acidity or alkalinity of the soil, influencing nutrient availability and plant growth.
- Soil Organic Matter: The decomposed plant and animal matter, contributing to soil fertility and structure.
- Soil Drainage: The rate and ease of water movement through the soil, affecting plant growth and nutrient availability.
- Soil Salinity: The concentration of soluble salts in the soil, impacting plant growth and water quality.
These characteristics are determined through a combination of field observations, laboratory analyses, and remote sensing techniques. In the field, trained soil scientists meticulously examine soil pits, collecting samples for analysis. Laboratory tests provide detailed information on chemical and physical properties, while aerial imagery and remote sensing data offer a broader perspective on soil patterns and distribution.
The Map as a Window: Interpreting Soil Survey Data
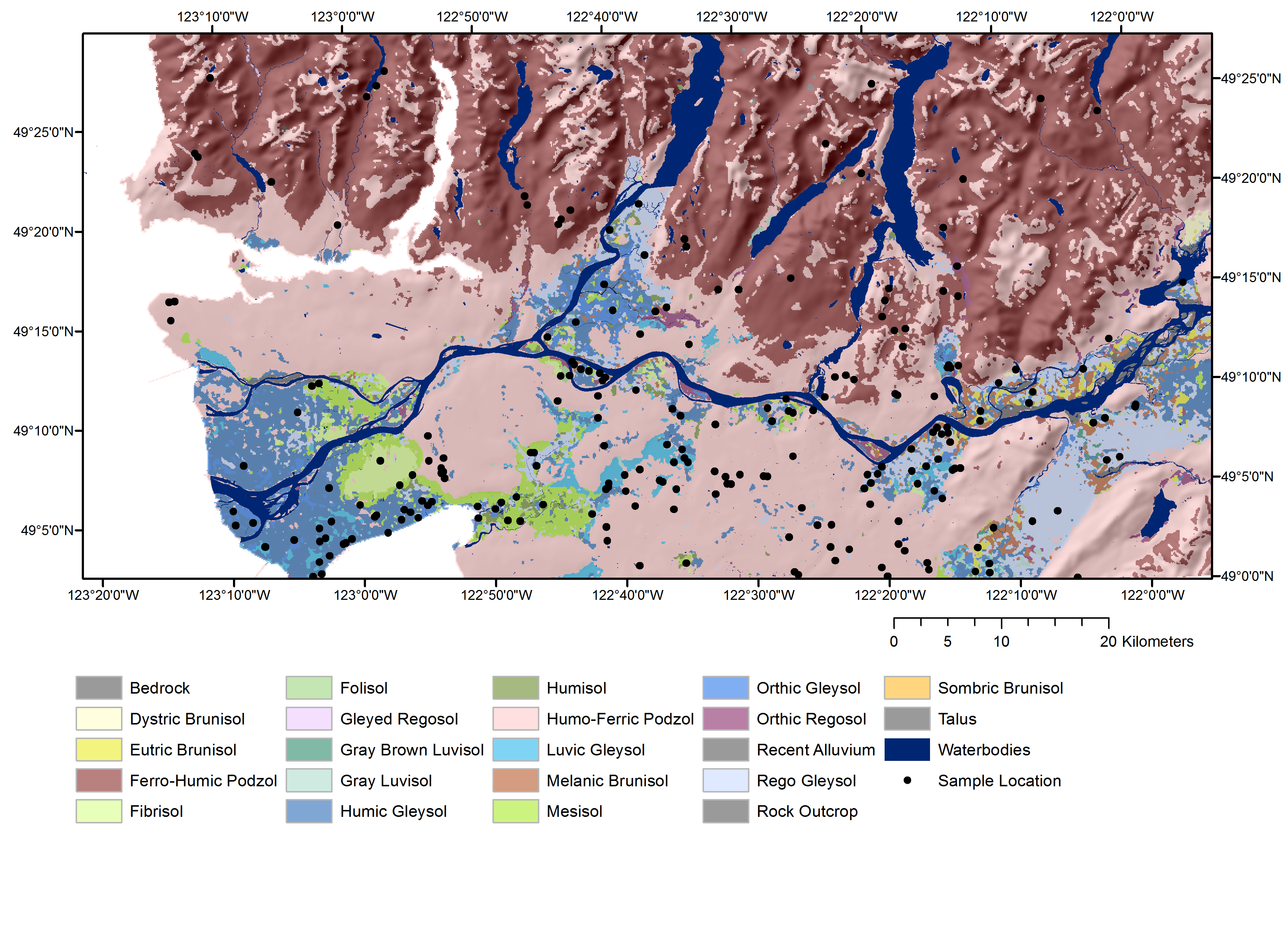
The collected data is then compiled and interpreted to create detailed soil maps. These maps typically depict the distribution of different soil types, along with their properties and limitations. Soil survey maps are often presented as a series of layers, each representing a specific soil characteristic or property. This multi-layered approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the soil landscape, enabling informed decision-making in various applications.
Beyond the Map: Applications of Soil Survey Mapping
Soil survey maps serve as a foundational tool for a wide range of applications, including:
- Agriculture: Soil maps help farmers optimize crop production by identifying areas best suited for specific crops, determining irrigation needs, and selecting appropriate fertilization strategies.
- Land Use Planning: Understanding soil properties and limitations guides land use planning, ensuring sustainable development and minimizing environmental impact.
- Environmental Management: Soil maps are essential for assessing environmental risks, such as erosion and contamination, and implementing effective mitigation strategies.
- Infrastructure Development: Soil surveys provide critical information for road construction, building foundations, and other infrastructure projects, ensuring stability and minimizing environmental disruption.
- Resource Management: Soil maps aid in managing water resources by identifying areas prone to flooding or drought, and facilitating efficient water allocation.
- Conservation Efforts: Soil surveys contribute to the conservation of soil resources by identifying areas requiring protection from degradation and implementing sustainable land management practices.
A Look at the Future: Advancements in Soil Survey Mapping
The field of soil survey mapping is constantly evolving, incorporating advancements in technology and data analysis. Emerging technologies such as:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software allows for the integration and analysis of spatial data, enabling the creation of highly detailed and interactive soil maps.
- Remote Sensing: High-resolution aerial imagery and satellite data provide a comprehensive overview of soil patterns and distribution, facilitating efficient and accurate mapping.
- Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture techniques integrate soil survey data with sensor networks and GPS technology to optimize crop management practices at a field-specific level.
- Digital Soil Mapping: Digital soil mapping uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to predict soil properties based on environmental factors, allowing for the creation of detailed soil maps for areas with limited field data.
These advancements are transforming soil survey mapping, enabling more accurate, efficient, and data-driven approaches to land management and environmental stewardship.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the difference between a soil survey and a soil map?
A soil survey is the process of collecting and analyzing soil data, while a soil map is a visual representation of the survey results, depicting the distribution and properties of different soil types.
2. How often are soil surveys updated?
The frequency of soil survey updates depends on factors such as land use changes, environmental pressures, and technological advancements. In general, soil surveys are typically updated every 10-20 years.
3. How can I access soil survey maps for my area?
Soil survey maps are often available through government agencies responsible for natural resource management, such as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) or equivalent organizations in other countries.
4. What are the limitations of soil survey mapping?
Soil survey mapping is a complex process that involves a degree of uncertainty. Factors such as soil variability, data availability, and technological limitations can influence the accuracy and precision of the maps.
5. How can I contribute to soil survey mapping?
Individuals can contribute to soil survey mapping by participating in citizen science projects, volunteering with local conservation organizations, or supporting research initiatives focused on soil science and mapping.
Tips for Effective Soil Survey Mapping
- Establish Clear Objectives: Define the specific goals and applications of the soil survey before embarking on the process.
- Choose Appropriate Methods: Select field sampling techniques and laboratory analyses that are suitable for the specific soil types and objectives of the survey.
- Integrate Multiple Data Sources: Combine field observations, laboratory analyses, and remote sensing data for a comprehensive understanding of soil properties.
- Ensure Data Quality: Implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the data collection, analysis, and mapping processes.
- Disseminate Information Effectively: Develop user-friendly soil maps and reports that are easily accessible and understood by stakeholders.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Soil
Soil survey mapping plays a crucial role in understanding and managing our planet’s most valuable resource. By providing a comprehensive and detailed picture of soil characteristics and distribution, soil surveys empower informed decision-making in agriculture, land use planning, environmental management, and other critical areas. As we face increasing pressures on land resources, the value of soil survey mapping will continue to grow, ensuring sustainable land use and environmental stewardship for generations to come.

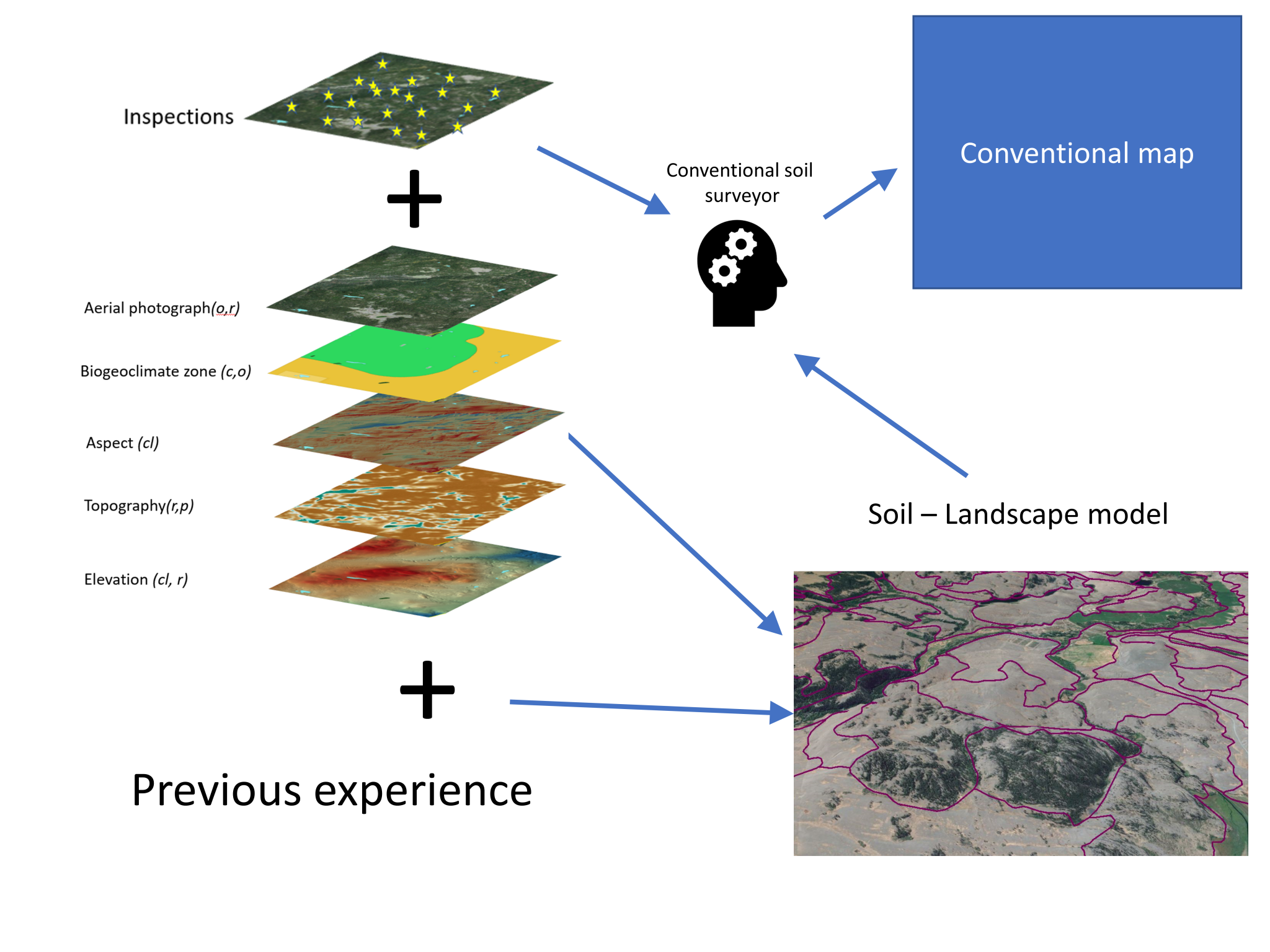
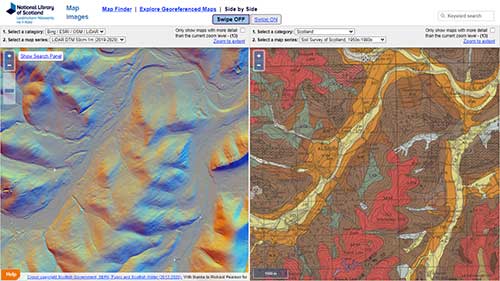


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Soil Survey Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!