Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
- 3.1 The Power of Visual Representation: Understanding Blood Through Concept Maps
- 3.2 Anatomy of a Blood Concept Map: A Step-by-Step Exploration
- 3.3 The Benefits of Blood Concept Maps: A Powerful Tool for Learning and Understanding
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding Blood Concept Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Creating Effective Blood Concept Maps: Maximizing Learning and Understanding
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Representation in Hematology
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
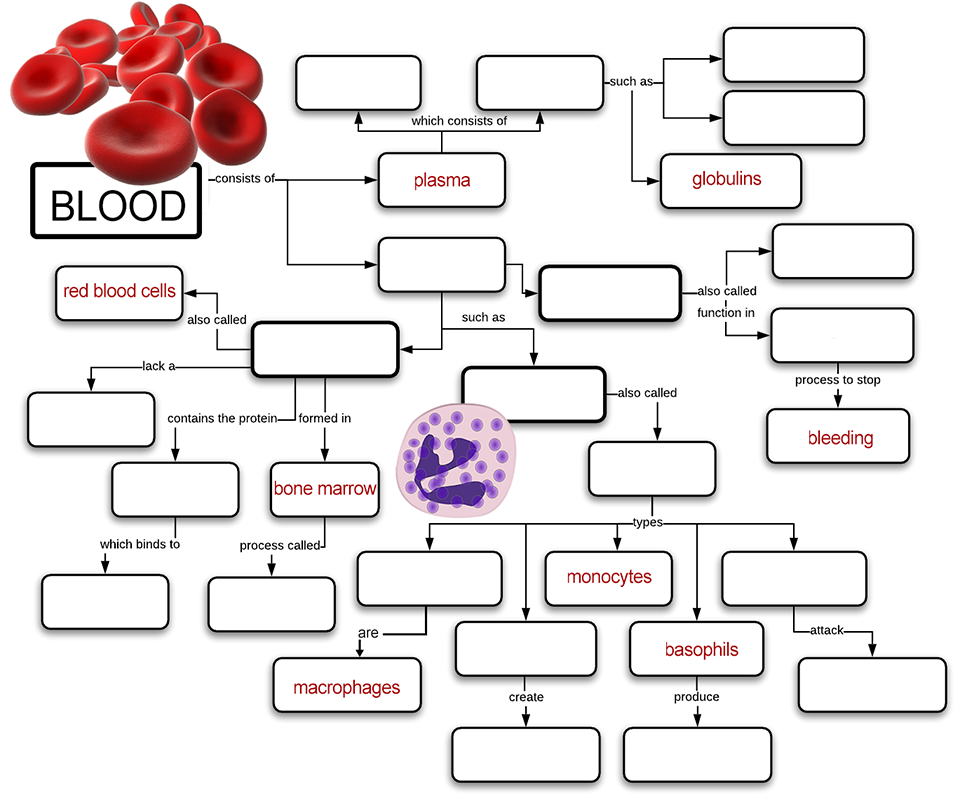
The intricate and vital nature of blood has fascinated scientists and medical professionals for centuries. Understanding its composition, functions, and interactions with the body is crucial for maintaining health and treating diseases. This guide delves into the concept of blood concept maps, exploring their structure, applications, and benefits in visualizing and comprehending the complex world of hematology.
The Power of Visual Representation: Understanding Blood Through Concept Maps
A concept map is a visual representation of knowledge, organizing information into a hierarchical structure with nodes (concepts) connected by links (relationships). When applied to the study of blood, concept maps provide a powerful tool for:
- Organizing Complex Information: Blood is a multifaceted entity, encompassing its cellular components, plasma constituents, physiological roles, and pathological implications. Concept maps offer a structured framework to organize these diverse elements, fostering clarity and coherence.
- Visualizing Relationships: By connecting nodes through links, concept maps highlight the intricate relationships between various blood components, functions, and diseases. This visual representation aids in understanding how changes in one aspect can impact others, fostering a holistic view.
- Promoting Active Learning: Creating a concept map requires active engagement with the material. Students and professionals are encouraged to synthesize information, identify key concepts, and establish meaningful connections, leading to deeper understanding and retention.
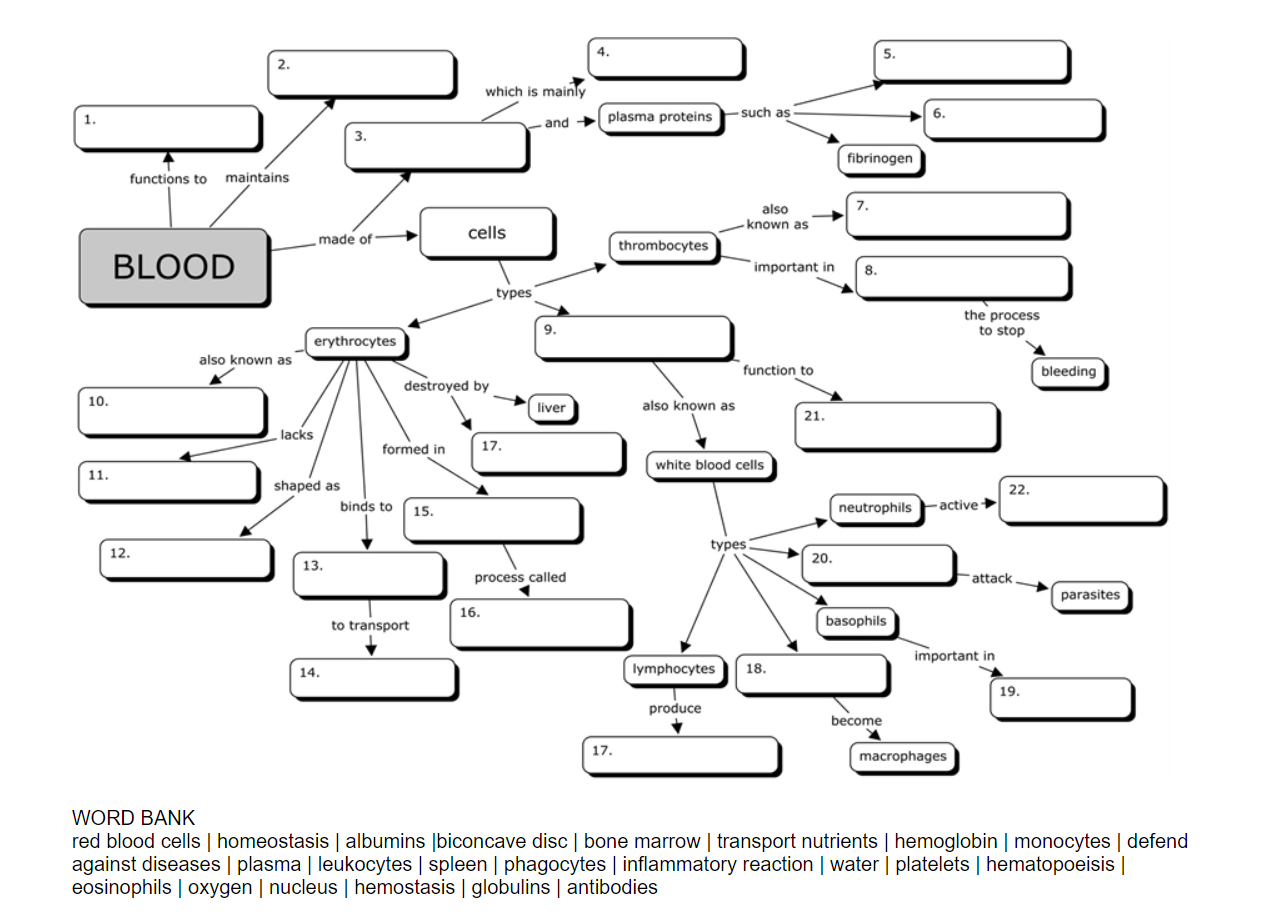
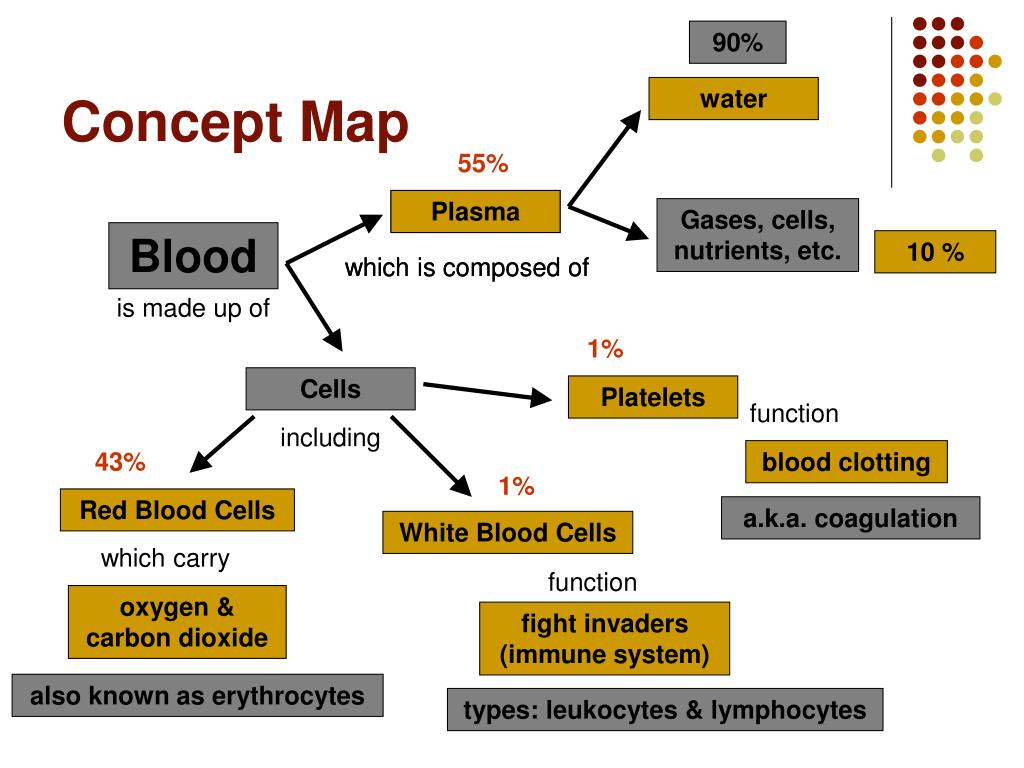
Anatomy of a Blood Concept Map: A Step-by-Step Exploration
A comprehensive blood concept map typically encompasses the following key elements:
1. Central Node: "Blood"
This central node serves as the foundation, representing the overall concept of blood.
2. Major Branches: Components of Blood
-
Cellular Components:
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Responsible for oxygen transport.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Involved in immune defense.
- Platelets (Thrombocytes): Essential for blood clotting.
-
Plasma:
- Water: The primary component, serving as a solvent.
- Proteins: Including albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen, with diverse functions.
- Electrolytes: Maintaining osmotic balance and nerve function.
- Nutrients: Providing energy and building blocks for cells.
- Waste Products: Removed by the kidneys and other organs.
3. Sub-Branches: Functions of Blood Components
-
Red Blood Cells:
- Oxygen transport from lungs to tissues.
- Carbon dioxide transport from tissues to lungs.
- Regulation of blood pH.
-
White Blood Cells:
- Phagocytosis: Engulfing and destroying pathogens.
- Antibody production: Targeting specific antigens.
- Cell-mediated immunity: Destroying infected or cancerous cells.
-
Platelets:
- Adhesion and aggregation at sites of injury.
- Formation of a platelet plug, initiating blood clotting.
-
Plasma:
- Transport of nutrients, hormones, and waste products.
- Regulation of blood volume and pressure.
- Maintenance of body temperature.
4. Connecting Links: Relationships and Interactions
- Blood Components and Functions: Links demonstrate how each component contributes to specific functions.
- Blood and Other Systems: Links illustrate the interactions between blood and other organ systems, such as the circulatory, respiratory, and immune systems.
- Blood and Diseases: Links highlight the impact of various diseases on blood components and functions, emphasizing the importance of blood analysis in diagnosis.
5. Additional Nodes: Blood-Related Concepts
- Hematopoiesis: The process of blood cell formation.
- Blood Types: The different blood groups based on antigens present on red blood cells.
- Blood Disorders: Including anemia, leukemia, and hemophilia.
- Blood Transfusion: The process of transferring blood from one individual to another.
The Benefits of Blood Concept Maps: A Powerful Tool for Learning and Understanding
The use of concept maps in the study of blood offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Comprehension: Visualizing the complex relationships between blood components, functions, and diseases fosters a deeper understanding of the subject.
- Improved Memory Retention: The process of creating and reviewing a concept map actively engages the learner, improving information retention and recall.
- Critical Thinking Development: Concept mapping encourages students and professionals to analyze information, identify key concepts, and establish logical connections, promoting critical thinking skills.
- Communication and Collaboration: Sharing and discussing concept maps facilitates effective communication and collaborative learning, allowing for diverse perspectives and insights.
- Problem-Solving and Decision-Making: By understanding the interplay of blood components and functions, individuals can better analyze and solve problems related to blood disorders and treatment strategies.
FAQs Regarding Blood Concept Maps: Addressing Common Questions
Q1: What are the key benefits of using concept maps in the study of blood?
A: Blood concept maps offer numerous benefits, including enhanced comprehension, improved memory retention, critical thinking development, effective communication, and improved problem-solving abilities.
Q2: How can I create an effective blood concept map?
A: Start by identifying the central concept (blood). Branch out into major components (cellular components and plasma). Further sub-divide these branches into specific elements and their functions. Connect nodes with links to demonstrate relationships and interactions. Include additional nodes for related concepts like hematopoiesis, blood types, and disorders.
Q3: What are some resources available for creating blood concept maps?
A: Numerous online tools and software programs facilitate concept map creation, including CmapTools, Mindomo, and XMind. You can also utilize traditional methods like pen and paper or digital drawing tools.
Q4: How can I use blood concept maps in my classroom or professional practice?
A: Utilize concept maps for teaching, learning, and reviewing blood-related topics. Encourage students to create their own maps or collaborate on group projects. Use concept maps to visualize complex concepts, explain diseases, and facilitate discussions on treatment strategies.
Q5: Are there any limitations to using blood concept maps?
A: While concept maps are a powerful tool, they may not capture all nuances and complexities of blood. They are best used in conjunction with other learning resources and should be considered a starting point for deeper exploration.
Tips for Creating Effective Blood Concept Maps: Maximizing Learning and Understanding
- Start with a clear goal: Determine the specific learning objective or concept you aim to represent.
- Use concise and accurate language: Employ clear and concise terms to represent concepts and relationships.
- Prioritize key concepts: Focus on the most essential aspects of blood, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Employ visual cues: Utilize different colors, shapes, and sizes to differentiate and highlight key elements.
- Review and refine: Regularly review and refine your concept map, adding new information and adjusting connections as needed.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Visual Representation in Hematology
Blood concept maps provide a powerful tool for visualizing, organizing, and understanding the intricate world of hematology. By embracing this visual representation, students, educators, and healthcare professionals can enhance their comprehension, improve memory retention, and foster critical thinking skills, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of this vital bodily fluid.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Complexities of Blood: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!