Unveiling Geographic Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Geographic Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Geographic Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Geographic Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Heat Maps
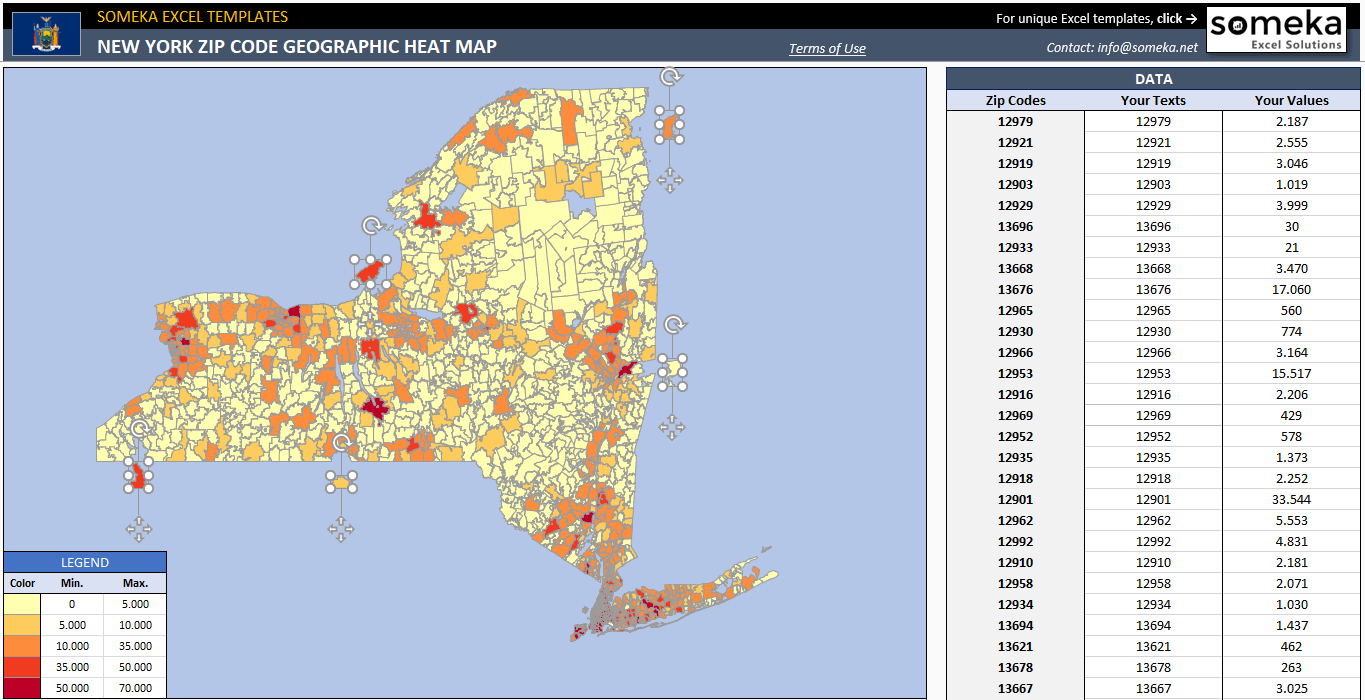
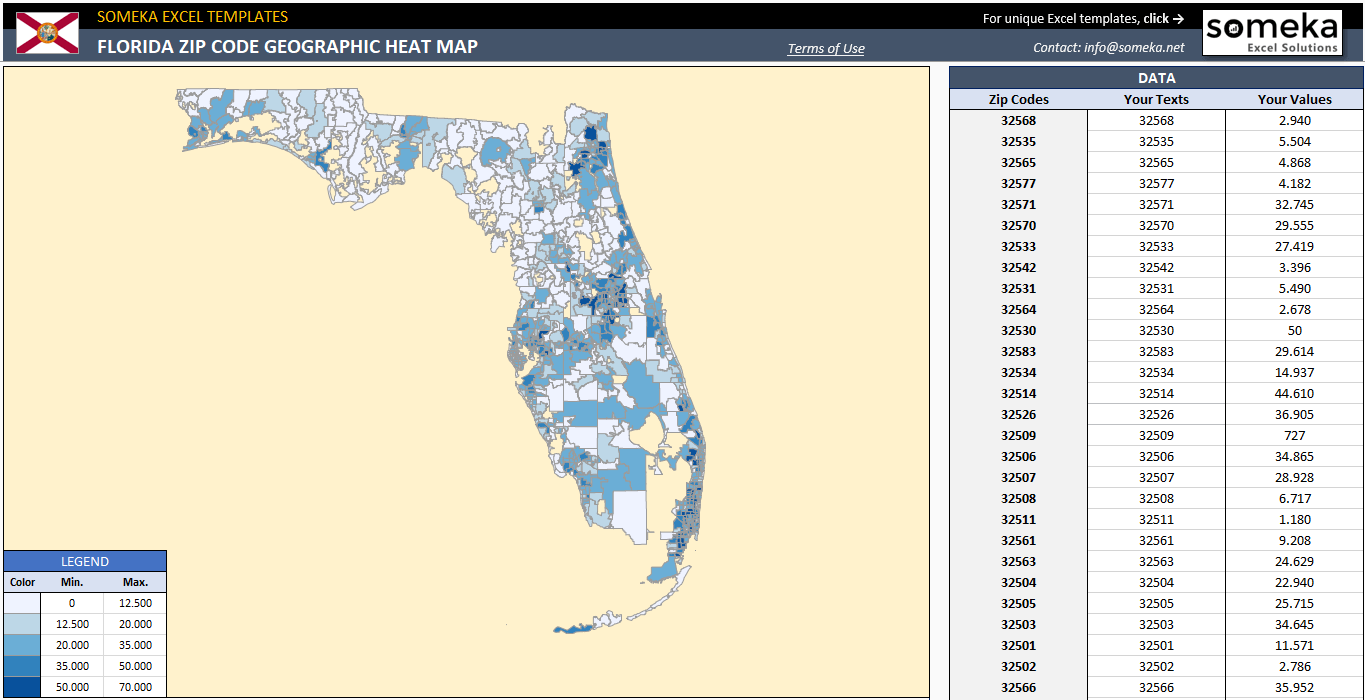
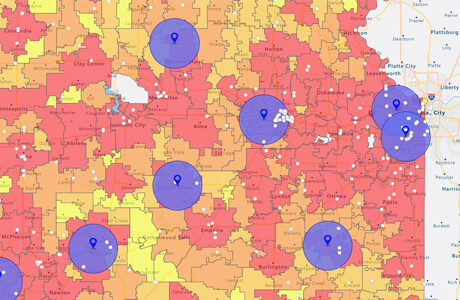
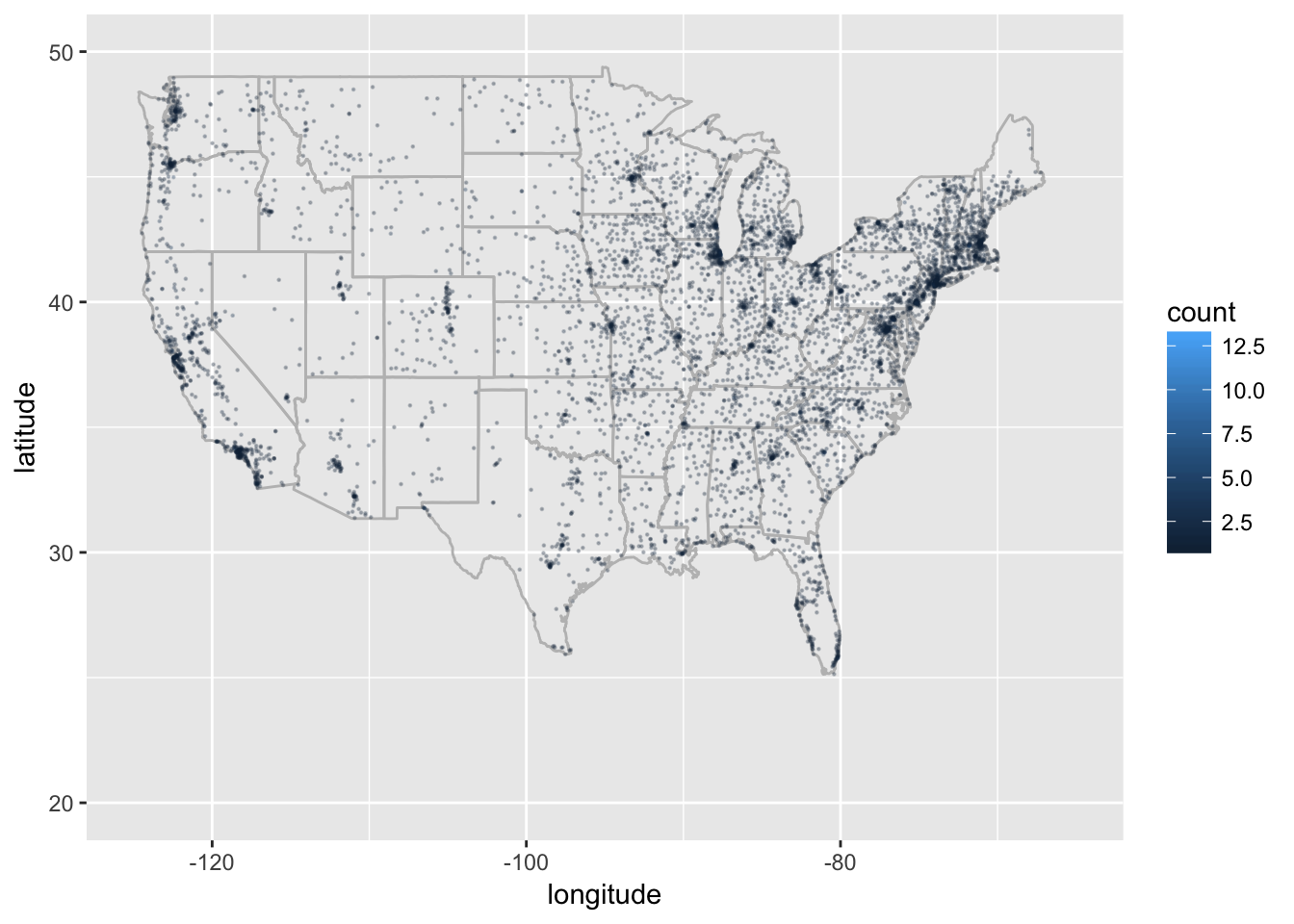
In a world increasingly driven by data, understanding geographic trends has become paramount. From urban planning to marketing strategies, the ability to visualize and analyze spatial data is essential for making informed decisions. One powerful tool in this endeavor is the zip code heat map, a visual representation of data distribution across geographic areas defined by postal codes. This article delves into the intricacies of zip code heat maps, exploring their applications, benefits, and limitations.
What is a Zip Code Heat Map?
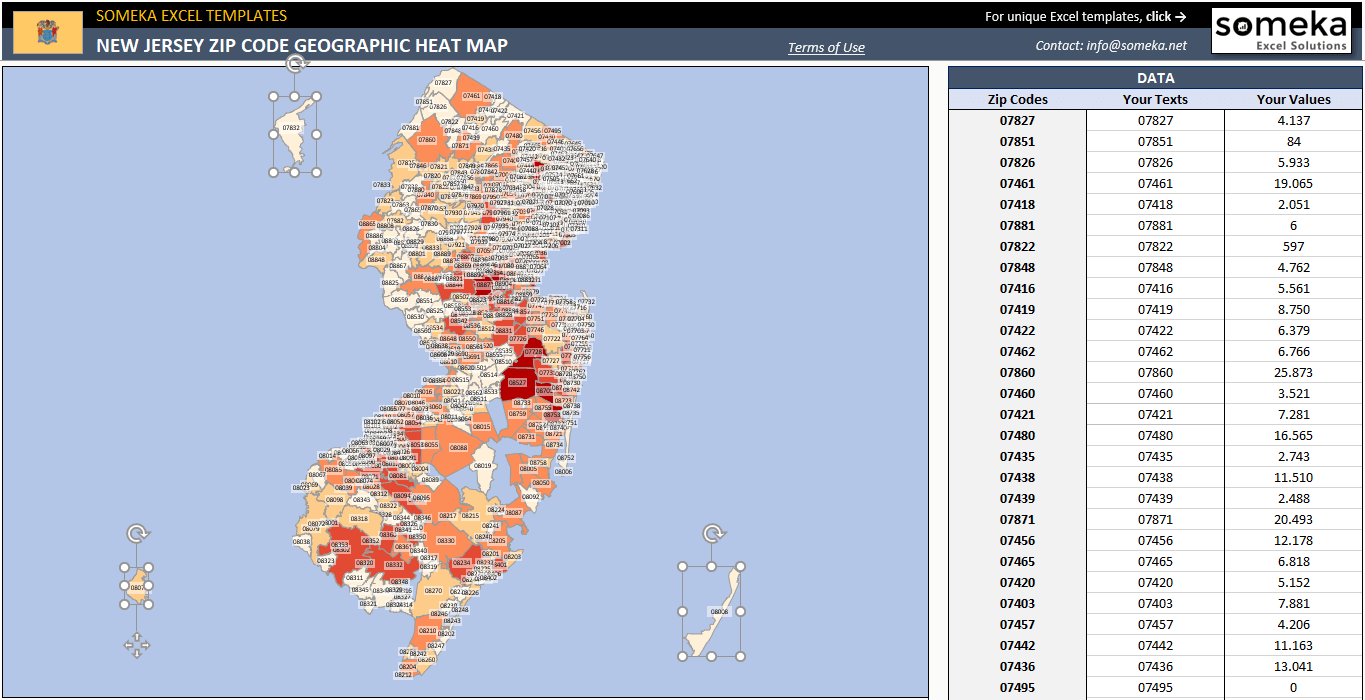
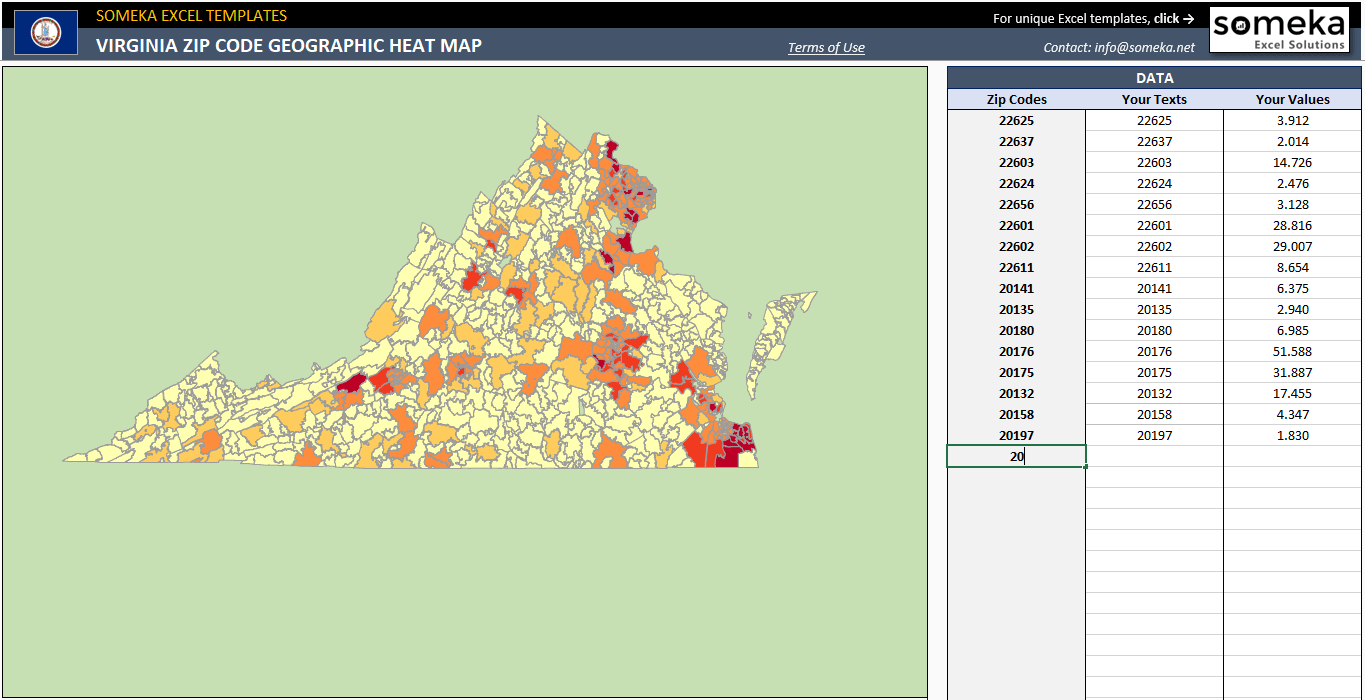
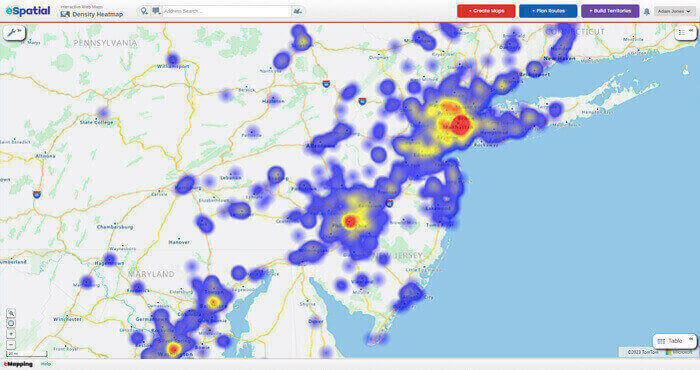
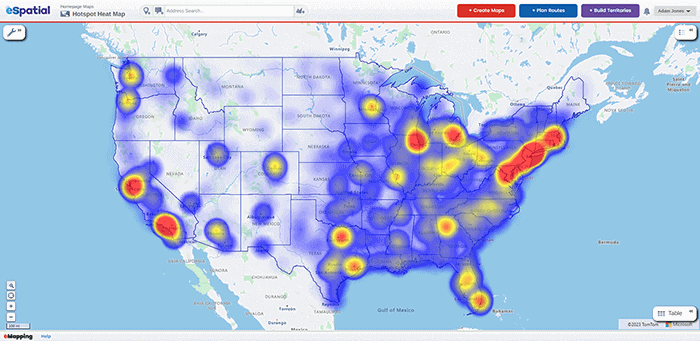
A zip code heat map is a graphical representation that uses color gradients to illustrate the intensity of a particular data point within different zip code areas. The intensity of the color, typically ranging from light to dark, corresponds to the volume or density of the data. This allows users to quickly identify areas with high concentrations of a specific phenomenon, be it population density, crime rates, business activity, or even consumer preferences.
Components of a Zip Code Heat Map:
- Base Map: The foundation of a zip code heat map is a geographical map, usually depicting a specific region or country. This map serves as the backdrop against which the data is overlaid.
- Zip Code Boundaries: Each zip code area is clearly delineated on the map, forming distinct polygons or regions. These boundaries provide the framework for data aggregation and visualization.
- Color Gradient: A color gradient is used to visually represent the data intensity. Typically, darker colors indicate higher values, while lighter colors denote lower values. The choice of color gradient should be carefully considered to ensure clarity and interpretability.
- Legend: A legend is crucial for understanding the color scale and its corresponding data values. It provides a key to interpreting the visual representation, enabling users to accurately translate color intensity into meaningful data insights.
Applications of Zip Code Heat Maps:
The versatility of zip code heat maps extends across diverse fields, making them indispensable tools for various purposes:
- Urban Planning: Identifying areas with high population density, identifying potential infrastructure needs, optimizing public transportation routes, and understanding demographic shifts.
- Marketing and Sales: Targeting specific customer segments based on location, understanding consumer preferences, optimizing marketing campaigns, and identifying potential new market opportunities.
- Real Estate: Analyzing property values, identifying desirable neighborhoods, understanding market trends, and assessing investment opportunities.
- Public Health: Tracking disease outbreaks, identifying areas with high crime rates, assessing environmental hazards, and allocating resources effectively.
- Business Intelligence: Understanding market competition, identifying customer demographics, optimizing supply chains, and making strategic business decisions.
Benefits of Using Zip Code Heat Maps:
- Visual Clarity: Heat maps provide a clear and intuitive visual representation of data distribution, enabling users to quickly identify patterns and trends.
- Data Aggregation: By aggregating data at the zip code level, heat maps simplify complex data sets and provide a concise overview of geographic variations.
- Data Exploration: Heat maps facilitate exploratory data analysis, allowing users to identify areas of interest and delve deeper into specific regions.
- Decision Support: Heat maps provide valuable insights that can inform decision-making in various fields, from urban planning to marketing strategies.
- Communication Tool: Heat maps effectively communicate complex data to stakeholders, enabling them to understand geographic patterns and trends.
Limitations of Zip Code Heat Maps:
While zip code heat maps offer significant advantages, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations:
- Data Granularity: Zip code boundaries can be relatively large, potentially masking finer-grained variations within a given area.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of data used in heat maps depends on the source and quality of information, which can influence the reliability of the visualizations.
- Oversimplification: Heat maps provide a simplified view of data distribution, potentially obscuring nuances and complexities that may be present.
- Misinterpretation: Without proper context and understanding, heat maps can be misinterpreted, leading to inaccurate conclusions.
- Privacy Concerns: Depending on the data used, zip code heat maps may raise privacy concerns, especially when visualizing sensitive information like health records or financial data.
Frequently Asked Questions about Zip Code Heat Maps:
Q: How do I create a zip code heat map?
A: Creating a zip code heat map requires a combination of data, software, and technical skills. You can use various tools, including:
- Geographic Information System (GIS) software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are powerful tools for creating professional-quality heat maps.
- Data Visualization Software: Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio offer user-friendly interfaces for creating interactive heat maps.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Platforms like Google Maps and Leaflet provide APIs for creating custom heat maps with code.
Q: What types of data can be visualized on a zip code heat map?
A: A wide range of data can be visualized on a zip code heat map, including:
- Demographic data: Population density, age distribution, income levels, education levels, and household size.
- Economic data: Business activity, employment rates, retail sales, and housing prices.
- Crime data: Crime rates, types of crime, and locations of incidents.
- Health data: Disease prevalence, mortality rates, access to healthcare, and vaccination rates.
- Environmental data: Air quality, water quality, pollution levels, and climate change impacts.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of a zip code heat map?
A: Ensuring the accuracy of a zip code heat map requires careful attention to data quality and validation:
- Source reliability: Verify the source of the data and assess its credibility and accuracy.
- Data cleaning: Clean and preprocess the data to remove errors, inconsistencies, and outliers.
- Data validation: Compare the data with other sources to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Visualization choices: Choose appropriate color gradients and legends to accurately represent the data without distortion.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective zip code heat maps?
A: Creating effective zip code heat maps requires careful planning and execution:
- Define clear objectives: Determine the specific purpose of the heat map and the insights you aim to convey.
- Select appropriate data: Choose data that is relevant to your objectives and aligns with the scale of the map.
- Choose an appropriate color gradient: Select a color gradient that is visually appealing, easy to interpret, and avoids misleading interpretations.
- Include a clear legend: Provide a legend that explains the color scale and corresponding data values.
- Consider context: Provide context for the data, such as time periods, geographic boundaries, and data sources.
- Test and refine: Create multiple iterations of the heat map and test them with users to ensure clarity and effectiveness.
Conclusion:
Zip code heat maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing and analyzing geographic data. By leveraging the power of visual representation, they enable users to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies across different zip code areas. While limitations exist, the benefits of using zip code heat maps far outweigh the drawbacks, making them indispensable for various fields, from urban planning to marketing and beyond. By carefully considering the data, visualization choices, and potential limitations, users can harness the power of zip code heat maps to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions based on geographically contextualized data.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Geographic Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Zip Code Heat Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!