The Power of Big Maps: Navigating the Complexities of Data
Related Articles: The Power of Big Maps: Navigating the Complexities of Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Big Maps: Navigating the Complexities of Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Big Maps: Navigating the Complexities of Data
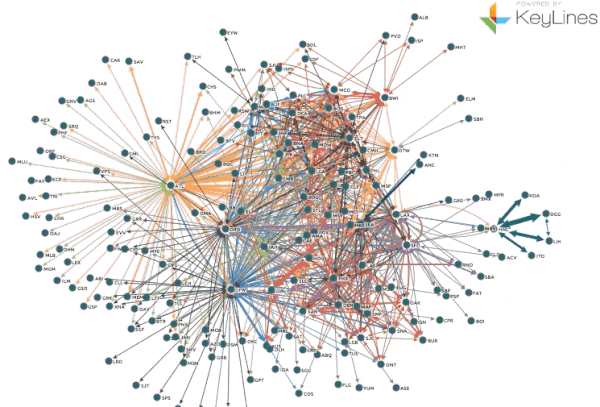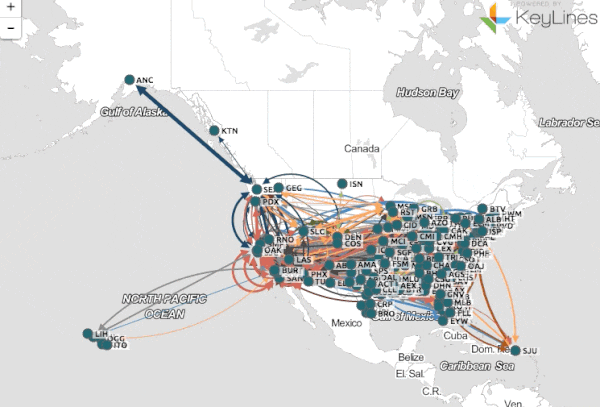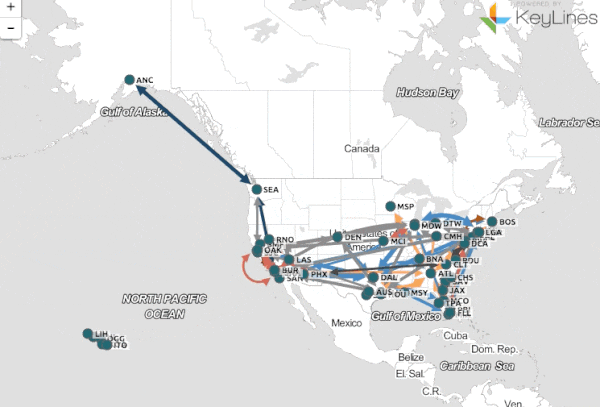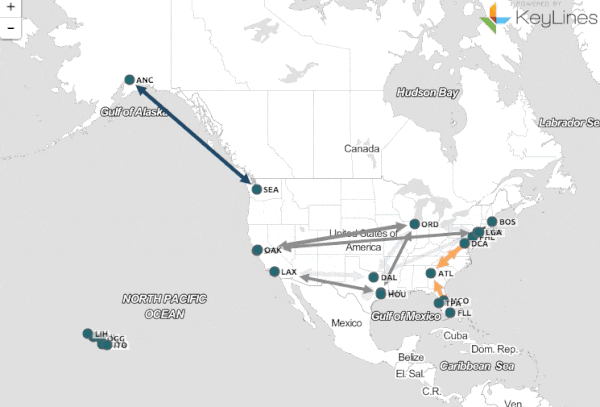
In an era of data deluge, where information flows relentlessly, the ability to decipher and leverage it effectively is paramount. This is where the concept of a "big map" emerges as a powerful tool, offering a comprehensive and insightful view of complex datasets. This article delves into the essence of big maps, exploring their construction, benefits, and applications in various domains.
Understanding the Essence of Big Maps
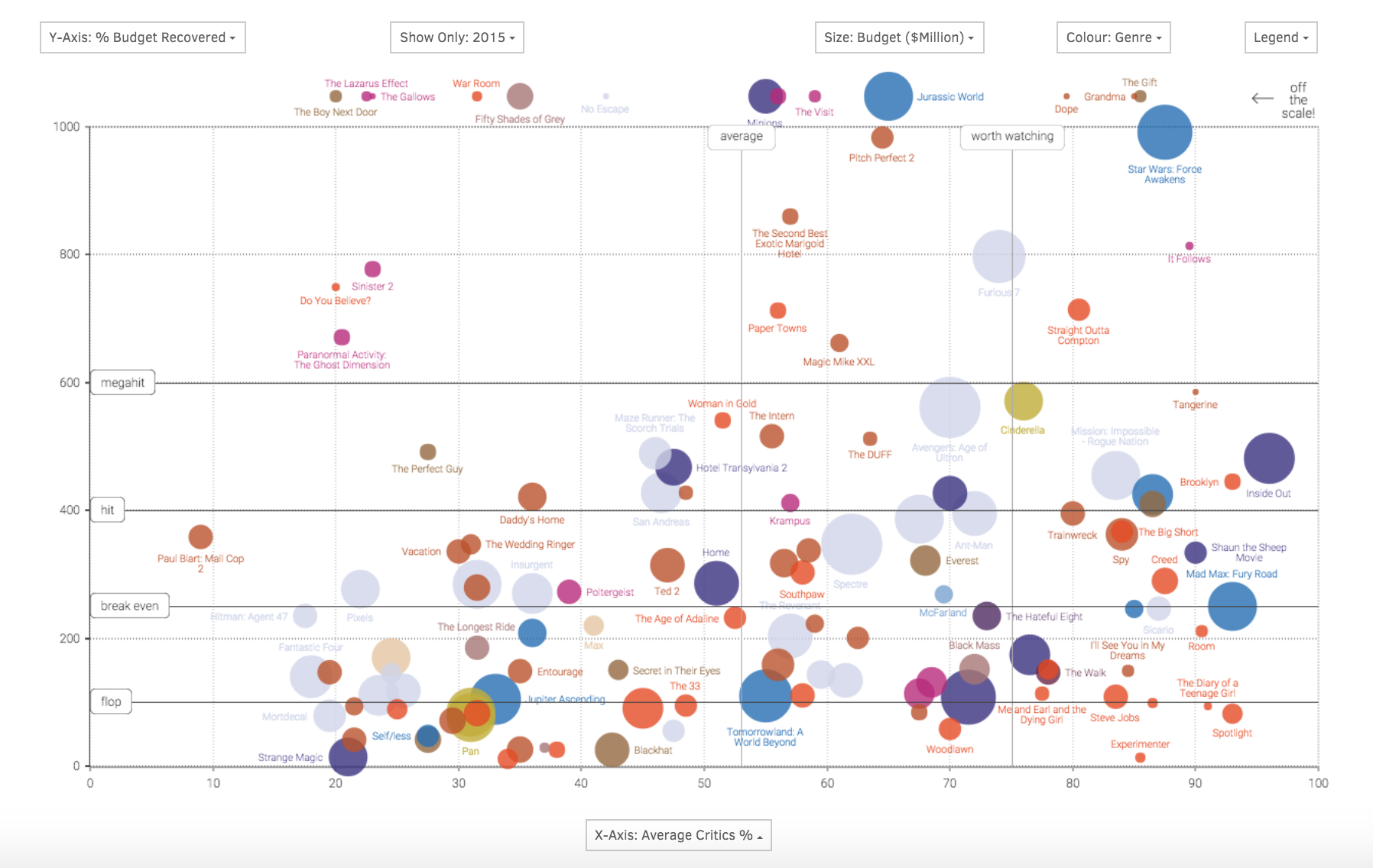
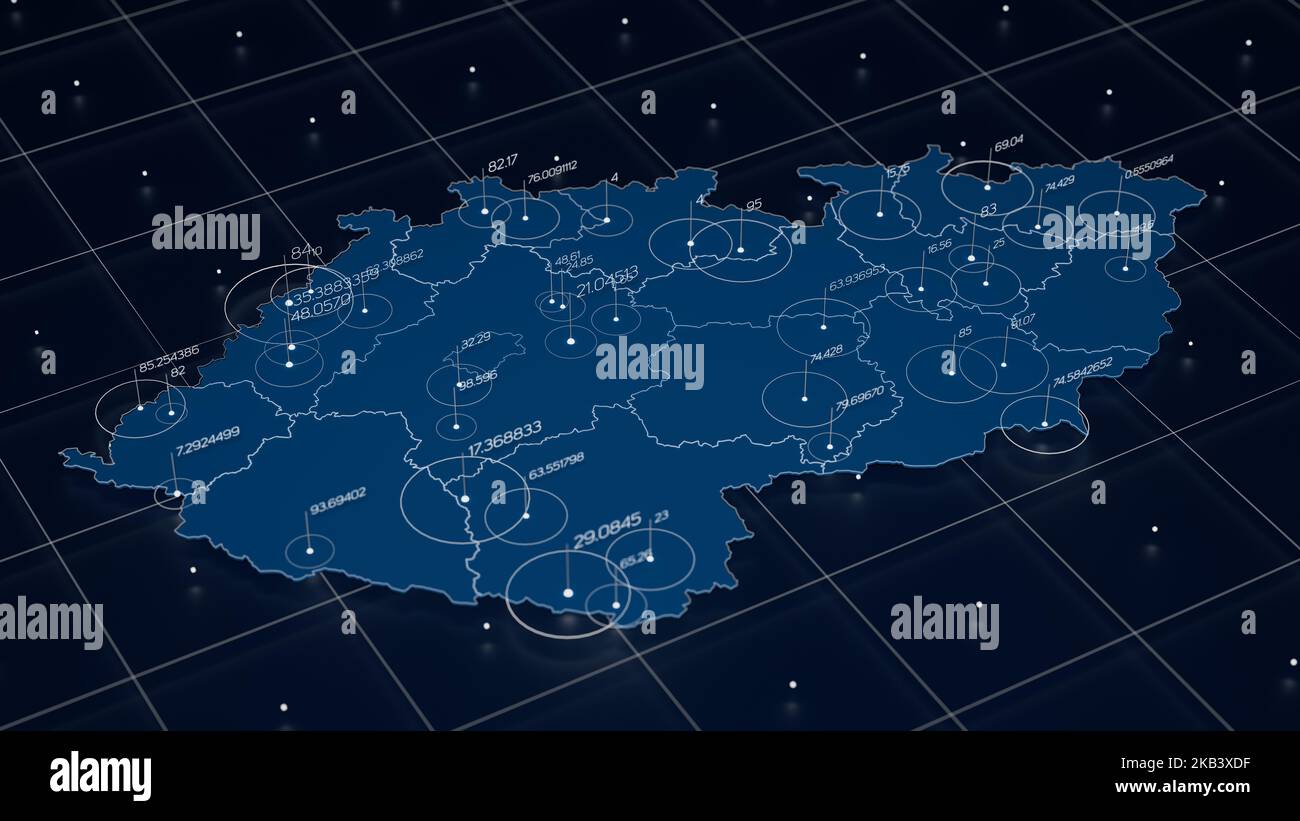
A big map transcends the traditional definition of a geographical map. It represents a visual representation of data, often complex and multidimensional, using various graphical elements like nodes, edges, and colors to illustrate relationships, patterns, and trends. These maps serve as a bridge between raw data and actionable insights, enabling users to grasp intricate information at a glance.
The Construction of a Big Map
The creation of a big map involves a systematic approach, encompassing several key steps:
-
Data Acquisition: Gathering relevant data from diverse sources, ensuring its accuracy and completeness. This step requires careful data cleaning and preprocessing to address inconsistencies and missing values.
-
Data Transformation: Converting raw data into a format suitable for visualization. This may involve aggregation, normalization, and other transformations to highlight meaningful patterns.
-
Visualization Selection: Choosing appropriate visualization techniques to represent the data effectively. This involves considering the type of data, the intended audience, and the specific insights to be conveyed.
-
Map Design: Structuring the map’s layout and visual elements to enhance readability and comprehension. This includes selecting colors, fonts, and icons that effectively communicate the data.
-
Interactive Features: Incorporating interactive elements, such as zoom, pan, and filtering capabilities, to allow users to explore the data dynamically and gain deeper insights.
Benefits of Big Maps
The application of big maps yields numerous benefits, contributing to enhanced decision-making and knowledge discovery:
-
Enhanced Comprehension: Big maps facilitate understanding of complex data by providing a visual representation of intricate relationships and patterns. This enables users to grasp the bigger picture and identify key trends that might be overlooked in raw data.
-
Data Exploration: Big maps allow users to explore data interactively, drilling down into specific areas of interest and uncovering hidden connections. This fosters a deeper understanding of the data and facilitates the identification of potential opportunities and risks.
-
Collaboration and Communication: Big maps provide a common ground for stakeholders to discuss and analyze data collaboratively. They enable effective communication of insights, fostering consensus and driving informed decision-making.
-
Improved Decision-Making: By visualizing complex data, big maps empower decision-makers to gain a holistic view of the situation, enabling them to make more informed and strategic decisions.
Applications of Big Maps
The versatility of big maps extends across various fields, facilitating data-driven insights and informed decision-making:
-
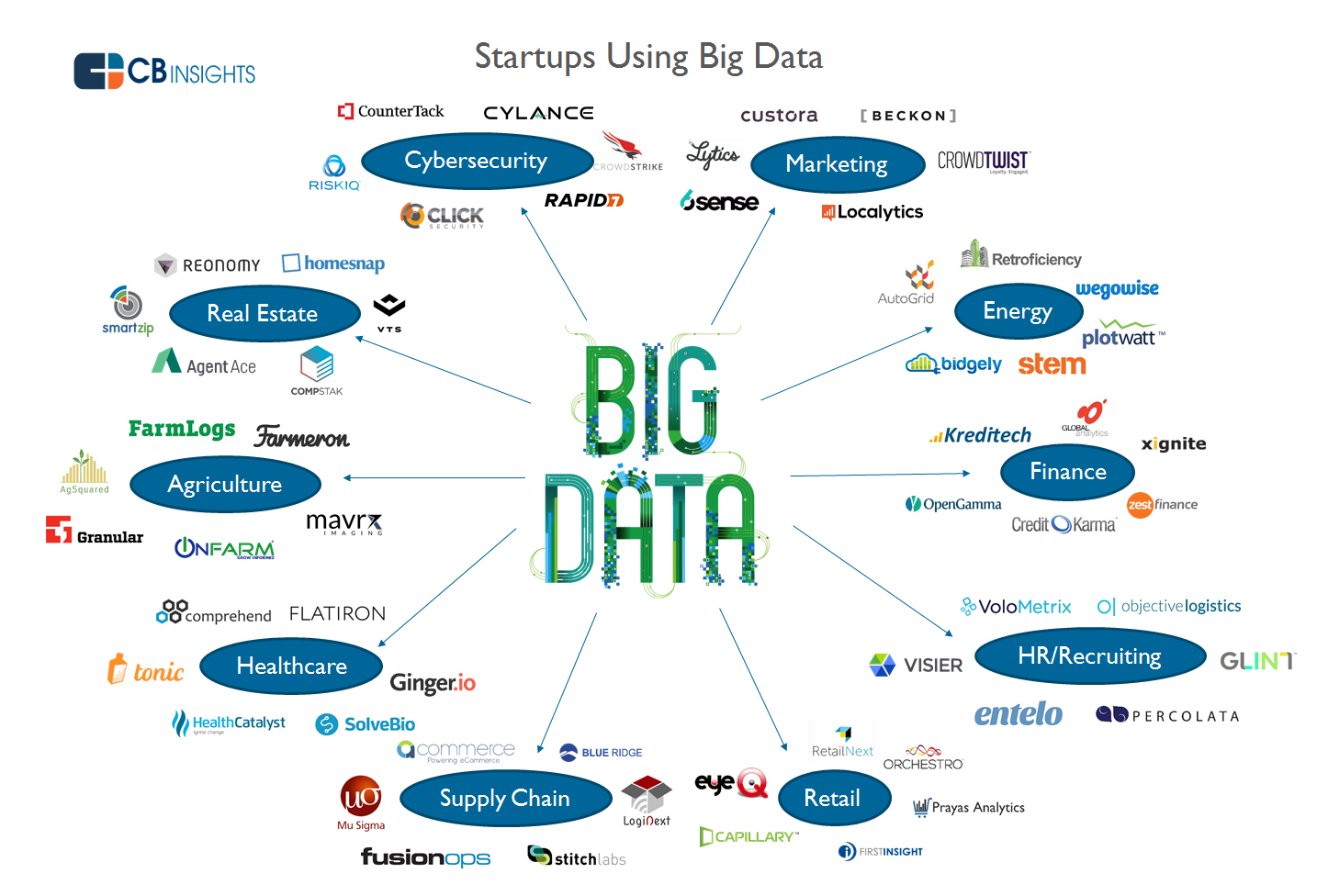
Business Intelligence: Big maps can be used to analyze customer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes, enabling businesses to make strategic decisions regarding product development, marketing campaigns, and resource allocation.
-
Healthcare: Big maps can visualize patient data, disease trends, and treatment outcomes, supporting medical research, personalized medicine, and public health initiatives.
-
Finance: Big maps can illustrate market trends, investment portfolios, and risk assessments, aiding financial analysts and investors in making informed decisions.
-
Social Sciences: Big maps can be used to visualize social networks, migration patterns, and demographic trends, contributing to research in sociology, anthropology, and political science.
-
Environmental Science: Big maps can represent climate data, pollution levels, and biodiversity patterns, supporting environmental monitoring, conservation efforts, and policy development.
FAQs about Big Maps
Q: What are the limitations of big maps?
A: While powerful, big maps have limitations. Overly complex maps can become overwhelming, hindering comprehension. Additionally, data quality and visualization choices can significantly impact the accuracy and effectiveness of the map.
Q: How can I create a big map?
A: Various software tools, such as Tableau, Power BI, and Gephi, offer functionalities for creating big maps. Understanding data visualization principles and adopting a structured approach are crucial for creating impactful maps.
Q: What are some best practices for designing big maps?
A: A clear and concise design is paramount. Choose appropriate colors, fonts, and icons for effective communication. Prioritize clarity over aesthetics, ensuring the map is easy to read and understand.
Q: Can big maps be used for real-time data visualization?
A: Yes, big maps can be used to visualize real-time data, offering dynamic insights into evolving situations. This requires integrating data feeds and incorporating interactive elements for real-time updates.
Tips for Using Big Maps Effectively
-
Define your goals: Clearly articulate the purpose of the map and the insights you aim to convey.
-
Choose the right visualization: Select a visualization technique that effectively represents the data and aligns with your goals.
-
Keep it simple: Avoid cluttering the map with unnecessary information. Focus on key insights and use clear and concise labels.
-
Encourage interaction: Incorporate interactive features to allow users to explore the data and gain deeper insights.
-
Iterate and refine: Continuously evaluate and refine your big map based on user feedback and evolving data.
Conclusion
Big maps offer a powerful approach to navigating the complexities of data, enabling users to grasp intricate relationships, identify patterns, and make informed decisions. By harnessing the power of visualization, big maps bridge the gap between raw data and actionable insights, driving innovation and progress across various domains. As data continues to proliferate, the role of big maps in facilitating data-driven decision-making will only become more critical.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Big Maps: Navigating the Complexities of Data. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!