The Land of Gilead: A Geographical and Biblical Exploration
Related Articles: The Land of Gilead: A Geographical and Biblical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Land of Gilead: A Geographical and Biblical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Land of Gilead: A Geographical and Biblical Exploration

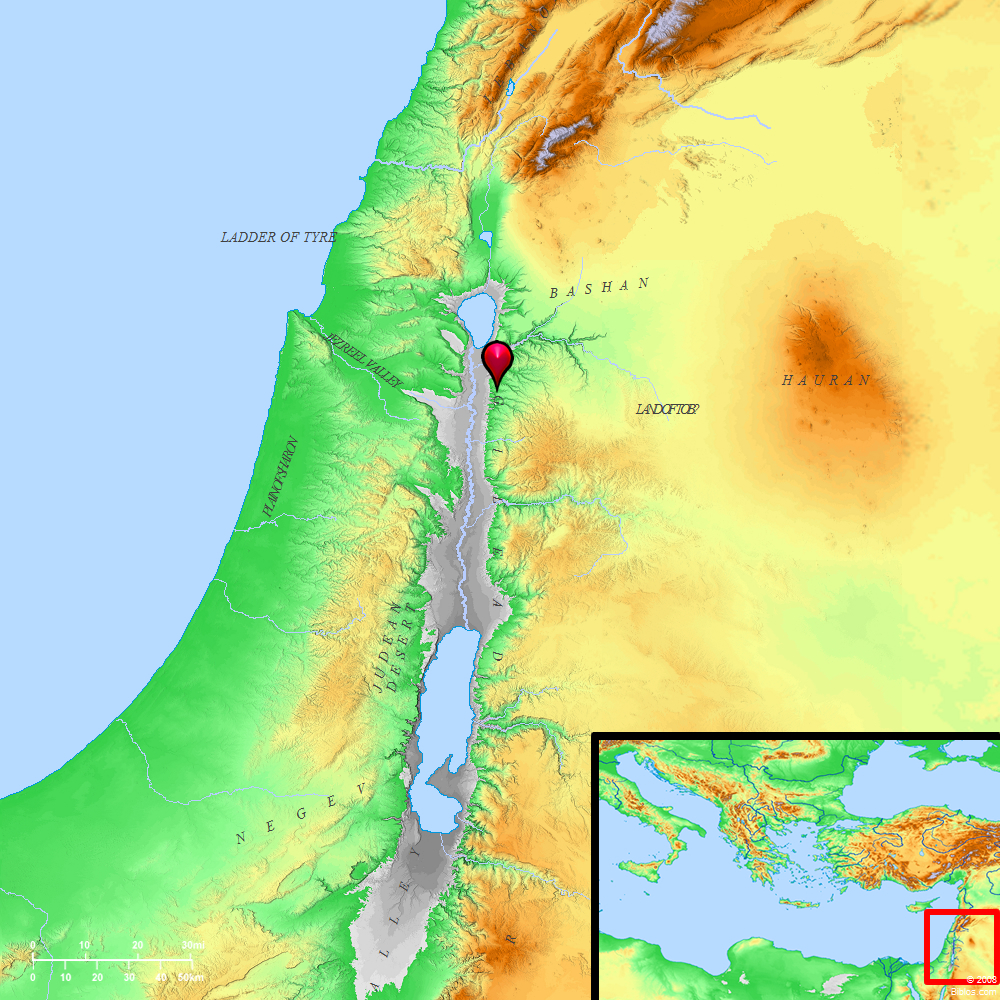
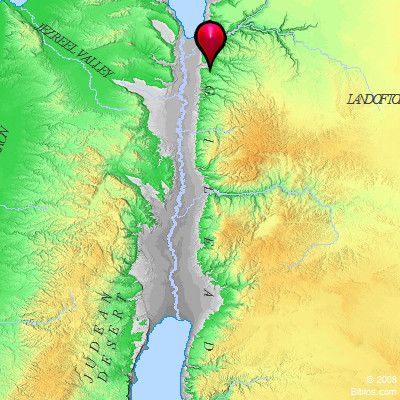
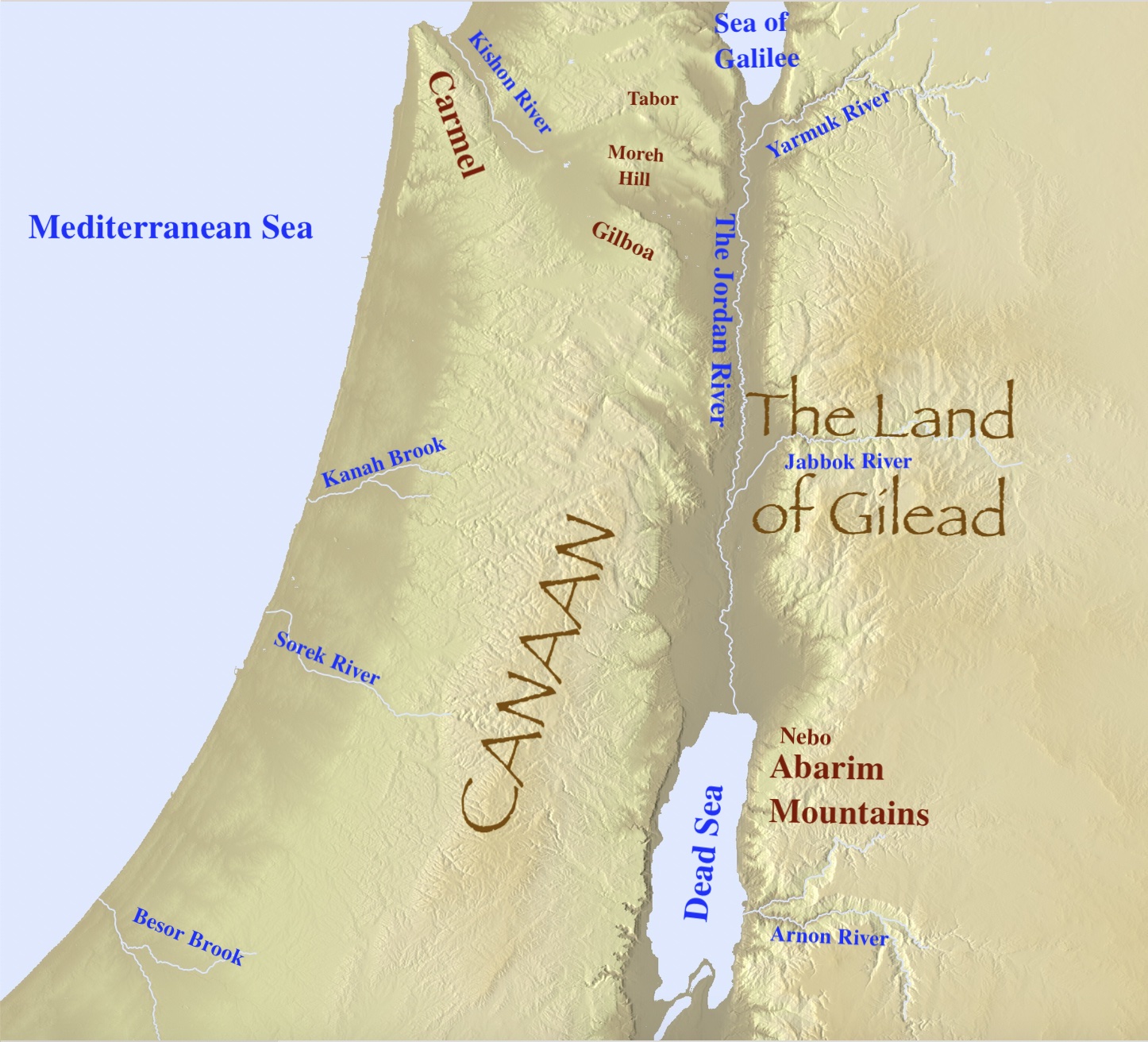
The region of Gilead, mentioned repeatedly in the Hebrew Bible, holds a significant place in biblical history and geography. Understanding its location and historical significance sheds light on the lives and journeys of key biblical figures, the development of Israelite society, and the broader narrative of the Old Testament.
Geographical Location and Boundaries:
Gilead, meaning "heap of stones" or "rocky place," refers to a mountainous region situated east of the Jordan River, encompassing the northern and central Transjordan. The region’s precise boundaries have been subject to debate among scholars, but it generally encompassed the following areas:
- North: The Yarmouk River, which formed the natural border between Gilead and Bashan.
- South: The Jabbok River, separating Gilead from the territory of Ammon.
- East: The eastern slopes of the Transjordanian plateau, extending towards the Arabian Desert.
- West: The Jordan River, separating Gilead from the lands of Israel proper.
Topographical Features:
Gilead’s landscape was characterized by its rugged terrain, with rolling hills, fertile valleys, and towering peaks. The region’s elevation varied significantly, ranging from the high plateaus in the east to the lower valleys bordering the Jordan River. This diverse topography provided a rich tapestry of agricultural potential, supporting a variety of crops and livestock.
Historical Significance:
Gilead’s strategic location and abundant resources made it a coveted territory throughout history. Its importance in the biblical narrative is evident in the following key points:
- Patriarchal Era: The region played a significant role in the lives of the patriarchs, particularly Jacob. Gilead is mentioned in connection with his son Manasseh, who inherited the territory, and his grandson Jair, who ruled over 30 cities in the region.
- Israelite Conquest: During the conquest of Canaan, Gilead was conquered by the tribes of Gad, Reuben, and Manasseh. The region became a crucial part of the Israelite kingdom, contributing significantly to its agricultural and military strength.
- Kingdom of Israel: During the period of the divided kingdom, Gilead remained a vital part of the northern kingdom of Israel. It was home to several prominent figures, including the prophet Elijah, who is said to have lived in the region and performed miracles there.
- Assyrian Conquest: In the 8th century BCE, the Assyrian Empire conquered the northern kingdom of Israel, including Gilead. The region was subsequently incorporated into the Assyrian Empire and experienced a significant population shift.
- Post-Exilic Period: Following the Babylonian exile, the region of Gilead was repopulated by Jewish communities who returned from exile. While its importance diminished somewhat, it continued to be a significant area for Jewish settlement and agricultural activity.
Biblical References and Significance:
Gilead is mentioned numerous times throughout the Hebrew Bible, highlighting its importance in various contexts:
- The Book of Genesis: Gilead is mentioned in connection with the patriarch Jacob and his son Manasseh, who inherited the territory. The region also played a role in the story of Jacob’s brother Esau, who settled in the nearby land of Seir.
- The Book of Numbers: The tribes of Reuben, Gad, and half of the tribe of Manasseh received Gilead as their inheritance after the conquest of Canaan.
- The Book of Judges: Gilead was the birthplace of Jephthah, a judge who led the Israelites to victory over the Ammonites.
- The Book of Kings: Gilead is mentioned in connection with the prophet Elijah, who is said to have lived in the region and performed miracles there.
- The Book of Jeremiah: The prophet Jeremiah prophesied against the inhabitants of Gilead, warning them of impending judgment.
Beyond Geography: The Symbolic Significance of Gilead:
Beyond its literal geographical location, Gilead also holds symbolic significance in the Bible:
- A Symbol of Strength and Resilience: The mountainous terrain of Gilead was often associated with strength and resilience. In the Bible, Gilead is depicted as a land of warriors and heroes, known for their courage and determination.
- A Source of Healing and Comfort: The balm of Gilead, a fragrant resin produced from trees in the region, was renowned for its medicinal properties. In the Bible, the balm of Gilead is used as a metaphor for healing and comfort.
- A Place of Refuge and Safety: Gilead was often described as a place of refuge and safety, a sanctuary from the dangers of the surrounding world. In the Bible, Gilead is depicted as a place where the Israelites could find protection and security.
FAQs:
-
Q: What is the difference between Gilead and Bashan?
A: Gilead and Bashan are distinct regions located east of the Jordan River. Gilead is situated south of Bashan, and the two regions are separated by the Yarmouk River. While both regions were known for their fertility and strategic importance, Bashan was characterized by its extensive plains and forests, while Gilead was known for its mountainous terrain.
-
Q: Why is Gilead mentioned in the Bible so often?
A: Gilead’s frequent mention in the Bible stems from its strategic location, abundant resources, and its role in the lives of key biblical figures. It was a vital territory for the Israelites, contributing to their agricultural and military strength, and was the home of prominent figures like Elijah and Jephthah.
-
Q: Is there any evidence for the balm of Gilead mentioned in the Bible?
A: While the exact nature of the balm of Gilead is debated, there is evidence that fragrant resins were produced in the region and used for medicinal purposes. Some scholars believe that the balm of Gilead may have been a type of myrrh or frankincense, both of which were known for their healing properties.
-
Q: What is the significance of the phrase "a balm in Gilead"?
A: The phrase "a balm in Gilead" is a metaphor for healing and comfort. It is used in the Bible to describe something that brings relief and solace in times of difficulty.
Tips for Studying Gilead in the Bible:
- Consult a Bible Atlas: A Bible atlas can provide a visual representation of Gilead’s location and its relationship to other biblical regions.
- Study the Historical Context: Understanding the historical context of the biblical texts is crucial for interpreting the references to Gilead. Consider the political landscape, the social structures, and the cultural norms of the time.
- Explore the Symbolic Significance: Pay attention to the symbolic language used in the Bible to describe Gilead. Consider how the region is used as a metaphor for strength, healing, refuge, and other concepts.
Conclusion:
The region of Gilead, with its rich history, diverse landscape, and symbolic significance, offers a fascinating window into the world of the Hebrew Bible. Its strategic location, its role in the lives of key biblical figures, and its enduring presence in biblical literature make it a crucial area of study for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of the Old Testament. By exploring the geographical and historical context of Gilead, we can gain valuable insights into the lives, journeys, and experiences of the biblical characters and the broader narrative of God’s interaction with his people.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Land of Gilead: A Geographical and Biblical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!