The Coast Mountains: A Majestic Spine of North America
Related Articles: The Coast Mountains: A Majestic Spine of North America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Coast Mountains: A Majestic Spine of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Coast Mountains: A Majestic Spine of North America

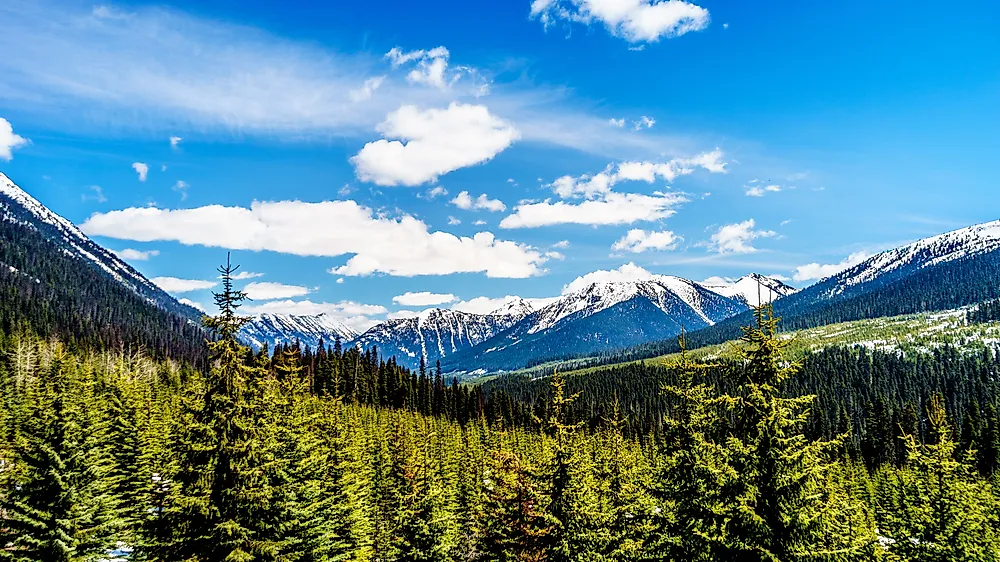
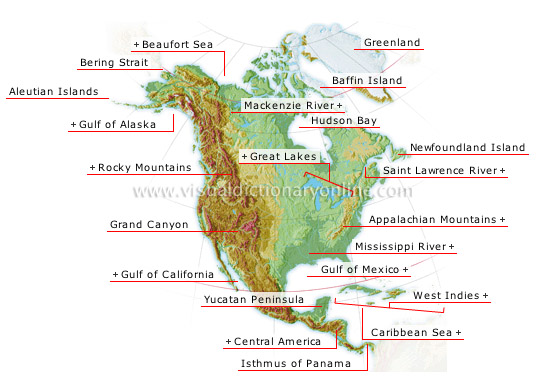
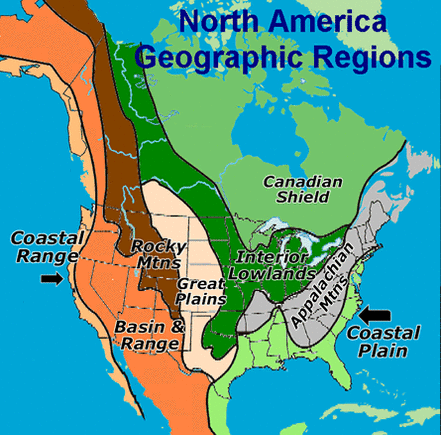
The Coast Mountains, a formidable mountain range stretching along the Pacific coast of North America, are a testament to the Earth’s dynamic geological forces. This imposing range, extending from southern British Columbia in Canada to the southeastern panhandle of Alaska, serves as a striking backdrop to the continent’s western edge, shaping the landscapes and influencing the ecosystems of the surrounding regions.
A Legacy of Tectonic Activity
The Coast Mountains owe their existence to the relentless forces of plate tectonics. Millions of years ago, the North American Plate collided with the Pacific Plate, pushing the oceanic plate beneath the continental plate in a process known as subduction. This subduction zone, responsible for the formation of the Cascade Range and the Aleutian Islands, also gave rise to the Coast Mountains. As the Pacific Plate descends beneath the North American Plate, it melts, creating magma that rises to the surface, leading to volcanic activity and the formation of the Coast Mountains.
A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes
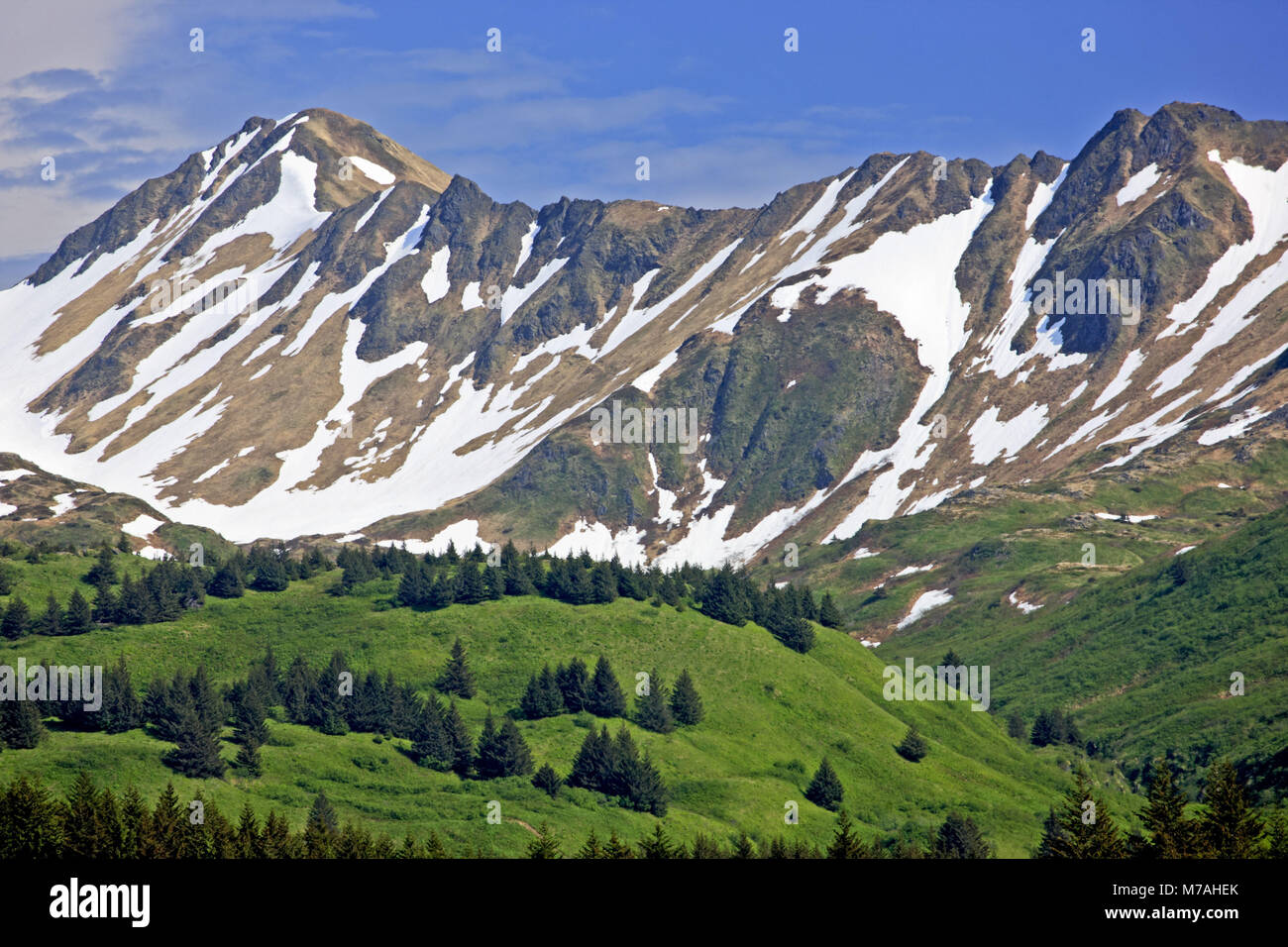
The Coast Mountains are not a homogenous entity, but rather a complex tapestry of diverse landscapes. From towering peaks like Mount Waddington, the highest point in the range, to cascading glaciers and pristine lakes, the Coast Mountains exhibit a remarkable variety of natural features.
- Glaciers and Icefields: The Coast Mountains are home to numerous glaciers and icefields, remnants of the last glacial period. These ice giants, like the vast Juneau Icefield in Alaska, are significant reservoirs of freshwater and play a vital role in shaping the landscape through erosion and deposition.
- Fjords and Inlets: The Pacific Ocean’s influence extends deep into the Coast Mountains, carving out spectacular fjords and inlets. These deep, narrow waterways, often lined with towering cliffs and dense forests, offer breathtaking scenery and provide access to remote areas within the range.
- Forests and Valleys: The lower slopes of the Coast Mountains are covered in lush forests, primarily dominated by towering coniferous trees like Sitka spruce, western hemlock, and Douglas fir. These forests provide vital habitats for a wide array of wildlife, including bears, wolves, and mountain goats.
- Alpine Meadows and Tundra: Above the treeline, the landscape transitions into alpine meadows and tundra. These high-altitude ecosystems, characterized by sparse vegetation and harsh conditions, are home to hardy species like marmots, pikas, and mountain sheep.
A Realm of Biodiversity
The Coast Mountains are not only a visual spectacle but also a haven for biodiversity. The diverse habitats within the range support a rich tapestry of flora and fauna, including:
- Marine Life: The fjords and inlets of the Coast Mountains provide a unique environment for marine life, hosting a diverse range of fish, shellfish, and marine mammals.
- Birds: The forests, meadows, and rocky cliffs of the Coast Mountains attract a wide array of bird species, including bald eagles, peregrine falcons, and numerous songbirds.
- Mammals: The range is home to a variety of mammals, including bears, wolves, mountain goats, elk, and deer.
Economic and Cultural Significance
The Coast Mountains hold significant economic and cultural importance for the surrounding communities.
- Hydropower: The abundant water resources of the Coast Mountains are harnessed to generate hydroelectric power, providing energy for communities throughout the region.
- Tourism: The stunning natural beauty of the Coast Mountains attracts millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to the local economies.
- Indigenous Culture: The Coast Mountains hold deep cultural significance for Indigenous peoples, who have lived in the region for millennia. Their traditional knowledge and practices are intertwined with the land and its resources.
Conservation and Challenges
The pristine landscapes and abundant wildlife of the Coast Mountains face a number of challenges, including:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns threaten the glaciers, icefields, and forests of the Coast Mountains.
- Development: Increased development, including logging, mining, and infrastructure projects, can fragment habitats and disrupt ecosystems.
- Pollution: Air and water pollution from industrial activities can have detrimental effects on the health of the Coast Mountains.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the unique ecosystems and cultural heritage of the Coast Mountains. Collaboration between governments, Indigenous communities, and conservation organizations is essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of this remarkable mountain range.
FAQs
- What is the highest peak in the Coast Mountains? Mount Waddington, located in British Columbia, is the highest peak in the Coast Mountains, reaching an elevation of 4,019 meters (13,186 feet).
- Are there any volcanoes in the Coast Mountains? While the Coast Mountains are not as volcanically active as the Cascade Range, there are a few extinct volcanoes within the range, such as Mount Garibaldi in British Columbia.
- How do the Coast Mountains influence the climate of the Pacific Northwest? The Coast Mountains act as a barrier to moisture-laden air from the Pacific Ocean, creating a rain shadow effect on the eastern side of the range. This results in a drier climate on the eastern slopes compared to the wetter western slopes.
- What are some popular activities in the Coast Mountains? The Coast Mountains offer a variety of recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, fishing, kayaking, skiing, and snowboarding.
- What is the significance of the Coast Mountains for Indigenous peoples? The Coast Mountains hold deep cultural significance for Indigenous peoples, who have lived in the region for millennia. Their traditional knowledge and practices are intertwined with the land and its resources.
Tips for Exploring the Coast Mountains
- Plan your trip carefully: The Coast Mountains can be a challenging environment, so it is important to plan your trip carefully, considering factors such as weather, elevation, and terrain.
- Respect the environment: Leave no trace of your visit by packing out all your trash and staying on designated trails.
- Be aware of wildlife: The Coast Mountains are home to a variety of wildlife, so be aware of your surroundings and take precautions to avoid encounters with dangerous animals.
- Check for trail closures: Trail closures may occur due to weather conditions or other factors, so check for updates before heading out.
- Be prepared for changing weather: The weather in the Coast Mountains can change rapidly, so be prepared for all conditions.
Conclusion
The Coast Mountains, a majestic spine of North America, are a testament to the Earth’s dynamic geological forces. This imposing range, with its towering peaks, cascading glaciers, and diverse ecosystems, offers a glimpse into the power and beauty of nature. The Coast Mountains are not only a visual spectacle but also a haven for biodiversity, a source of economic activity, and a place of deep cultural significance. As we continue to explore and appreciate this remarkable mountain range, it is crucial to prioritize conservation efforts to ensure its long-term health and sustainability.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Coast Mountains: A Majestic Spine of North America. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!