Russia’s Geographic Landscape: A Bridge Between Continents
Related Articles: Russia’s Geographic Landscape: A Bridge Between Continents
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Russia’s Geographic Landscape: A Bridge Between Continents. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Russia’s Geographic Landscape: A Bridge Between Continents
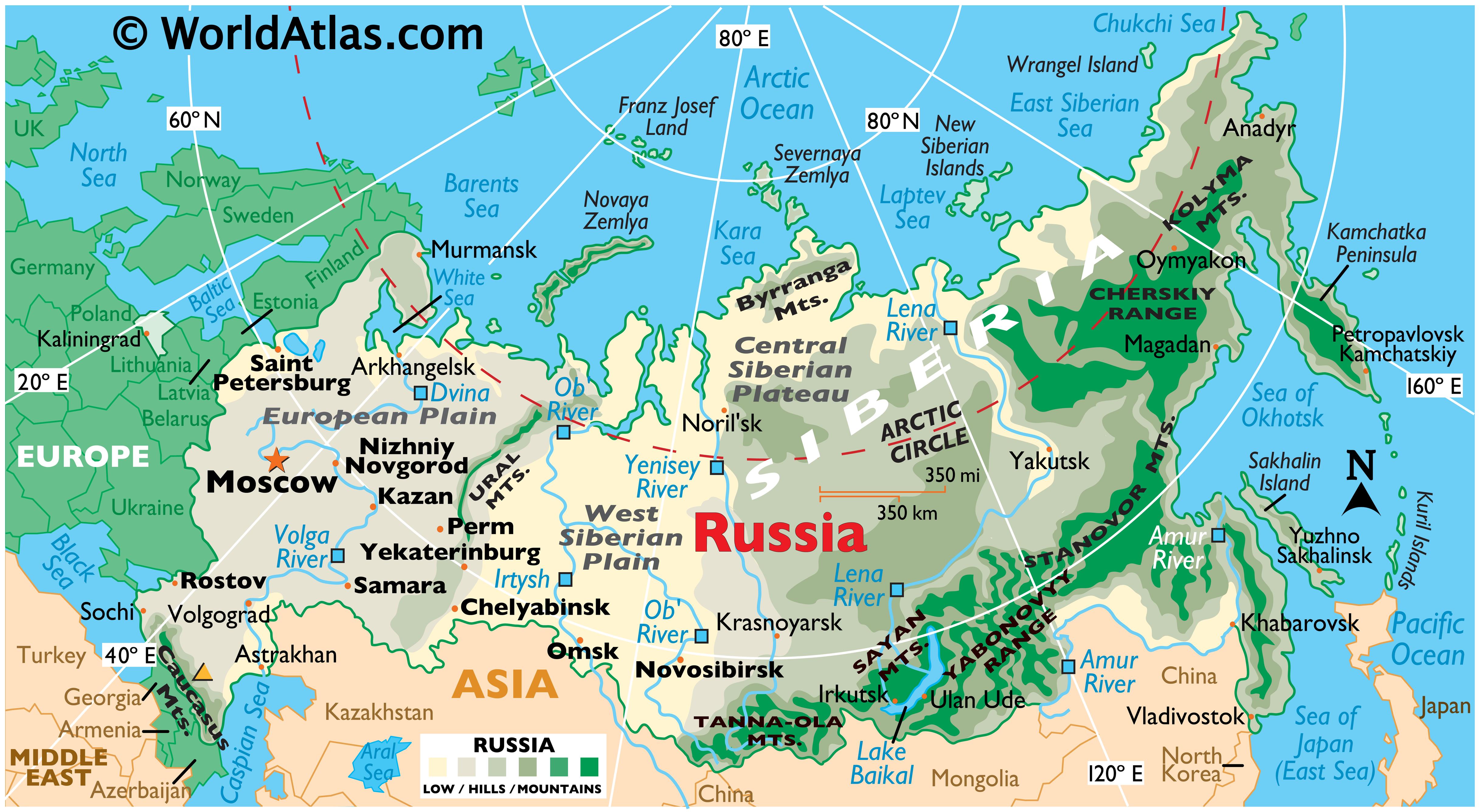
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, occupies a vast expanse across two continents, Europe and Asia. Its geographical position is a defining characteristic, shaping its history, culture, and global influence. Understanding Russia’s location on the map is crucial for comprehending its geopolitical significance, natural resources, and diverse landscapes.
A Land of Extremes:
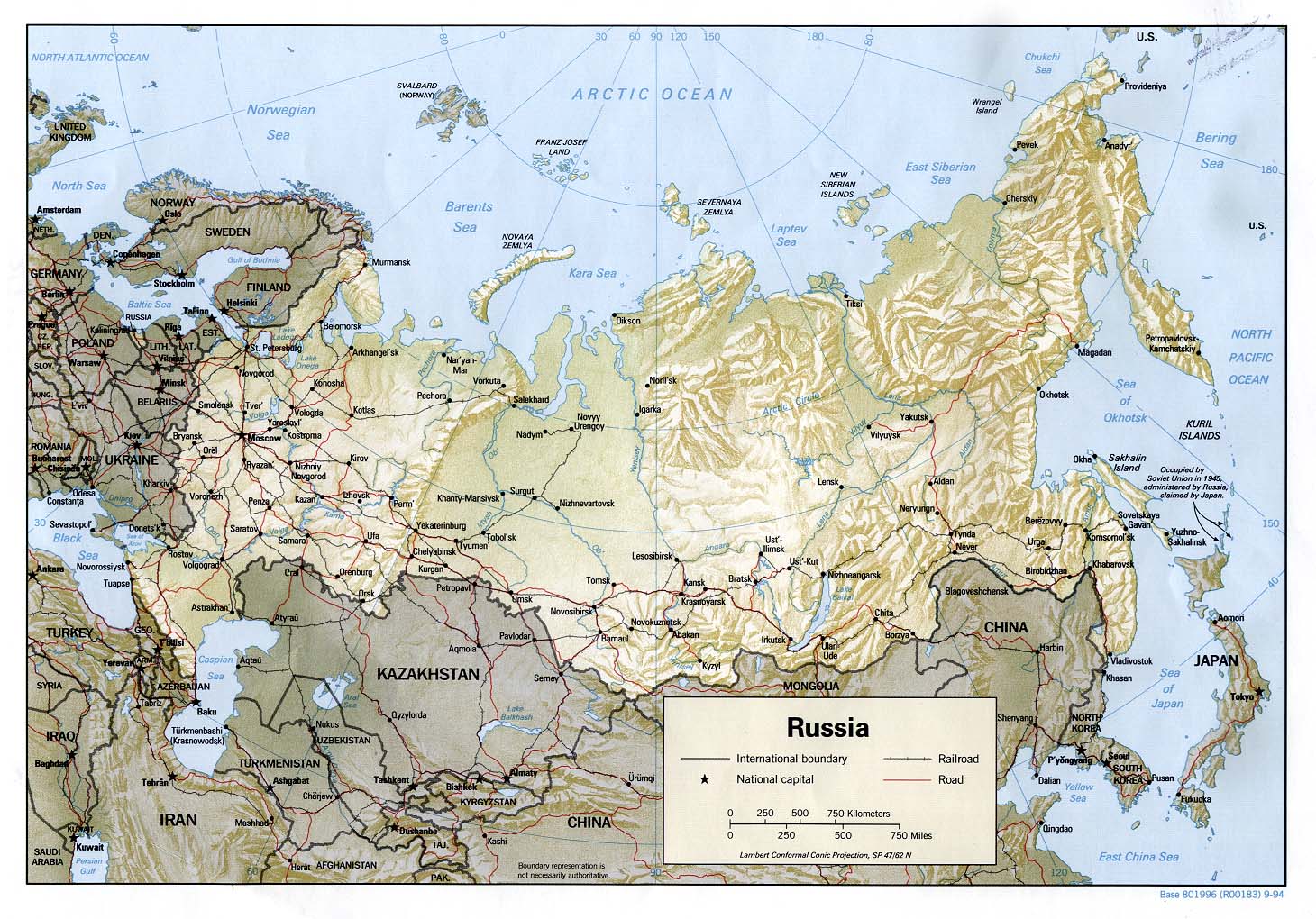
Russia’s territory stretches over 11 time zones, encompassing a diverse array of landscapes. From the frozen tundra of the Arctic to the sun-drenched steppes of the south, the country experiences a wide range of climates and ecosystems. The Ural Mountains, a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, run through the heart of Russia, dividing the country into its European and Asian parts.
Key Geographic Features:
- The Arctic: Russia holds the longest Arctic coastline in the world, with access to vast reserves of natural resources, including oil and gas. The Northern Sea Route, a maritime passage through the Arctic Ocean, offers potential for economic development and trade.
- The Ural Mountains: These mountains mark the traditional boundary between Europe and Asia and serve as a significant geographical feature. They are rich in mineral resources, contributing to Russia’s industrial development.
- The Siberian Plain: Spanning over 7 million square kilometers, Siberia is the largest region in Russia and one of the largest in the world. It is home to vast forests, frozen permafrost, and abundant natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.
- The Caucasus Mountains: Located in the southwest, the Caucasus Mountains are a barrier between Russia and the Black Sea, offering strategic importance and a diverse range of ecosystems.
- The Black Sea: A warm-water sea, the Black Sea provides access to international trade routes and serves as a vital shipping hub for Russia.
Geopolitical Implications:
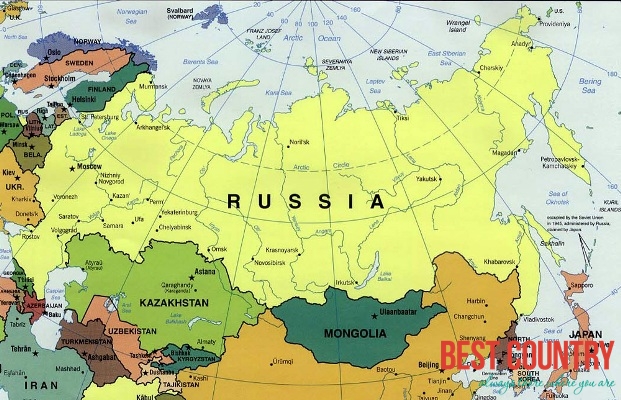
Russia’s vast size and strategic location have significantly impacted its geopolitical role throughout history. It shares borders with 14 countries, including major powers like China, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan. This proximity has led to complex relationships and historical conflicts, shaping the country’s foreign policy and international relations.
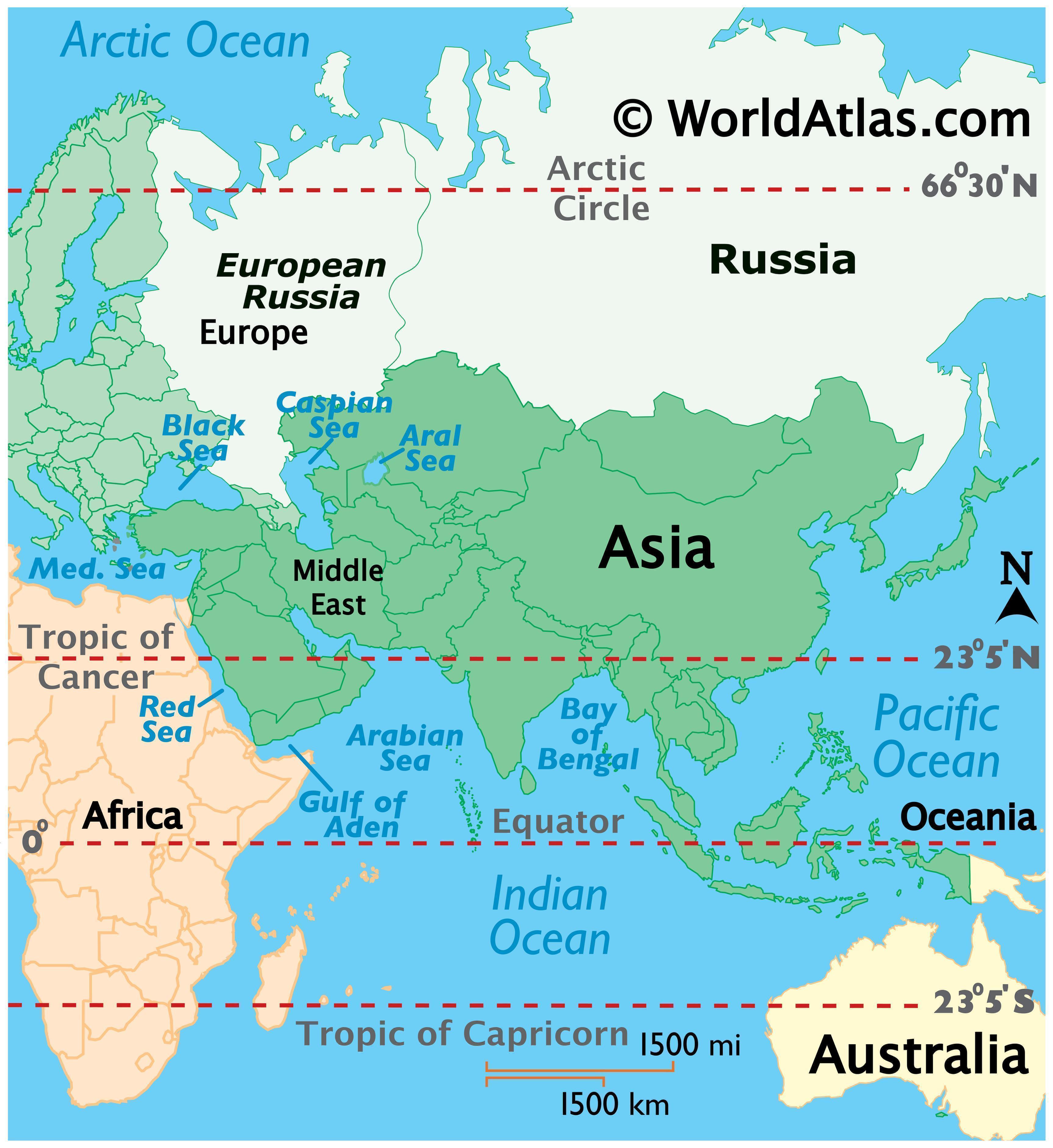
- Land Bridge Between Continents: Russia’s location as a bridge between Europe and Asia has historically facilitated cultural exchange and trade. The Trans-Siberian Railway, a vital infrastructure project, connects Moscow to the Pacific Ocean, showcasing the country’s role in connecting the two continents.
- Strategic Buffer Zone: Russia’s vast territory serves as a strategic buffer zone between the West and East, influencing regional security dynamics and geopolitical alliances.
- Access to Key Waterways: Russia’s access to the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, and the Arctic Ocean provides significant strategic advantages, facilitating trade, transportation, and military operations.
Economic and Environmental Significance:
Russia’s location on the map also plays a crucial role in its economic and environmental landscape.
- Natural Resources: Russia is a major producer of oil, gas, minerals, timber, and other natural resources. These resources are crucial to the country’s economy and contribute significantly to global energy markets.
- Environmental Challenges: Russia faces significant environmental challenges due to its vast size and diverse ecosystems. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution pose threats to its natural resources and biodiversity.
- Potential for Development: Russia’s vast territory offers significant potential for economic development, particularly in the Arctic region and Siberia. However, these areas also face challenges related to infrastructure, climate, and environmental protection.
FAQs about Russia’s Location on the Map:
1. Is Russia a European or Asian country?
Russia spans both Europe and Asia, with the Ural Mountains serving as the traditional boundary between the two continents. The majority of Russia’s landmass and population are located in Asia, but the country’s historical, cultural, and political ties are deeply intertwined with Europe.
2. What countries border Russia?
Russia shares borders with 14 countries: Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, and North Korea.
3. What are the main geographical features of Russia?
Russia’s main geographical features include the Arctic, the Ural Mountains, the Siberian Plain, the Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea. These features contribute to the country’s diverse landscapes, natural resources, and strategic importance.
4. How does Russia’s location affect its economy?
Russia’s location provides access to vast natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals, which contribute significantly to its economy. However, the country also faces challenges related to infrastructure, climate, and environmental protection in developing these resources.
5. What are the geopolitical implications of Russia’s location?
Russia’s strategic location as a bridge between Europe and Asia has historically influenced its geopolitical role. It serves as a buffer zone between the West and East, impacting regional security dynamics and international relations.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Location on the Map:
- Use a physical map: Examining a physical map of Russia can help visualize the country’s vast size, diverse landscapes, and key geographical features.
- Study the borders: Understanding the countries that border Russia provides insight into its geopolitical relationships and historical interactions.
- Explore the major cities: Identifying major cities and their locations can help understand the distribution of population, economic activity, and cultural centers.
- Learn about the climate zones: Understanding the different climate zones across Russia can provide insights into the country’s agricultural potential, environmental challenges, and diverse ecosystems.
- Research historical events: Studying historical events that have occurred in different regions of Russia can shed light on the country’s geopolitical evolution and its relationship with neighboring countries.
Conclusion:
Russia’s location on the map is a defining characteristic, shaping its history, culture, and global influence. Its vast territory, diverse landscapes, and strategic position have played a crucial role in its economic development, geopolitical dynamics, and environmental challenges. Understanding Russia’s geographical landscape provides a deeper understanding of its complex history, present-day realities, and future potential.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Russia’s Geographic Landscape: A Bridge Between Continents. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!