Navigating the Veins of Australia: An Exploration of the River Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Veins of Australia: An Exploration of the River Network
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Veins of Australia: An Exploration of the River Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Veins of Australia: An Exploration of the River Network

Australia, a land of diverse landscapes and ancient history, is intricately woven together by a vast network of rivers. These waterways, some mighty and enduring, others ephemeral and fleeting, play a crucial role in the nation’s ecological balance, economic development, and cultural identity. Understanding the intricate tapestry of Australia’s river systems is essential for appreciating the country’s natural heritage and its ongoing challenges.
The Diverse Character of Australian Rivers
Australia’s rivers are as diverse as the continent itself. From the mighty Murray-Darling Basin, spanning over 1 million square kilometers, to the ephemeral streams of the arid interior, each river system exhibits unique characteristics shaped by geology, climate, and human intervention.
- The Murray-Darling Basin: This vast network, encompassing the Murray, Darling, and Murrumbidgee rivers, is the lifeblood of eastern Australia. It sustains agriculture, provides drinking water for millions, and supports diverse ecosystems.
- The Great Dividing Range Rivers: Flowing from the eastern highlands, rivers like the Hunter, Hawkesbury, and Brisbane play a vital role in urban water supply and irrigation, while also providing habitats for diverse wildlife.
- The Western Australian Rivers: The arid interior of Western Australia is home to unique river systems, often characterized by intermittent flows and diverse landscapes. The Fitzroy River, the largest in the region, sustains significant cultural and ecological value.
- The Northern Rivers: The tropical north of Australia is home to rivers like the Daly, the Roper, and the Mitchell, which are influenced by monsoonal rains and support diverse ecosystems, including the iconic Kakadu National Park.
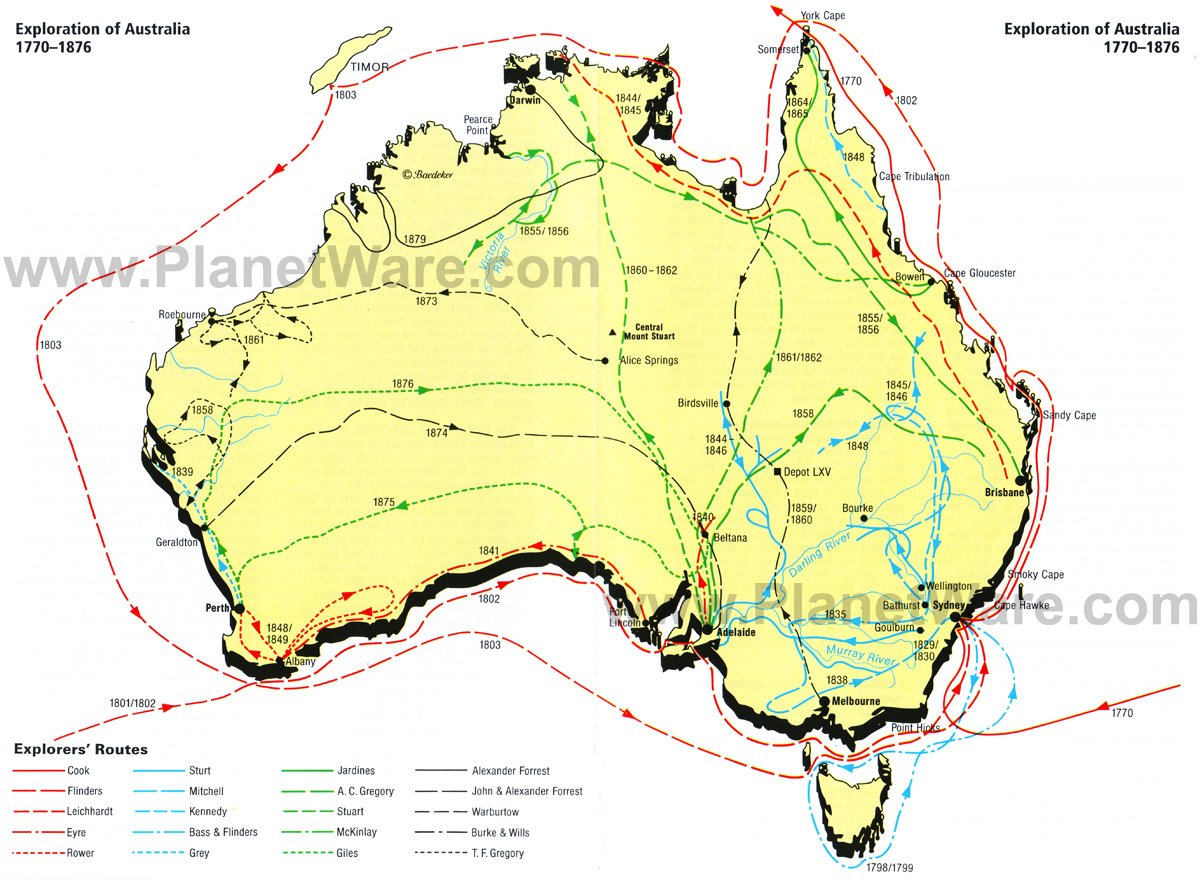
A River Map: Unlocking the Secrets of the Land
An Australian river map is a valuable tool for understanding the interconnectedness of the continent’s waterways. It provides a visual representation of the major river systems, their tributaries, and their flow patterns. This information is crucial for:
- Water Management: Understanding the flow patterns and interconnections of river systems is essential for managing water resources sustainably. It allows for the development of efficient irrigation systems, the protection of vulnerable ecosystems, and the mitigation of drought risks.
- Environmental Protection: River maps highlight the critical role of waterways in supporting biodiversity. They provide information about the distribution of key habitats, the impact of human activities on river health, and the need for conservation efforts.
- Economic Development: River systems are vital for agriculture, tourism, and transportation. A river map helps identify potential development opportunities, assess the environmental impact of proposed projects, and guide sustainable economic growth.
- Cultural Understanding: Australian rivers have deep cultural significance for Indigenous communities. River maps can assist in understanding traditional land management practices, identifying culturally important sites, and promoting cultural heritage.
Navigating the Challenges: A Focus on Sustainability
While Australia’s rivers are a source of life and opportunity, they also face significant challenges, including:
- Drought and Climate Change: Australia’s arid climate and increasing droughts are placing immense pressure on water resources. Climate change is exacerbating these challenges, leading to changes in rainfall patterns, increased evaporation, and altered river flows.
- Water Extraction: Human activities, particularly agriculture and urban development, have led to significant water extraction from rivers, impacting flow regimes and threatening ecosystems.
- Pollution: Runoff from agriculture, industrial activity, and urban areas can pollute rivers, harming aquatic life and affecting human health.
- Infrastructure Development: Dams, weirs, and other infrastructure can alter river flows, fragment habitats, and disrupt ecological processes.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Australian Rivers
Q: What are the longest rivers in Australia?
A: The Murray River, stretching over 2,500 kilometers, is the longest river in Australia. The Darling River, flowing for over 2,700 kilometers, is the longest river entirely within Australia.
Q: What is the significance of the Murray-Darling Basin?
A: The Murray-Darling Basin is the largest river system in Australia, providing water for agriculture, urban centers, and diverse ecosystems. It is also a vital source of cultural and economic activity.
Q: How are Australian rivers impacted by climate change?
A: Climate change is altering rainfall patterns, increasing evaporation, and leading to more frequent and severe droughts, impacting river flows and threatening ecosystems.
Q: What are the major threats to Australian rivers?
A: Australian rivers face threats from water extraction, pollution, infrastructure development, and the impacts of climate change.
Tips for Understanding and Protecting Australia’s Rivers
- Become informed: Educate yourself about the importance of Australia’s rivers, the challenges they face, and the role you can play in protecting them.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose products that minimize water consumption, support responsible agriculture, and advocate for sustainable water management practices.
- Get involved: Participate in river clean-up events, volunteer with environmental organizations, and advocate for policies that protect rivers.
- Reduce your water footprint: Conserve water at home, in the garden, and at work.
- Support Indigenous land management: Recognize the traditional knowledge and practices of Indigenous communities in managing water resources.
Conclusion: A Call for Stewardship
Australia’s rivers are a vital part of the continent’s natural heritage, providing life-sustaining resources and supporting diverse ecosystems. Understanding the complex dynamics of these waterways is crucial for ensuring their health and resilience. By fostering a greater appreciation for the interconnectedness of rivers and the challenges they face, we can work towards a future where these vital waterways continue to thrive. The future of Australia’s rivers depends on our collective commitment to sustainable management, conservation, and responsible stewardship.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Veins of Australia: An Exploration of the River Network. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!