Navigating the Land of the Bible: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel in Biblical Times
Related Articles: Navigating the Land of the Bible: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel in Biblical Times
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Land of the Bible: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel in Biblical Times. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Land of the Bible: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel in Biblical Times
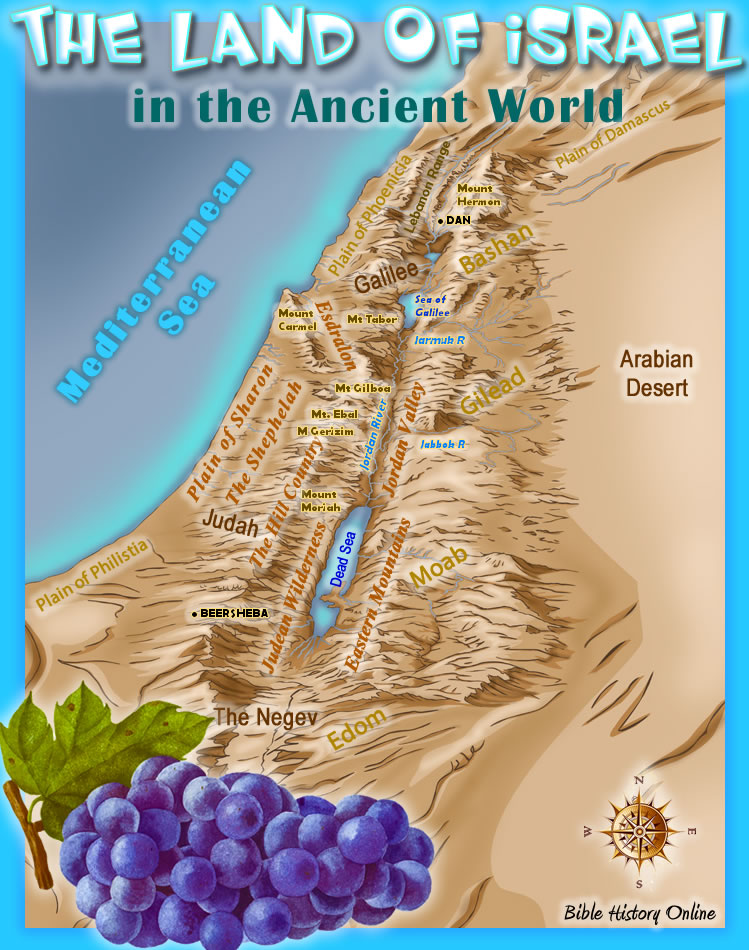
The land of Israel, as depicted in the Bible, is not a static entity but a dynamic landscape that witnessed the unfolding of history, faith, and cultural development. Understanding the geography of this region during biblical times provides invaluable insight into the stories, events, and people that shaped the narrative of the Bible. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the map of Israel in biblical times, encompassing its physical features, historical context, and significance in understanding the biblical text.
The Physical Landscape:
The land of Israel, roughly corresponding to the modern state of Israel and its surrounding territories, is a geographically diverse region. It is characterized by a narrow coastal plain along the Mediterranean Sea, followed by a series of hills and valleys that rise towards the east. This topography significantly influenced the lives of the people who inhabited the region, impacting their agricultural practices, trade routes, and even their religious beliefs.
The Coastal Plain:
This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea was a vital area for agriculture and trade. The coastal cities like Jaffa, Ashdod, and Ashkelon served as important ports, connecting the region to the wider Mediterranean world. This region played a significant role in the lives of the Philistines, who established their kingdom along the coast, and later, the Israelites who established their own coastal cities.
The Central Highlands:
This region, known as the "Shephelah," is characterized by rolling hills and valleys, ideal for grazing livestock and cultivating crops. The central highlands were the heartland of the Israelite kingdoms, with cities like Jerusalem, Hebron, and Bethlehem serving as important religious and political centers. The rugged terrain of the highlands also provided strategic advantages, enabling the Israelites to defend their territory against invaders.
The Jordan Rift Valley:
This geological depression, running north-south along the eastern border of the land of Israel, is home to the Jordan River and the Dead Sea. The valley’s unique microclimate allowed for the cultivation of date palms and other crops, making it an important agricultural region. The Jordan River also served as a natural boundary, separating the land of Israel from the Transjordanian plateau.
The Transjordanian Plateau:
Located east of the Jordan River, this plateau was home to various groups, including the Moabites, Ammonites, and Edomites. The region was characterized by its rugged terrain and arid climate, making it less suitable for agriculture but providing natural defenses.
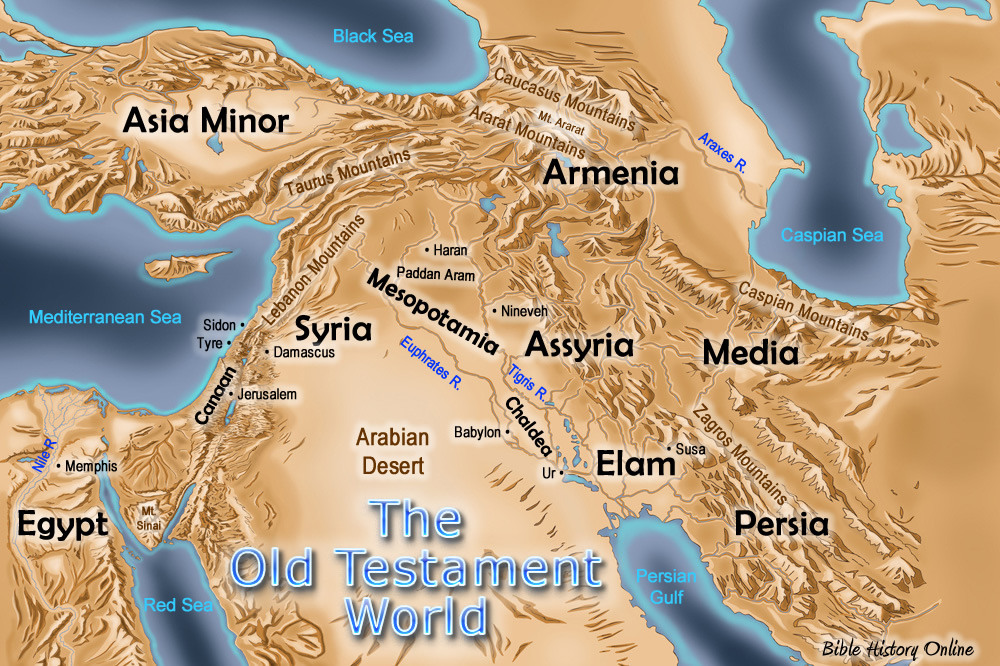
Historical Context:
The map of Israel in biblical times reflects the dynamic history of the region. From the Bronze Age, when the land was ruled by various Canaanite city-states, to the Iron Age, which saw the rise and fall of the Israelite kingdoms, the map evolved with each historical event.
The Canaanite Period:
The Canaanite period, spanning the Bronze Age, witnessed the development of sophisticated city-states along the coastal plain and in the central highlands. These cities were centers of trade, religion, and cultural influence, with their own distinct identities and political structures. The Israelites arrived in this region, claiming it as their promised land, and their interactions with the Canaanites shaped their early history.
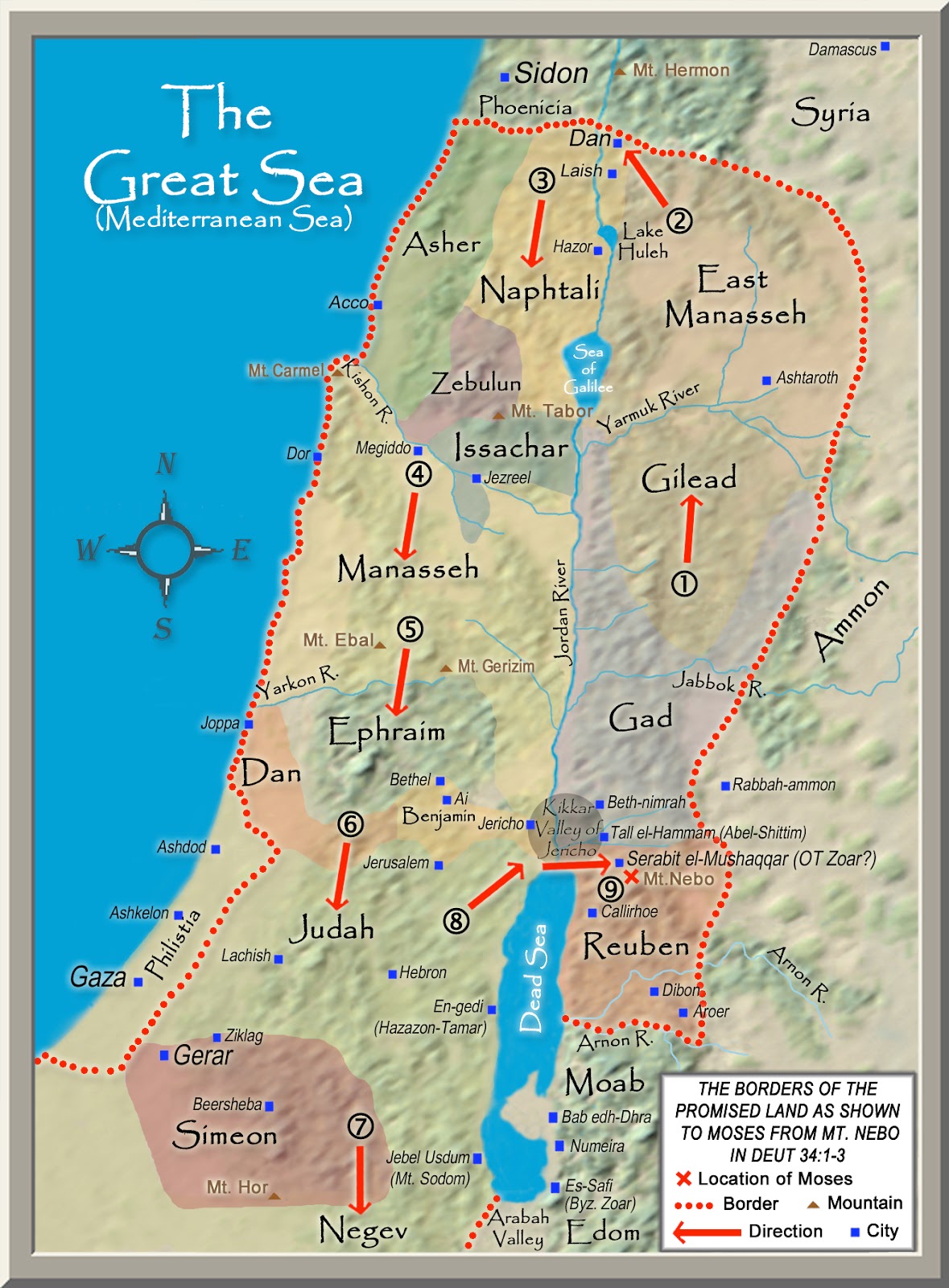
The Israelite Period:
The Iron Age marked the emergence of the Israelite kingdoms, with the establishment of the United Kingdom under Saul, David, and Solomon. This period saw the consolidation of Israelite power, the expansion of their territory, and the development of their religious and cultural traditions. The division of the kingdom into Israel and Judah, followed by their eventual conquest by foreign powers, left a lasting impact on the map of the region.
The Babylonian Exile and the Return:
The destruction of the Israelite kingdoms by the Babylonians in the 6th century BCE marked a significant turning point in the region’s history. The Babylonian Exile, which saw the deportation of many Israelites to Babylon, led to a period of cultural and religious upheaval. The subsequent return to the land of Israel under the Persian Empire brought about a gradual reconstruction of the temple and the reestablishment of Jewish life in the region.
The Hellenistic and Roman Periods:
The conquest of the region by the Greeks under Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE ushered in the Hellenistic period, characterized by the spread of Greek culture and influence. The Roman conquest in the 1st century BCE brought about a new era of political and social change, with the region becoming part of the Roman Empire. This period saw the rise of the Herodian dynasty, which played a significant role in the reconstruction of the Temple in Jerusalem and the development of the region’s infrastructure.
The Significance of the Map:
The map of Israel in biblical times serves as a vital tool for understanding the narrative of the Bible. It allows us to visualize the geographical setting of biblical stories, providing context for the events, characters, and themes that shaped the religious and cultural history of the region.
Benefits of Studying the Map:
- Understanding the Context of Biblical Stories: The map helps us understand the physical environment in which the biblical narratives unfolded, providing context for the events, characters, and themes that shaped the religious and cultural history of the region.
- Visualizing the Journeys of Biblical Figures: The map allows us to visualize the journeys of biblical figures, tracing their movements across the land of Israel and understanding the geographical factors that influenced their decisions and actions.
- Appreciating the Diversity of the Land: The map reveals the diversity of the land of Israel, highlighting its physical features, cultural landscapes, and historical significance. This understanding enhances our appreciation for the richness and complexity of the biblical narrative.
- Connecting the Bible to History: The map connects the biblical text to the broader historical context of the region, revealing the interplay of religious, political, and social factors that shaped the lives of the people who inhabited the land of Israel.
FAQs:
Q: What is the relationship between the map of Israel in biblical times and the modern state of Israel?
A: The modern state of Israel occupies a region that broadly corresponds to the land of Israel in biblical times. However, the borders of the modern state are not identical to those of the ancient kingdoms, and the region has undergone significant demographic and political changes since the biblical era.
Q: What are the major cities and towns depicted on the map of Israel in biblical times?
A: Major cities and towns on the map of Israel in biblical times include:
- Jerusalem: The capital city of both the United Kingdom and the Kingdom of Judah, Jerusalem held immense religious and political significance.
- Hebron: An ancient city in the Judean highlands, Hebron was considered the burial place of the patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob.
- Bethlehem: A town in the Judean highlands, Bethlehem was the birthplace of King David and, later, the birthplace of Jesus Christ according to Christian tradition.
- Nazareth: A town in the Galilee region, Nazareth was the home of Jesus Christ during his childhood and early adulthood.
- Caesarea Maritima: A port city built by Herod the Great, Caesarea Maritima became an important administrative center during the Roman period.
Q: How did the map of Israel change over time during the biblical period?
A: The map of Israel underwent significant changes throughout the biblical period:
- The Canaanite period: The land was divided into various Canaanite city-states, each with its own territory and political structure.
- The Israelite period: The Israelites gradually expanded their territory, conquering neighboring city-states and establishing their own kingdoms.
- The Babylonian Exile: The destruction of the Israelite kingdoms by the Babylonians led to a period of political instability and territorial fragmentation.
- The Persian period: The return of the Israelites from exile under the Persian Empire led to the gradual reestablishment of Jewish life in the region.
Tips for Using the Map:
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the different geographical regions, such as the coastal plain, the central highlands, and the Jordan Rift Valley. These features influenced the lives of the people who lived there.
- Trace the journeys of biblical figures: Identify the routes taken by important figures, such as Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. This helps you understand the context of their stories and the challenges they faced.
- Compare the map to biblical texts: Refer to specific passages in the Bible that describe geographical locations and events. This will deepen your understanding of the biblical narrative and its connection to the land of Israel.
- Use the map as a tool for study and reflection: The map can be a valuable tool for personal study and reflection. It can help you visualize the biblical world and engage with the stories and teachings of the Bible in a more meaningful way.
Conclusion:
The map of Israel in biblical times serves as a vital key to understanding the narrative of the Bible. By exploring the physical landscape, historical context, and cultural significance of the region, we gain a deeper appreciation for the stories, events, and people that shaped the history of the land of Israel and the enduring legacy of the biblical text. The map is not merely a geographical representation but a window into the past, offering insights into the lives, beliefs, and struggles of the people who lived in this land and whose stories continue to resonate with us today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Land of the Bible: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Israel in Biblical Times. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!