Navigating the Celestial Highway: A Deep Dive into Satellite Orbits Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Celestial Highway: A Deep Dive into Satellite Orbits Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Celestial Highway: A Deep Dive into Satellite Orbits Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Celestial Highway: A Deep Dive into Satellite Orbits Maps
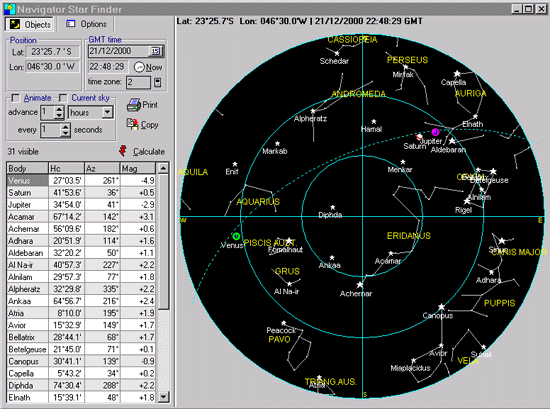
The Earth is enveloped in a complex network of artificial satellites, each diligently fulfilling its purpose. From relaying communication signals to monitoring weather patterns, these celestial voyagers play a crucial role in our modern lives. To understand the intricate dance of these satellites, we turn to satellite orbits maps, visual representations of the pathways these spacecraft traverse around our planet.
Understanding the Fundamentals: A Glimpse into Orbital Mechanics
Before delving into the intricacies of satellite orbits maps, a basic understanding of orbital mechanics is essential. A satellite’s orbit is determined by a delicate balance between its velocity and the Earth’s gravitational pull. The higher the satellite’s velocity, the farther it will travel from the Earth before being pulled back down. This interplay creates a continuous elliptical path around the planet.
Key Orbital Parameters: Defining a Satellite’s Journey
Several key parameters define a satellite’s orbit:
- Altitude: The distance between the satellite and the Earth’s surface.
- Inclination: The angle between the orbital plane and the Earth’s equator. An inclination of 0° represents an equatorial orbit, while 90° signifies a polar orbit.
- Period: The time it takes for a satellite to complete one full orbit around the Earth.
- Eccentricity: A measure of how elliptical the orbit is. A circular orbit has an eccentricity of 0, while a highly elongated orbit has an eccentricity close to 1.
Types of Orbits: A Spectrum of Satellite Trajectories
Based on their altitude, inclination, and eccentricity, satellites occupy various types of orbits, each tailored to specific purposes:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Situated between 160 to 2,000 kilometers above the Earth’s surface, LEO orbits are home to numerous satellites, including the International Space Station, Earth observation satellites, and many communication satellites. Their proximity to Earth allows for faster data transmission and detailed imaging.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Ranging from 2,000 to 35,786 kilometers above the Earth, MEO orbits are often used for navigation and positioning satellites, like those in the Global Positioning System (GPS).
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): Located at an altitude of 35,786 kilometers, GEO satellites maintain a fixed position relative to a specific point on Earth. This unique characteristic makes them ideal for broadcasting and telecommunications, ensuring continuous coverage over a specific region.
- Highly Elliptical Orbit (HEO): These highly eccentric orbits are characterized by significant variations in altitude, bringing the satellite closer to the Earth at its perigee (closest point) and farther away at its apogee (farthest point). HEO orbits are employed for communication and surveillance purposes, enabling coverage over vast geographical areas.
Satellite Orbits Maps: Visualizing the Celestial Network
Satellite orbits maps serve as powerful tools for visualizing the intricate network of satellites orbiting our planet. These maps provide a comprehensive overview of:
- Satellite locations: They depict the real-time positions of numerous satellites, offering a dynamic perspective of their movement.
- Orbital parameters: Maps often display key parameters like altitude, inclination, and eccentricity, providing insights into the characteristics of each orbit.
- Satellite types: Different colors or symbols can be used to differentiate between various types of satellites, such as communication, navigation, or Earth observation satellites.
- Ground tracks: Maps can display the paths traced by satellites on the Earth’s surface, helping to understand their coverage areas.
The Benefits of Satellite Orbits Maps: Unveiling the Power of Visualization
Satellite orbits maps offer a multitude of benefits, making them indispensable tools for various applications:
- Space Situational Awareness: By visualizing the locations and trajectories of satellites, these maps aid in preventing collisions and managing the increasing density of space objects.
- Communication Network Optimization: Maps help in understanding the coverage areas of communication satellites, enabling efficient network design and deployment.
- Earth Observation and Monitoring: By visualizing the orbits of Earth observation satellites, maps facilitate the planning of missions and the analysis of collected data.
- Navigation and Positioning: Maps aid in understanding the positioning and timing of navigation satellites, crucial for accurate GPS navigation.
- Scientific Research: By visualizing the orbits of scientific research satellites, maps support the planning and execution of space missions and the analysis of collected data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Satellite Orbits Maps
Q: How are satellite orbits maps created?
A: Satellite orbits maps are typically created using data from ground-based tracking stations and space-based sensors. This data is processed and visualized using specialized software, resulting in real-time or historical representations of satellite orbits.
Q: What are the different types of satellite orbits maps?
A: Satellite orbits maps can be static or dynamic, 2D or 3D, and can be tailored to specific applications. Some maps focus on specific regions, satellite types, or orbital parameters, while others provide a comprehensive overview of the entire satellite network.
Q: How can I access satellite orbits maps?
A: Many online resources and software applications provide access to satellite orbits maps. Some websites offer free, interactive maps, while others require subscriptions or licenses.
Q: What are the limitations of satellite orbits maps?
A: Satellite orbits maps are only as accurate as the data they are based on. The data may be delayed or incomplete, and the maps may not always reflect the real-time positions of all satellites. Additionally, maps may not always display all relevant orbital parameters.
Tips for Using Satellite Orbits Maps Effectively
- Choose the right map for your needs: Different maps are designed for different purposes. Consider the specific application and choose a map that provides the necessary information.
- Understand the map’s limitations: Be aware of the data sources, accuracy, and limitations of the map before making any decisions based on it.
- Explore interactive features: Many maps offer interactive features, such as zooming, panning, and filtering. Utilize these features to gain a deeper understanding of the data.
- Combine with other data sources: Integrate satellite orbits maps with other data sources, such as ground-based observations or weather data, to gain a more comprehensive perspective.
Conclusion: A Glimpse into the Future of Satellite Orbits Maps
Satellite orbits maps have become essential tools for understanding and managing the ever-growing network of satellites orbiting our planet. Their ability to visualize complex orbital dynamics empowers us to make informed decisions regarding space situational awareness, communication network optimization, Earth observation, navigation, and scientific research. As the number of satellites continues to increase, the importance of these maps will only grow, enabling us to navigate the celestial highway with greater precision and efficiency.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Celestial Highway: A Deep Dive into Satellite Orbits Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!