Navigating Mumbai: A Guide to the City’s Metro Network
Related Articles: Navigating Mumbai: A Guide to the City’s Metro Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Mumbai: A Guide to the City’s Metro Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Mumbai: A Guide to the City’s Metro Network

Mumbai, India’s bustling financial and cultural hub, is a city renowned for its vibrant energy and dense population. Navigating this metropolis can be a daunting task, especially for those unfamiliar with its labyrinthine streets and intricate public transportation system. However, in recent years, the Mumbai Metro has emerged as a game-changer, offering a reliable and efficient mode of transportation for millions of commuters.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Mumbai Metro map, its operational lines, future expansions, and the benefits it offers to the city and its residents.
Understanding the Mumbai Metro Network
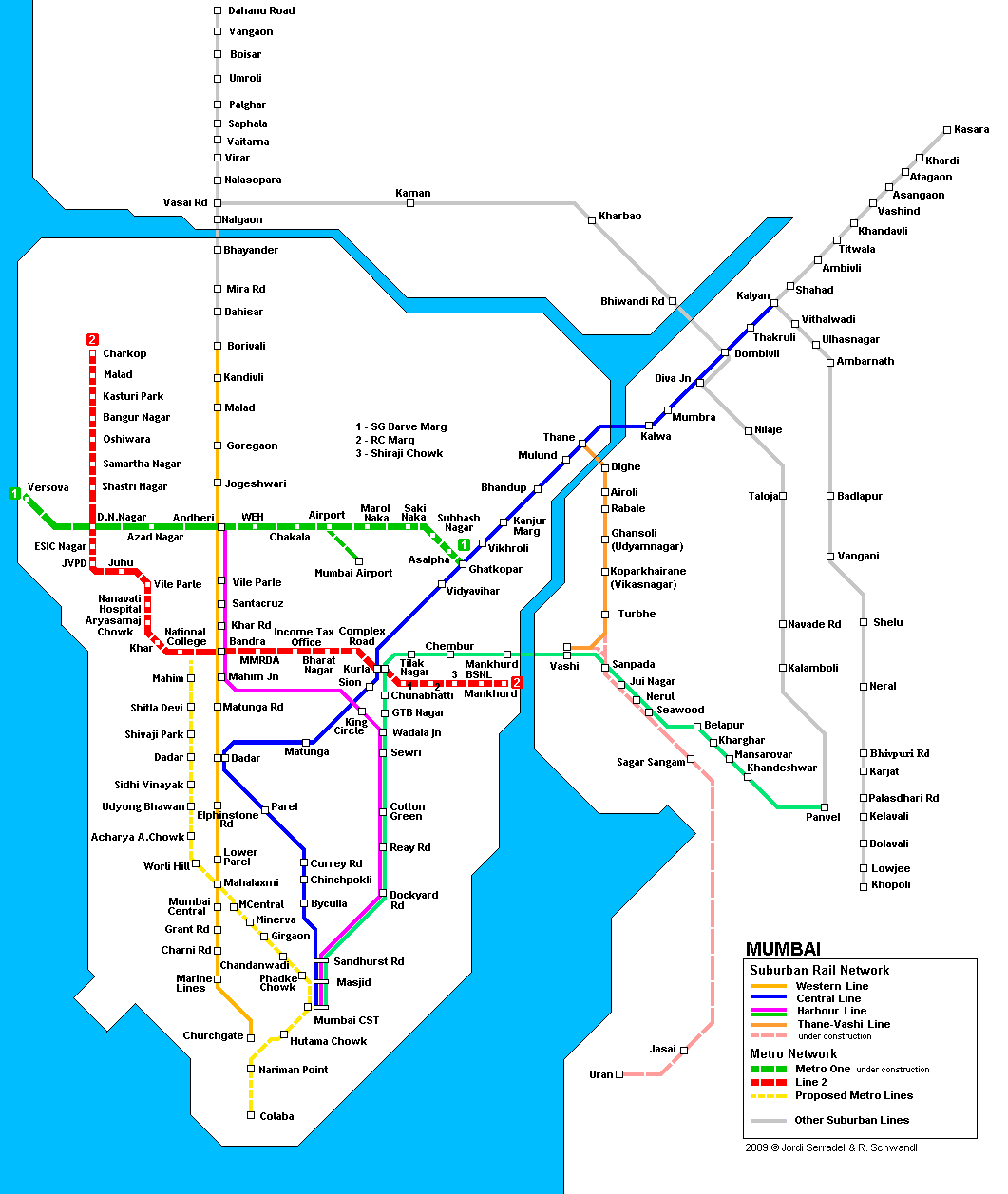
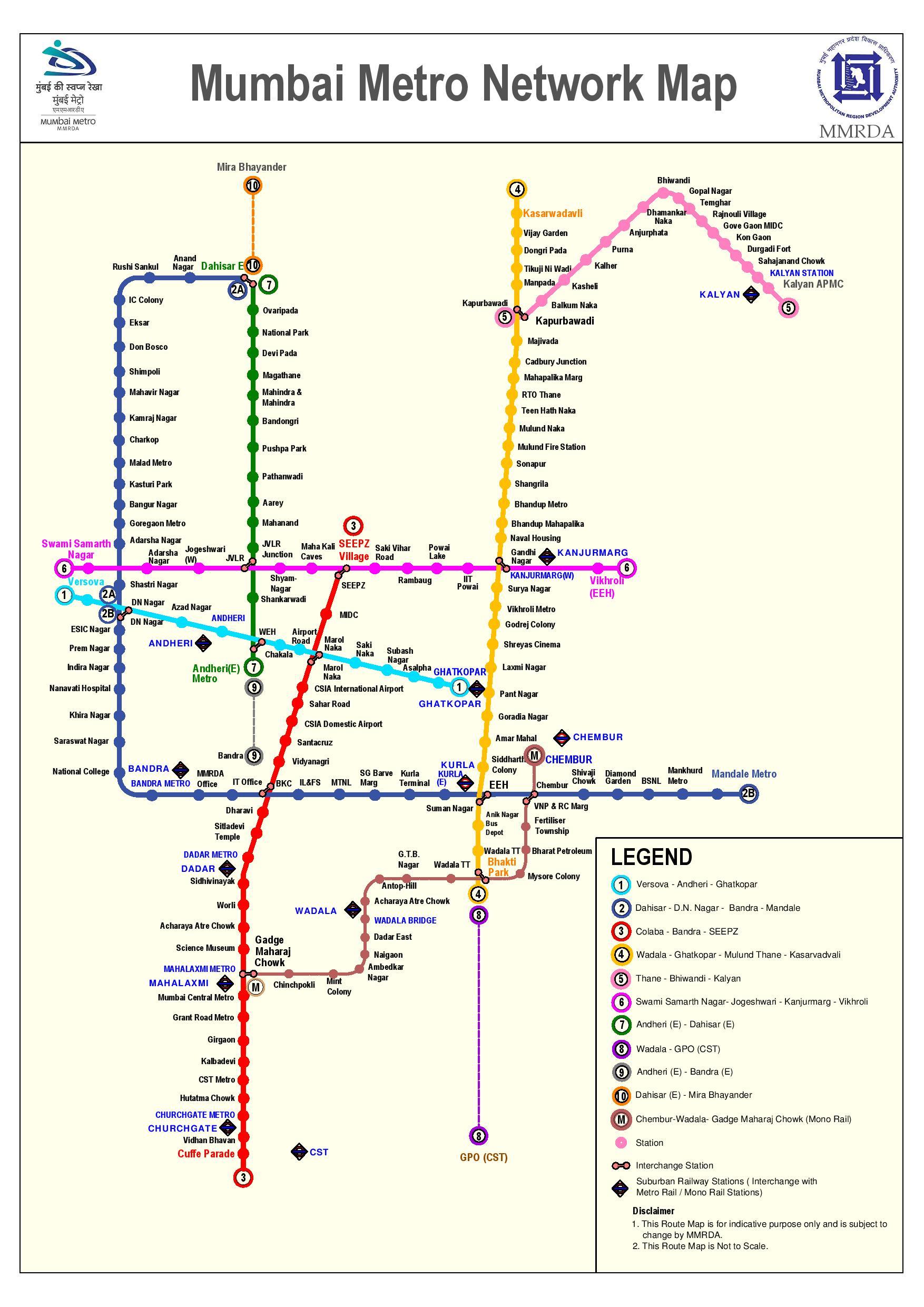
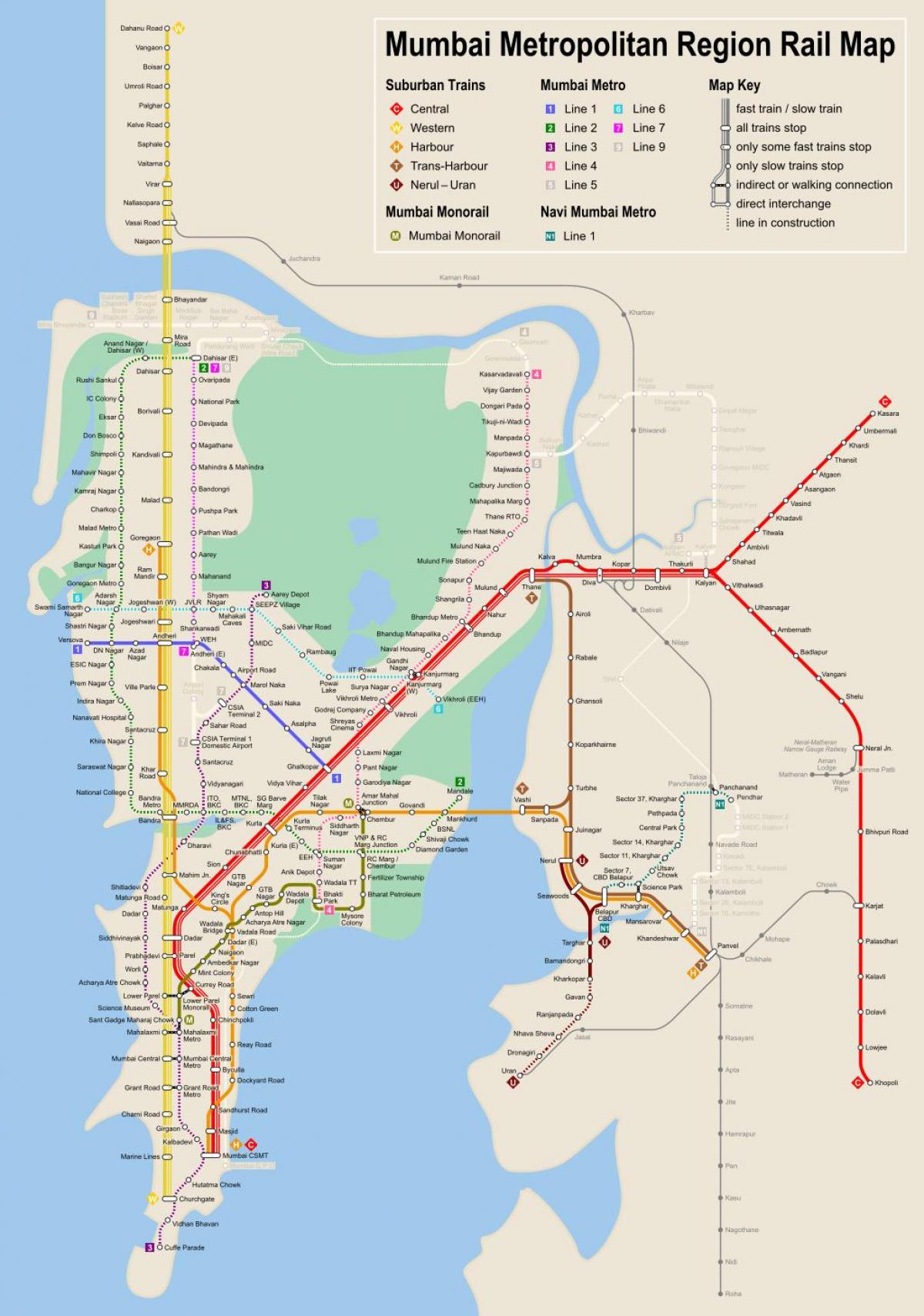
The Mumbai Metro, officially known as the Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation Limited (MMRCL), is a rapid transit system that operates on an extensive network of elevated and underground lines. The system is currently comprised of seven operational lines, with several more under construction or in planning stages.
Operational Lines:
-
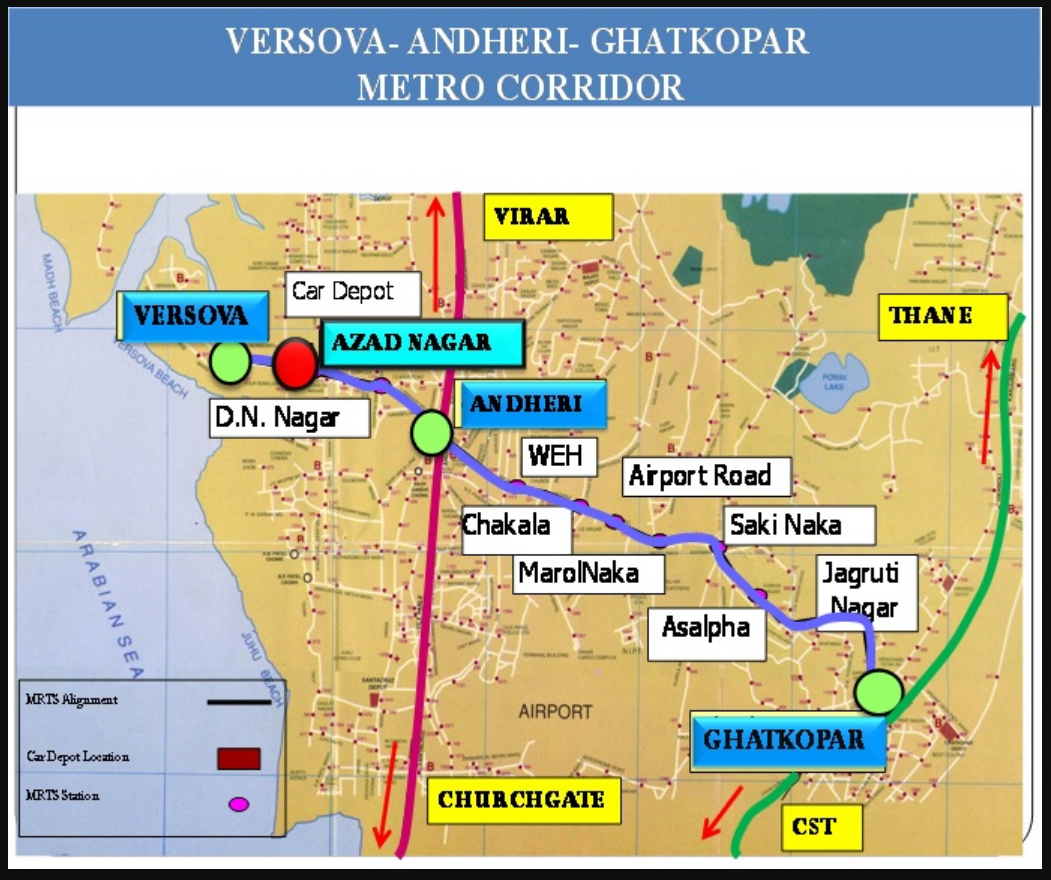
Line 1 (Versova-Andheri-Ghatkopar): This was the first operational line of the Mumbai Metro, inaugurated in 2014. It runs from Versova in the west to Ghatkopar in the east, traversing through important areas like Andheri, a commercial and residential hub.
-
Line 2 (Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus-Dahisar): This line, also known as the "Eastern Line," connects the historic Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus (CST) railway station to Dahisar in the north. It runs through important areas like the city center, Dadar, and Borivali.
-
Line 3 (Aqua Line): This line is a 33.5 km long elevated corridor connecting Colaba in south Mumbai to SEEPZ (Santacruz Electronic Export Processing Zone) in the west. It is known for its aesthetically pleasing aqua-colored stations and is a major transportation artery for the city’s western suburbs.
-
Line 4 (Wadala-Ghatkopar): This line, also known as the "Monorail," is a 8.9 km long monorail system connecting Wadala to Ghatkopar. It is a unique addition to Mumbai’s transportation network and serves as a feeder to other metro lines.
-
Line 7 (Andheri East-Dahisar East): This line, also known as the "Metro 7," is a 16.5 km long elevated corridor connecting Andheri East to Dahisar East. It is a major transportation artery for the city’s northern suburbs.
-
Line 8 (Ghatkopar-Mankhurd): This line, also known as the "Metro 8," is a 19 km long underground corridor connecting Ghatkopar to Mankhurd. It is a major transportation artery for the city’s eastern suburbs.
-
Line 9 (Dahisar-Mira-Bhayandar): This line, also known as the "Metro 9," is a 23.5 km long elevated corridor connecting Dahisar to Mira-Bhayandar. It is a major transportation artery for the city’s northern suburbs.
Future Expansions:
The Mumbai Metro network is undergoing rapid expansion, with several new lines under construction and in planning stages. These expansions aim to connect more areas of the city, enhance connectivity, and reduce congestion. Some of the key upcoming lines include:
- Line 2A (Dahisar East-DN Nagar): This line will extend the existing Line 2 from Dahisar East to DN Nagar, connecting the western suburbs to the city center.
- Line 2B (D N Nagar-Mandale): This line will further extend Line 2 from DN Nagar to Mandale, providing improved connectivity to the western suburbs.
- Line 6 (Swami Samarth Nagar-Vikhroli): This line will run from Swami Samarth Nagar in the north to Vikhroli in the east, connecting the north-eastern suburbs to the city center.
- Line 10 (Gaimukh-Shivaji Chowk): This line will connect Gaimukh in the north to Shivaji Chowk in the south, providing a vital transportation link between the northern and southern parts of the city.
Benefits of the Mumbai Metro:
The Mumbai Metro has brought numerous benefits to the city, making it a crucial part of its infrastructure and contributing significantly to the city’s development:
- Reduced Congestion: The metro system provides an efficient alternative to road travel, reducing traffic congestion on the city’s already overcrowded roads.
- Improved Travel Time: With its dedicated tracks and high-speed trains, the metro offers faster travel times compared to other modes of transportation, especially during peak hours.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing reliance on private vehicles, the metro system helps to decrease carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation.
- Economic Growth: The metro network has spurred economic growth by providing easier access to employment opportunities and facilitating faster movement of goods and services.
- Social Inclusion: The metro system makes it easier for people from all walks of life to access various parts of the city, promoting social inclusion and reducing transportation disparities.
FAQs about the Mumbai Metro:
Q: How do I purchase a metro ticket?
A: Metro tickets can be purchased from ticket vending machines located at stations or from ticket counters. You can also use a contactless smart card called "Mumbai 1 Card" for multiple journeys.
Q: What are the operating hours of the Mumbai Metro?
A: The metro operates from approximately 5:30 AM to 11:30 PM, with varying timings depending on the line and day of the week.
Q: Are there any restrictions on carrying luggage on the metro?
A: You are allowed to carry luggage on the metro, but oversized or heavy luggage may require special arrangements.
Q: Are there any facilities for people with disabilities?
A: All metro stations are equipped with ramps, lifts, and other facilities to ensure accessibility for people with disabilities.
Q: Are there any safety measures in place on the metro?
A: The metro system has strict safety measures in place, including CCTV cameras, security personnel, and emergency procedures.
Tips for Using the Mumbai Metro:
- Plan your journey in advance: Use the Mumbai Metro app or website to plan your route and check the latest timetable.
- Arrive early: During peak hours, the metro can be crowded, so it is advisable to arrive early to avoid delays.
- Be aware of your surroundings: Keep an eye on your belongings and be cautious of pickpockets.
- Follow the instructions of station staff: Pay attention to announcements and follow the instructions of station staff.
- Be courteous to other passengers: Allow passengers to disembark before boarding and avoid blocking the aisles.
Conclusion:
The Mumbai Metro has transformed the city’s transportation landscape, providing a reliable, efficient, and sustainable mode of transportation for millions of commuters. Its network continues to expand, connecting more areas and improving connectivity across the city. By understanding the Mumbai Metro map and its operational lines, commuters can navigate the city with greater ease and efficiency, contributing to a more sustainable and vibrant urban environment. As the city continues to grow and evolve, the Mumbai Metro will play an increasingly vital role in shaping its future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Mumbai: A Guide to the City’s Metro Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!