Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of Europe
Related Articles: Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of Europe
Europe, a continent of diverse landscapes and climates, experiences a wide spectrum of weather phenomena. From the scorching summers of the Mediterranean to the frigid winters of Scandinavia, understanding the weather patterns across this vast region is crucial for various sectors, including agriculture, tourism, transportation, and even public health. This intricate dance of atmospheric forces is beautifully captured and analyzed through weather maps, providing valuable insights into the current and future meteorological conditions across Europe.
Understanding the Basics: Elements of a Weather Map
Weather maps are visual representations of meteorological data, providing a snapshot of the atmospheric conditions over a specific geographical area. They are typically composed of various elements, each carrying unique information about the weather:
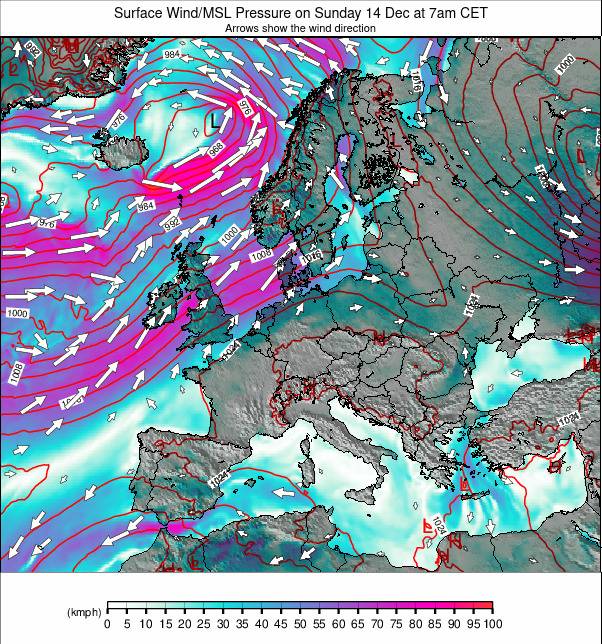
- Isobars: Lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. These lines reveal areas of high pressure (anticyclones) and low pressure (cyclones), which play a significant role in determining wind direction and intensity.
- Isotherms: Lines connecting points of equal temperature. These lines illustrate the temperature distribution across the region, highlighting areas of warmer and colder temperatures.
- Fronts: Boundaries between different air masses, marked by lines with symbols. Cold fronts, depicted by blue triangles, represent the leading edge of a cold air mass displacing warmer air, often associated with rapid temperature drops and potential precipitation. Warm fronts, marked by red semicircles, represent the leading edge of a warm air mass pushing against cooler air, often associated with gradual temperature rises and widespread precipitation.
- Wind Arrows: Indicate wind direction and speed. The arrow points towards the direction from which the wind is blowing, while the length of the arrow represents the wind speed.
- Precipitation Symbols: Represent different types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. The density of the symbols indicates the intensity of the precipitation.
- Cloud Cover: Depicts the amount of cloud cover in a specific area, ranging from clear skies to completely overcast conditions.
Interpreting the Data: Unveiling the Weather Story
By analyzing these elements, weather maps allow us to understand the current weather conditions and predict potential future changes. For example, observing the movement of fronts can help forecast the arrival of precipitation, temperature changes, and wind shifts. High-pressure systems are often associated with clear skies and calm conditions, while low-pressure systems can bring stormy weather and strong winds.
The Importance of Weather Maps: A Multifaceted Impact
Weather maps are essential tools for various sectors, influencing critical decisions and ensuring safety and efficiency:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather maps to plan planting and harvesting schedules, manage irrigation, and protect crops from adverse weather conditions. Understanding potential frost, heatwaves, or heavy rainfall is crucial for ensuring successful harvests.
- Tourism: Tourists and travel agencies use weather maps to plan trips, choose destinations based on preferred weather conditions, and avoid potential hazards like storms or extreme temperatures.
- Transportation: Airlines, shipping companies, and road authorities rely on weather maps to monitor potential disruptions caused by storms, fog, or heavy snow. They use this information to adjust flight routes, reschedule journeys, and ensure safe travel.
- Public Health: Weather maps are crucial for monitoring heatwaves, cold snaps, and other extreme weather events that can impact public health. This information allows authorities to issue warnings, activate emergency protocols, and provide necessary support to vulnerable populations.
Beyond the Snapshot: The Role of Weather Models
While weather maps provide a snapshot of the current conditions, weather models go a step further, using complex mathematical equations and computer simulations to predict future weather patterns. These models incorporate various data sources, including atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation, to generate forecasts for specific time periods.
Navigating the Complexity: FAQs About Weather Maps
1. What are the different types of weather maps?
There are various types of weather maps, each focusing on specific aspects of the weather:
- Synoptic Maps: Provide a general overview of the weather conditions across a large region, typically showing isobars, fronts, and wind patterns.
- Surface Maps: Depict weather conditions at ground level, including temperature, pressure, wind, and precipitation.
- Upper Air Maps: Show atmospheric conditions at different altitudes, including temperature, wind, and humidity.
- Satellite Images: Provide visual representations of cloud cover, precipitation, and other atmospheric phenomena.
2. How accurate are weather maps and forecasts?
The accuracy of weather maps and forecasts depends on various factors, including the complexity of the weather system, the quality of data used, and the computational power of the models. While forecasts have improved significantly over the years, they are not always perfect and can be subject to errors.
3. How can I access weather maps and forecasts?
Weather maps and forecasts are readily available through various sources, including:
- National Meteorological Services: Organizations like the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States and the Met Office in the UK provide comprehensive weather information and forecasts.
- Online Weather Websites: Numerous online platforms offer weather maps, forecasts, and other meteorological data, including AccuWeather, Weather Underground, and the Weather Channel.
- Mobile Apps: Many weather apps provide detailed weather information, including maps, forecasts, and real-time updates.
4. What are the limitations of weather maps?
While weather maps offer valuable insights into the weather, they also have limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of weather maps can vary, with some providing a detailed view of specific areas while others offer a broader overview.
- Temporal Resolution: Forecasts are typically generated for specific time periods, such as hourly, daily, or weekly, and may not capture short-term fluctuations in the weather.
- Model Accuracy: Weather models are constantly being refined, but they are still subject to errors and limitations, especially in predicting complex weather events.
Tips for Effective Weather Map Interpretation
- Understand the symbols and conventions used on the map. Familiarize yourself with the different symbols representing pressure, temperature, fronts, precipitation, and wind.
- Pay attention to the date and time of the map. Weather conditions can change rapidly, so it’s essential to use the most up-to-date information.
- Consider the scale of the map. A map covering a large area may not provide detailed information about specific locations.
- Compare different sources of information. Consult multiple weather maps and forecasts to get a comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
- Be aware of the limitations of weather models. Forecasts are not always accurate, and unexpected weather events can occur.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Navigating the Atmospheric Landscape
Weather maps are indispensable tools for understanding and predicting the weather across Europe. They provide valuable insights into current conditions, potential future changes, and the impact of weather on various sectors. By understanding the elements of a weather map and interpreting the data effectively, we can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and navigate the complex and ever-changing atmospheric landscape. As technology continues to advance, weather maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in our lives, providing critical information to guide our decisions and ensure our safety and well-being.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of Europe. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!