Deciphering the Climate Tapestry of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at its Diverse Climates
Related Articles: Deciphering the Climate Tapestry of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at its Diverse Climates
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Climate Tapestry of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at its Diverse Climates. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Climate Tapestry of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at its Diverse Climates

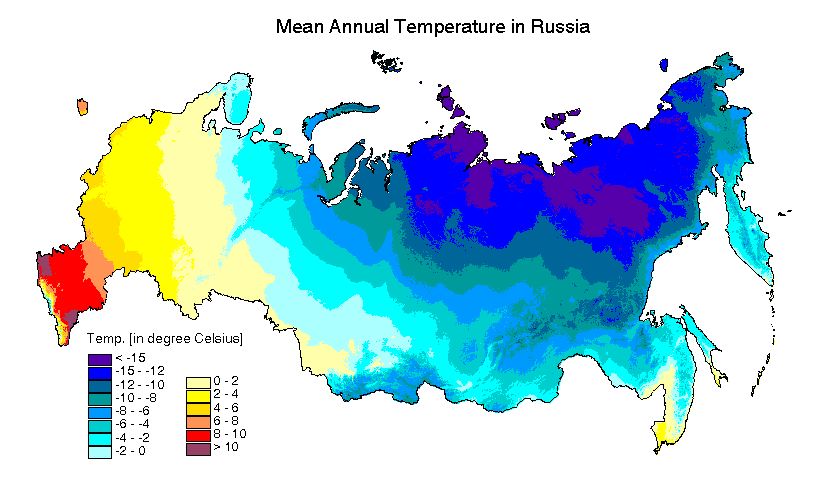
Russia, the largest country in the world, spans vast stretches of land encompassing a multitude of geographical features and climatic zones. Understanding the intricate tapestry of Russia’s climate is crucial for a myriad of reasons, from agriculture and resource management to infrastructure development and public health. This comprehensive exploration delves into the nuances of Russia’s climate map, highlighting its importance and offering insights into its diverse and often extreme weather patterns.
A Mosaic of Climates:
The climate map of Russia is a testament to the country’s vast size and geographical diversity. The vast expanse of Siberia, stretching across northern and eastern Russia, is dominated by a frigid, continental climate characterized by long, cold winters and short, warm summers. The average temperature in Siberia can plummet to -50°C (-58°F) in winter, with permafrost, permanently frozen ground, extending for miles.
Moving westward, the climate transitions to a more temperate, humid continental climate, particularly in the European part of Russia. This region experiences warmer summers and colder winters, with precipitation spread throughout the year. The Black Sea coast, nestled in the southwestern corner of Russia, enjoys a milder, subtropical climate with warm, humid summers and mild winters.
Factors Shaping the Climate:
Several key factors contribute to the diverse climates observed across Russia:
- Latitude: Russia’s vast latitudinal extent, stretching from the Arctic Circle to the Black Sea, is a primary driver of its diverse climates. The higher the latitude, the colder the climate.
- Distance from the Ocean: Russia’s vast continental landmass and its distance from the moderating influence of large bodies of water contribute to the extreme temperature swings observed in much of the country.
- Mountain Ranges: The Ural Mountains and the Caucasus Mountains act as significant barriers, influencing precipitation patterns and creating microclimates in their lee.
- Ocean Currents: The warm North Atlantic Current brings a moderating influence to the northwestern regions of Russia, while the cold Arctic Current influences the northern and eastern coasts.
The Importance of Understanding Russia’s Climate:
The climate map of Russia is not just a scientific curiosity. It holds immense practical significance, influencing various aspects of life and development:
- Agriculture: Understanding the climatic conditions in different regions is essential for determining suitable crops, optimizing planting schedules, and mitigating the impact of extreme weather events.
- Resource Management: The climate map provides valuable insights into the distribution of natural resources, including water, forests, and minerals, facilitating their sustainable management.
- Infrastructure Development: Climate considerations are paramount in designing and constructing infrastructure, particularly in regions prone to extreme temperatures, heavy snowfall, or permafrost.
- Public Health: The climate map helps understand the prevalence of certain diseases, the potential for heatwaves or extreme cold, and the need for public health interventions.
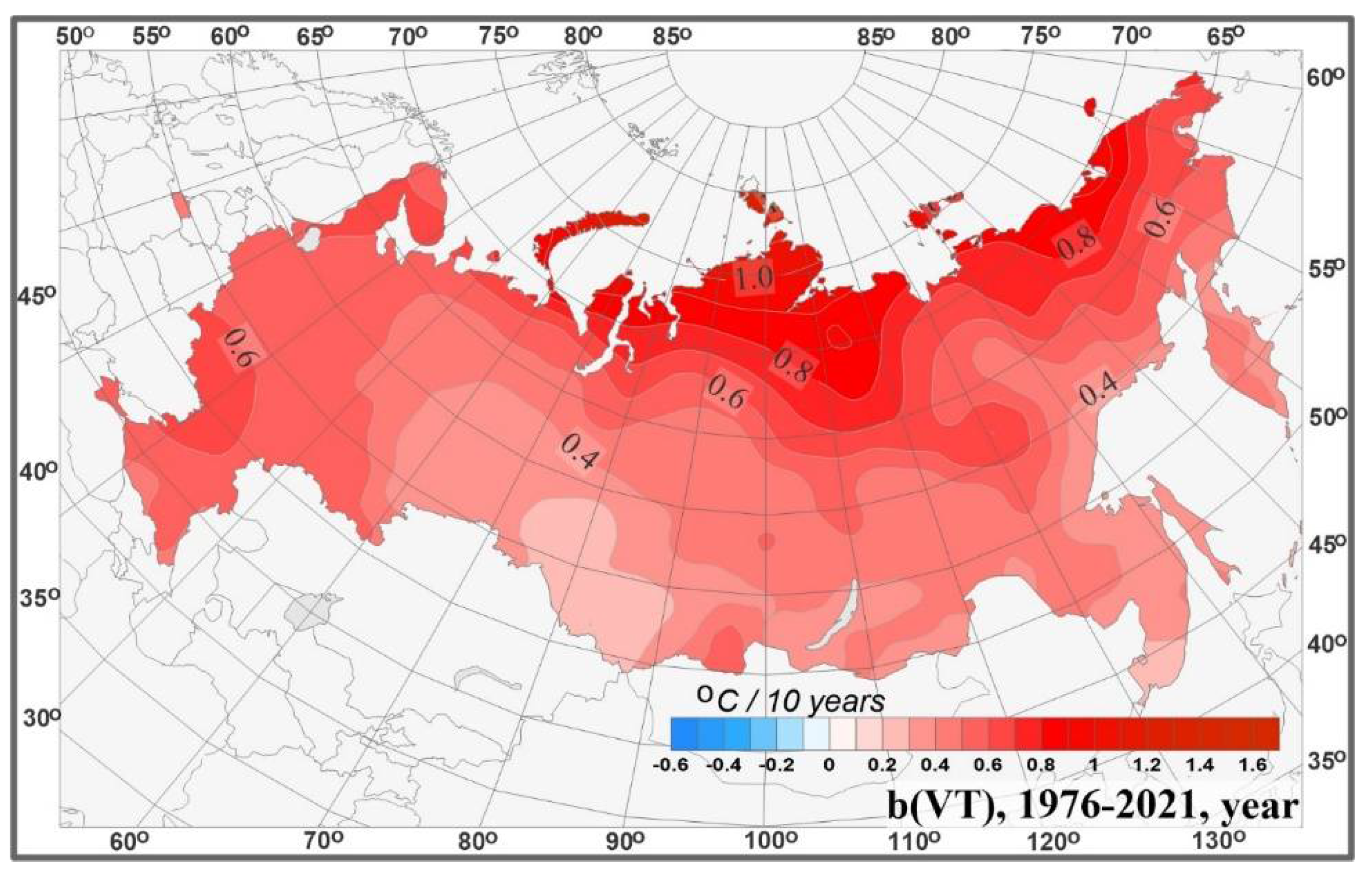
- Climate Change Impacts: Monitoring climate change impacts on Russia’s diverse ecosystems and understanding their implications for human populations is crucial for adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions about Russia’s Climate Map:
Q: What are the coldest and warmest regions of Russia?
A: The coldest region in Russia is Siberia, with average winter temperatures plummeting to -50°C (-58°F). The warmest region is the Black Sea coast, where summers are warm and humid.
Q: What are the major climate zones in Russia?
A: Russia’s climate map features various zones, including:
- Arctic: Characterized by extremely cold temperatures, long winters, and short, cool summers.
- Subarctic: Similar to the Arctic, but with slightly milder temperatures and longer summers.
- Humid Continental: Experiences warm summers and cold winters with precipitation distributed throughout the year.
- Steppe: Dry, semi-arid climate with hot summers and cold winters.
- Subtropical: Found along the Black Sea coast, with warm, humid summers and mild winters.
Q: How does climate change affect Russia?
A: Climate change is having significant impacts on Russia, including:
- Rising temperatures: Average temperatures are rising across Russia, particularly in the Arctic region.
- Melting permafrost: The thawing of permafrost poses significant challenges for infrastructure and ecosystems.
- Changes in precipitation patterns: Some regions are experiencing increased precipitation, while others are becoming drier.
- Increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events: Russia is experiencing more frequent and severe heatwaves, droughts, and floods.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Russia’s Climate Map:
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to reputable organizations like the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the Russian Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring (Roshydromet) for accurate climate data.
- Utilize online tools: Interactive climate maps and data visualization tools can provide insights into specific regions and their climate characteristics.
- Consider regional variations: Remember that Russia’s vast size results in significant regional variations in climate, so generalizations should be avoided.
- Stay informed about climate change impacts: Monitor research and reports on climate change impacts in Russia to understand potential future changes.
Conclusion:
The climate map of Russia is a complex and dynamic representation of the country’s diverse and often extreme weather patterns. Understanding the nuances of this map is crucial for sustainable development, resource management, and adapting to the challenges posed by climate change. By utilizing reliable data sources, engaging with scientific research, and staying informed about ongoing climate trends, we can gain valuable insights into the complexities of Russia’s climate and its profound impact on the country’s future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Climate Tapestry of Russia: A Comprehensive Look at its Diverse Climates. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!