Charting the Course: A History of Maps in the United States
Related Articles: Charting the Course: A History of Maps in the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Course: A History of Maps in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Course: A History of Maps in the United States

The United States, a nation built on exploration and expansion, has a rich and fascinating history of mapmaking. From the earliest hand-drawn sketches to the intricate digital atlases of today, maps have played a crucial role in shaping the country’s identity, development, and understanding of its place in the world. This article delves into the evolution of maps in the United States, examining their diverse purposes, evolving technologies, and enduring impact.
Early Encounters: The Dawn of American Cartography
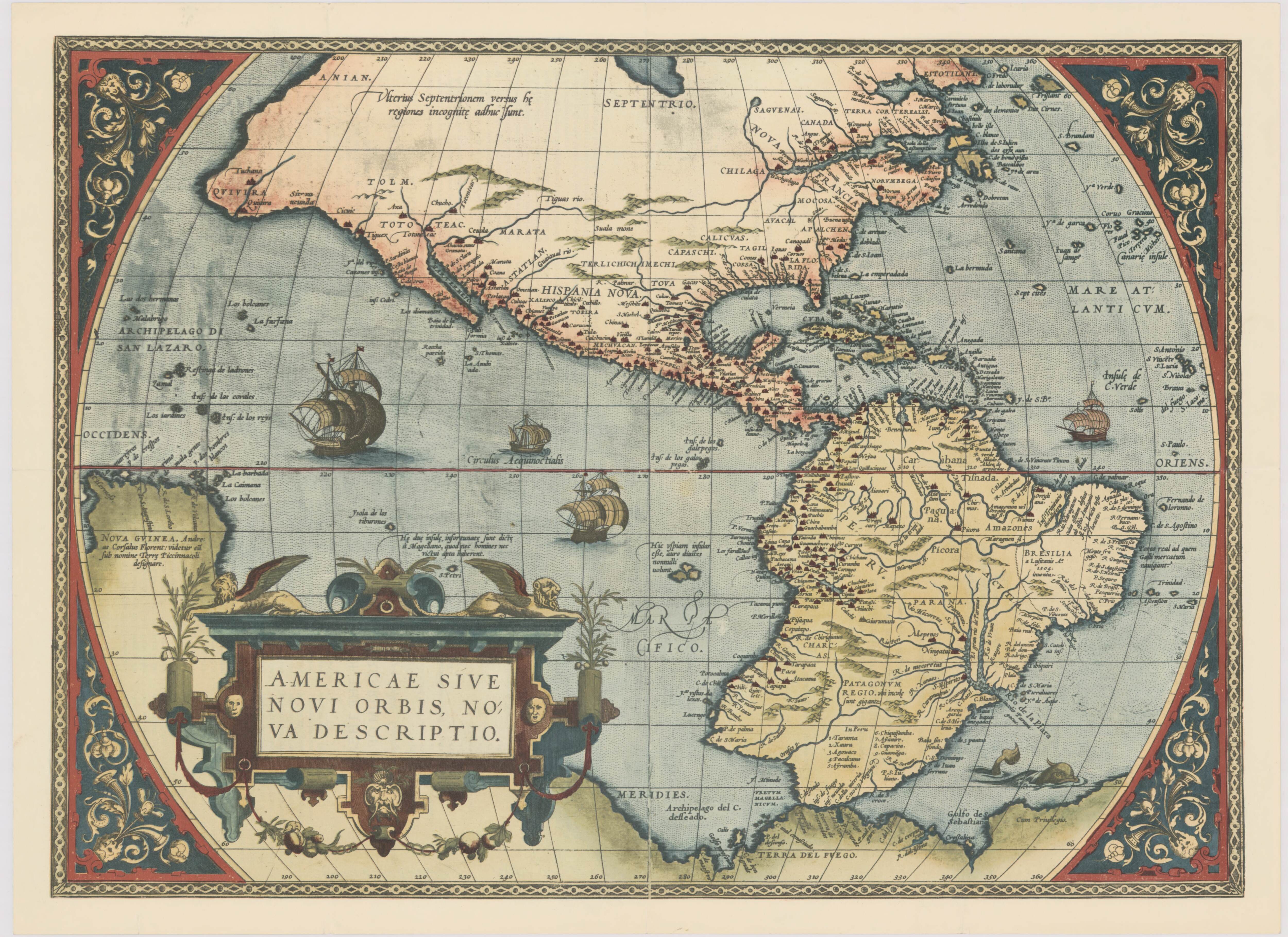
The first maps of the region that would become the United States were crafted by European explorers seeking new lands and trade routes. These early maps, often crude and inaccurate, were based on limited observations and hearsay, relying on the accounts of indigenous peoples and the imagination of cartographers. Notable examples include the maps of Giovanni da Verrazzano, who explored the Atlantic coast in the 16th century, and Samuel de Champlain, who charted the St. Lawrence River and the Great Lakes.
Colonial Expansion and the Rise of Accuracy
As European colonization intensified in the 17th and 18th centuries, the need for more accurate maps became paramount. Land surveys, resource extraction, and military campaigns demanded precise depictions of the terrain. Colonial cartographers, often trained in Europe, began using advanced surveying techniques and instruments, such as the compass and theodolite, to create more detailed and reliable maps. These maps, often engraved on copper plates, were crucial for navigating waterways, establishing settlements, and understanding the vastness of the new territories.
The American Revolution and the Birth of a Nation
The American Revolution further propelled the development of cartography. Military maps, used by both sides of the conflict, proved essential for planning battles, coordinating troop movements, and understanding the strategic landscape. Maps also played a role in shaping public opinion, with cartographers using visual representations to illustrate the injustices of British rule and promote the cause of independence.
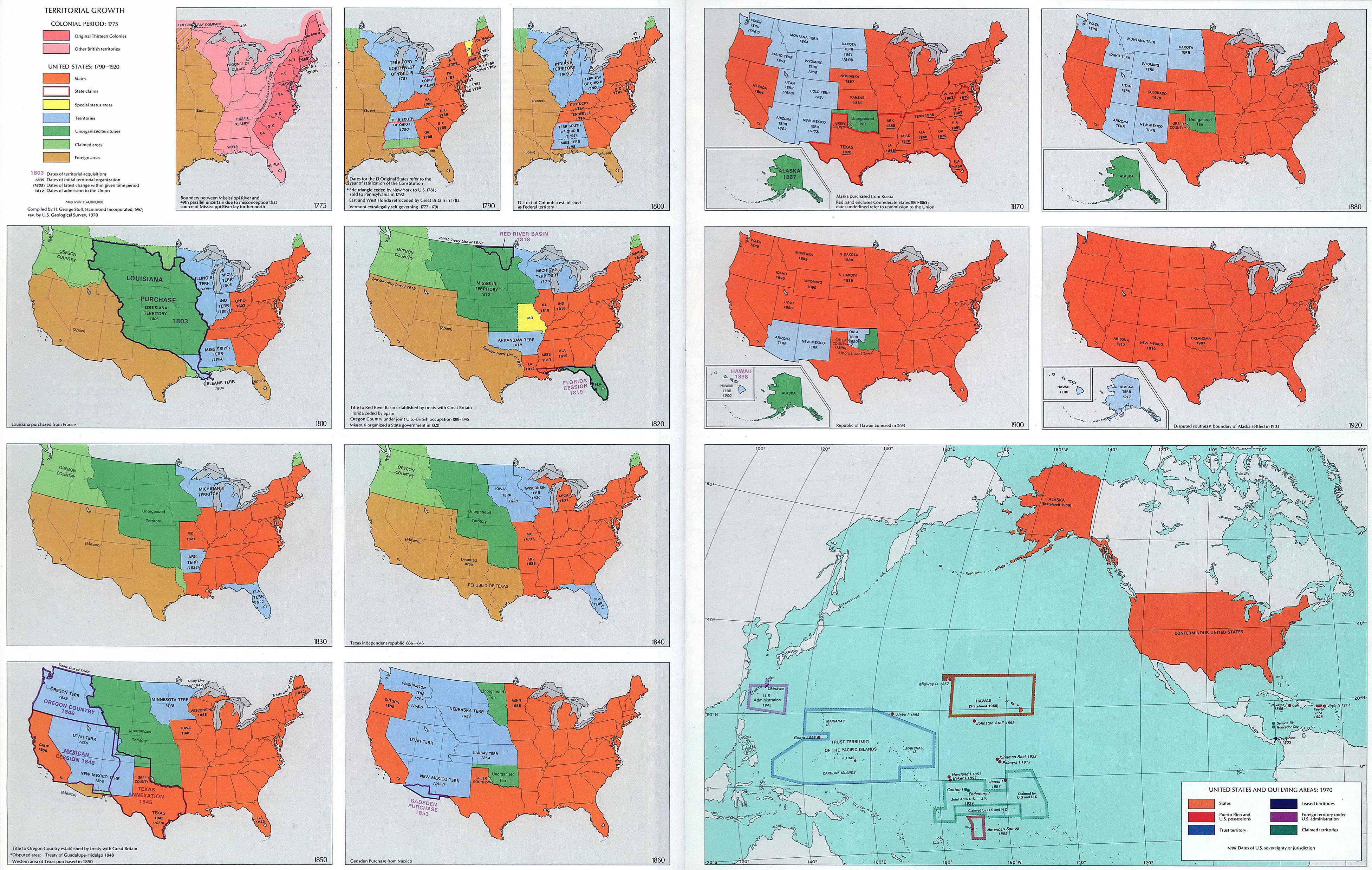
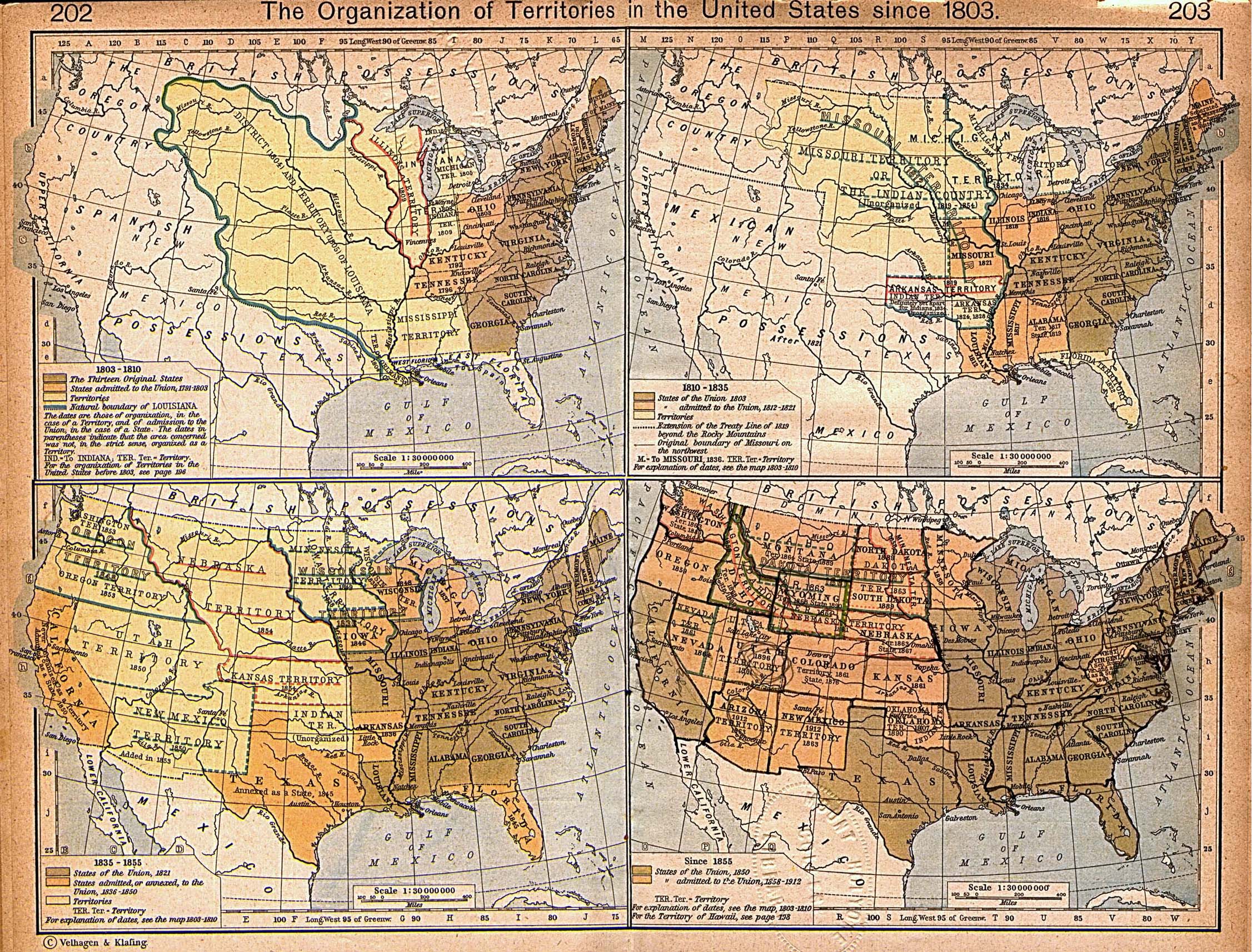
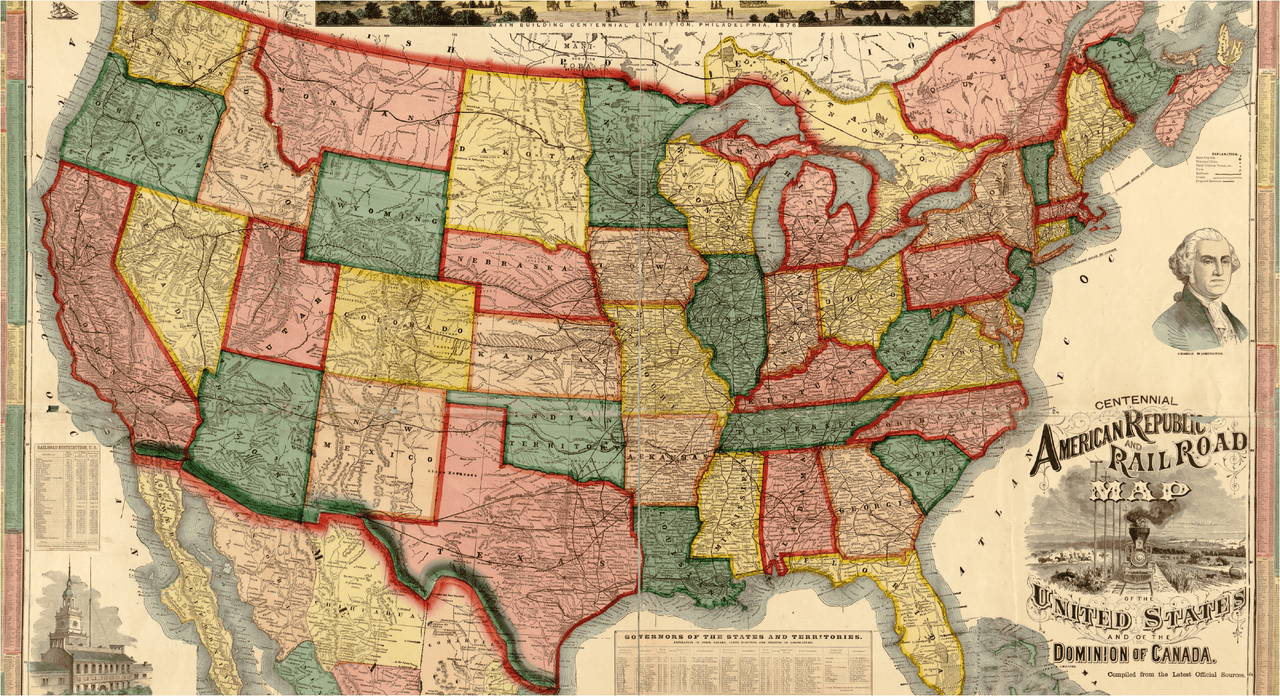
Westward Expansion and the Mapping of the Frontier
The 19th century witnessed a dramatic expansion of the United States westward, fueled by the Louisiana Purchase and the Oregon Trail. This westward movement demanded extensive mapping efforts to guide settlers, establish trade routes, and explore uncharted territories. The United States government, recognizing the strategic importance of accurate maps, established the United States Coast Survey in 1807 and the United States Geological Survey in 1879. These agencies, employing skilled surveyors and cartographers, meticulously mapped the vast expanse of the country, providing invaluable information for resource management, infrastructure development, and scientific exploration.
The Industrial Revolution and the Rise of Mapmaking Technology
The Industrial Revolution ushered in a new era of technological advancements that revolutionized mapmaking. The development of lithography, a printing process that allowed for mass production of maps, made them more accessible to a wider audience. The invention of the camera, coupled with aerial photography, provided new perspectives and detailed views of the landscape. These advancements enabled the creation of more complex and detailed maps, encompassing a wider range of information, from topography and population density to transportation networks and resource distribution.
The 20th Century: From Paper to Pixels
The 20th century witnessed a shift from paper maps to digital representations. The development of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in the 1960s revolutionized mapmaking, allowing for the integration and analysis of vast amounts of spatial data. GIS software enabled cartographers to create interactive and dynamic maps, incorporating layers of information such as elevation, demographics, and environmental data. The advent of the internet further democratized access to maps, making them readily available to anyone with a computer and an internet connection.
The Digital Age and the Future of Maps
Today, maps are no longer static representations of the world but dynamic tools for understanding and interacting with it. Online mapping services, such as Google Maps and OpenStreetMap, provide real-time traffic updates, navigation assistance, and a wealth of information about locations. The use of satellite imagery, aerial photography, and sensor data enables the creation of highly detailed and accurate maps, providing unprecedented insights into the environment, infrastructure, and human activity.
FAQs about US Map History
1. What were the primary motivations behind early American mapmaking?
Early American mapmaking was driven by a combination of factors, including exploration, navigation, resource extraction, and military campaigns. Explorers sought to chart new territories and discover new trade routes, while colonial authorities needed maps for land surveys, resource management, and defense.
2. How did the American Revolution influence the development of cartography?
The American Revolution highlighted the importance of accurate maps for military planning and strategy. Both sides of the conflict relied heavily on maps to coordinate troop movements, plan battles, and understand the terrain. The revolution also fostered a growing sense of national identity, reflected in maps that depicted the newly formed United States.
3. What were the key contributions of the United States Coast Survey and the United States Geological Survey?
The United States Coast Survey, established in 1807, focused on mapping the coastline and waterways, providing essential information for navigation and trade. The United States Geological Survey, founded in 1879, broadened the scope of mapping to include the entire country, creating detailed maps of topography, geology, and natural resources.
4. How did the Industrial Revolution impact mapmaking?
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant technological advancements that revolutionized mapmaking. The development of lithography enabled mass production of maps, making them more accessible to the public. The invention of the camera and aerial photography provided new perspectives and detailed views of the landscape, allowing for more complex and accurate maps.
5. What are the key features of GIS and how has it transformed mapmaking?
GIS, developed in the 1960s, allows for the integration and analysis of vast amounts of spatial data. It enables cartographers to create interactive and dynamic maps, incorporating layers of information such as elevation, demographics, and environmental data. GIS has revolutionized mapmaking by providing a powerful tool for understanding complex spatial relationships and solving real-world problems.
Tips for Understanding US Map History
- Explore historical maps: Visiting museums, libraries, and online archives can offer a glimpse into the evolution of American cartography. Examining early maps reveals the limitations and biases of the time, while later maps showcase advancements in technology and accuracy.
- Consider the context: Maps are not just static representations of the world but reflect the values, beliefs, and agendas of their creators. Analyzing the context in which a map was created can provide insights into the motivations behind its creation and the information it conveys.
- Appreciate the diverse applications of maps: Maps have served a wide range of purposes throughout history, from navigation and exploration to resource management, military planning, and social analysis. Understanding these diverse applications reveals the multifaceted nature of cartography and its enduring relevance.
- Engage with contemporary maps: Explore online mapping services and digital atlases to appreciate the power of modern cartography. These tools provide real-time information, interactive features, and a vast array of data layers, offering a dynamic and immersive experience.
Conclusion
Maps have been instrumental in shaping the history of the United States, from guiding explorers and settlers to informing military strategy and promoting national development. Their evolution, driven by technological advancements and changing societal needs, reflects the country’s growth and its ever-evolving relationship with its landscape. From the hand-drawn sketches of early explorers to the sophisticated digital atlases of today, maps continue to play a vital role in our understanding of the world and our place within it.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Course: A History of Maps in the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!