A Nation in the Making: The United States Map in 1776
Related Articles: A Nation in the Making: The United States Map in 1776
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Nation in the Making: The United States Map in 1776. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Nation in the Making: The United States Map in 1776
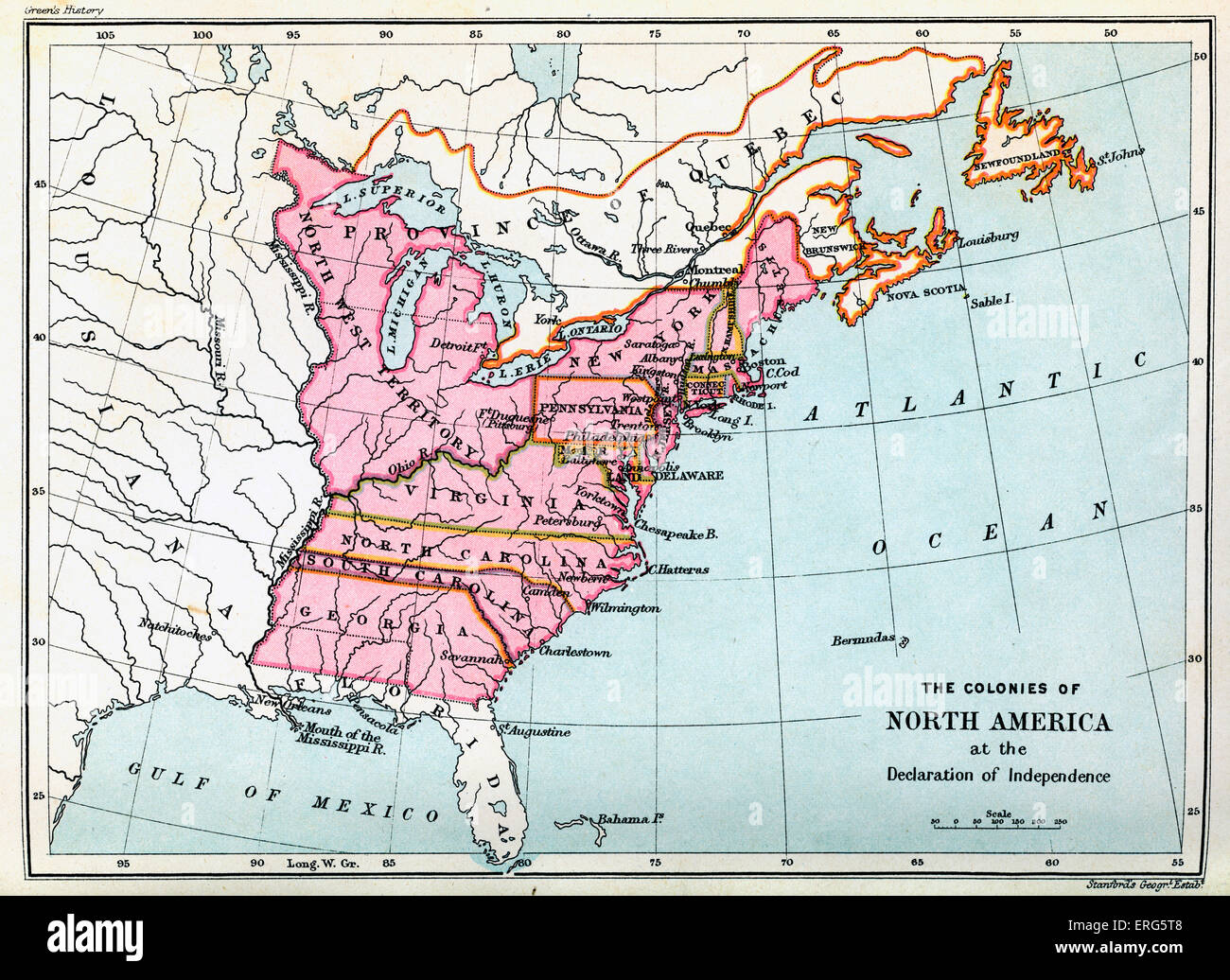
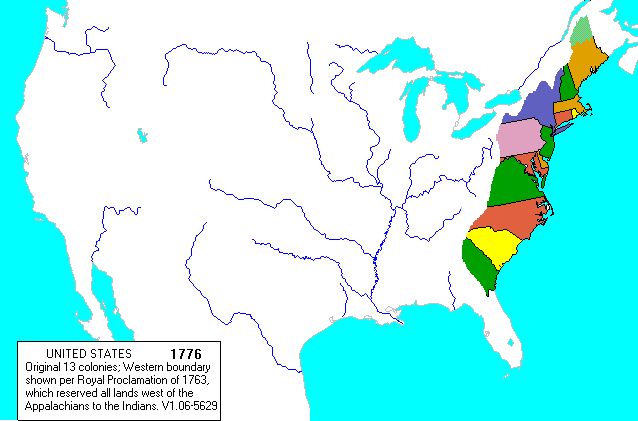
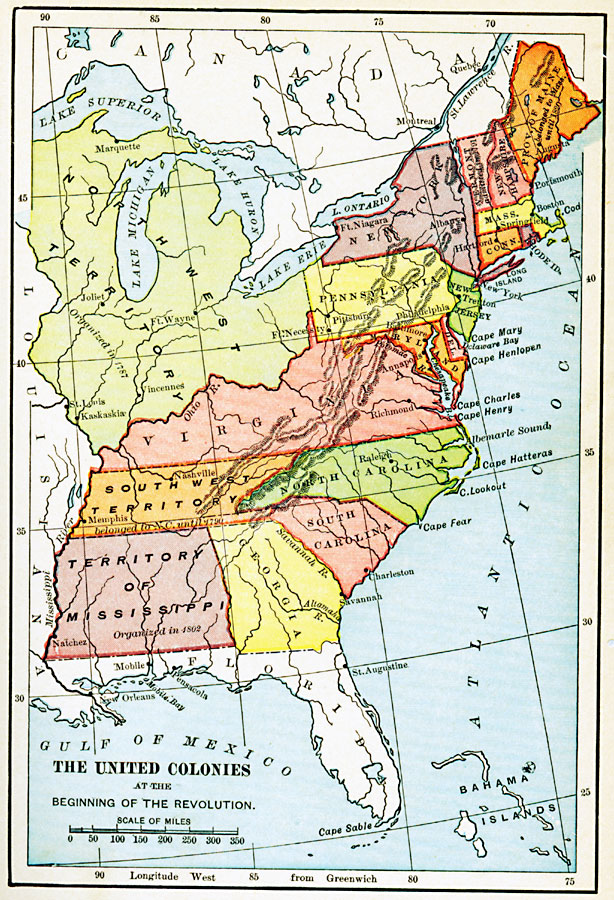
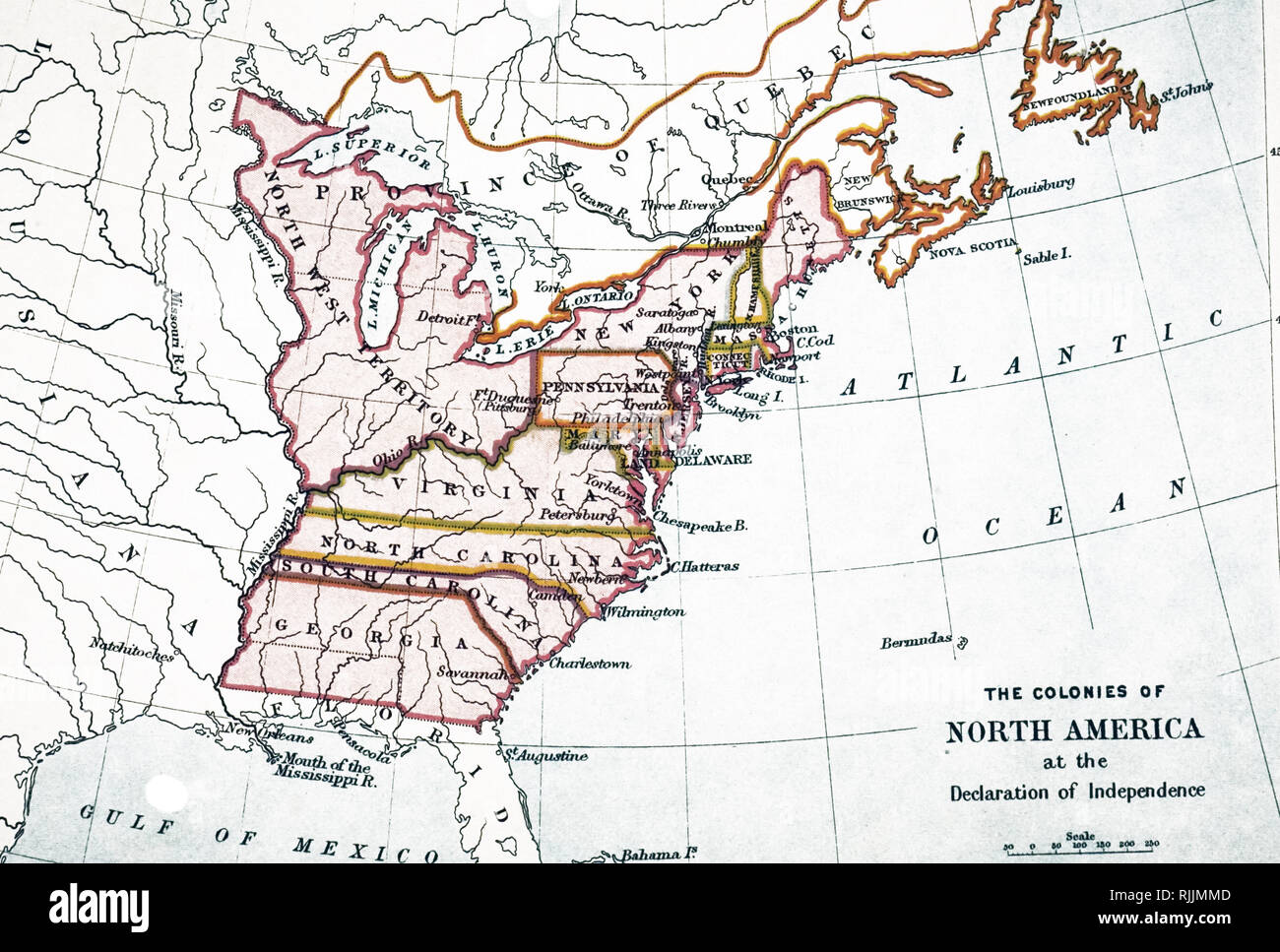
The year 1776 marked a pivotal moment in American history – the declaration of independence from British rule. This bold act of self-determination, however, did not automatically translate into a cohesive and unified nation. The newly declared United States, at its inception, was a patchwork of thirteen colonies, each with its own distinct identity, governance, and aspirations. Understanding the geographical landscape of these colonies, as depicted on a map of 1776, offers invaluable insight into the challenges and opportunities faced by the nascent nation.
A Divided Landscape:
The map of 1776 reveals a geographically diverse territory stretching along the Atlantic coast. From the rugged terrain of New Hampshire in the north to the subtropical climate of Georgia in the south, each colony possessed unique characteristics that shaped its development and identity.
-
New England: The northern colonies of New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut were characterized by their rocky coastlines, dense forests, and harsh winters. These factors contributed to the development of a strong maritime culture, with fishing and shipbuilding becoming vital industries. The region also witnessed early settlements of Puritan religious groups, which shaped the social and political landscape of the colonies.
-
The Middle Colonies: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware, known as the Middle Colonies, enjoyed a more temperate climate and fertile soil, making them ideal for agriculture. This region attracted a diverse population, including immigrants from various European countries, contributing to a more cosmopolitan and commercially oriented society.
-
The Southern Colonies: Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, collectively known as the Southern Colonies, were characterized by vast expanses of fertile land suitable for large-scale plantation agriculture. The cultivation of cash crops like tobacco, rice, and indigo created a wealthy planter class, fostering a society with a strong emphasis on land ownership and slavery.
The Boundaries of Independence:
The map of 1776 highlights the geographical boundaries of the newly declared nation, demonstrating the challenges of uniting such a diverse and geographically dispersed territory.
-
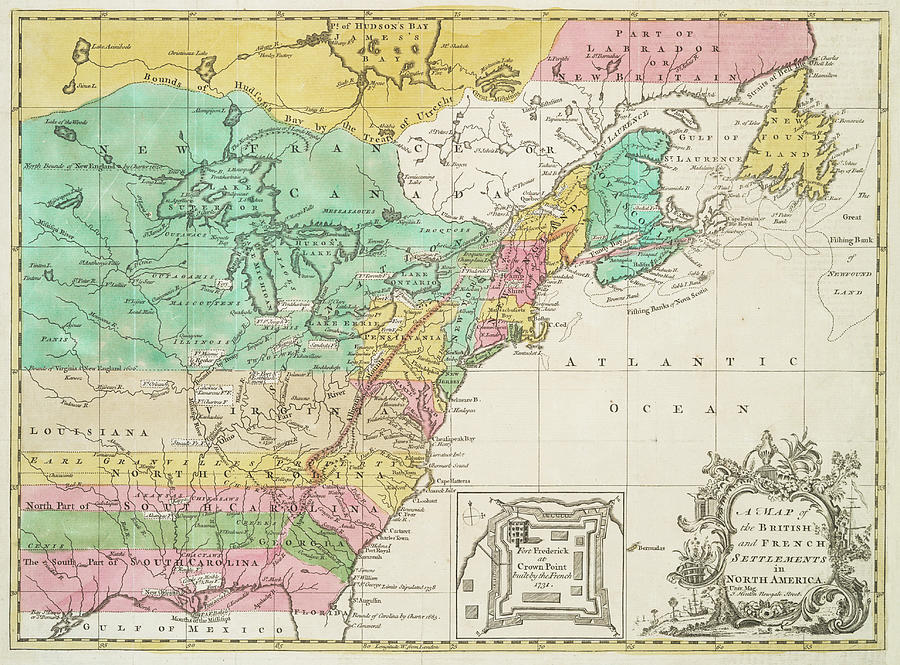
The Western Frontier: The Appalachian Mountains marked the western edge of the colonies, a formidable natural barrier that limited westward expansion. The vast expanse of territory beyond the mountains, claimed by the British, represented a potential source of conflict and opportunity for the fledgling nation.
-
The Northern Border: The northern boundary of the United States remained contested with Great Britain, specifically regarding the territories of Maine and Vermont. This unresolved issue contributed to tensions between the newly formed nation and its former colonial power.
-
The Southern Frontier: The southern colonies faced challenges related to the Spanish presence in Florida and the presence of Native American tribes who resisted encroachment on their ancestral lands. These disputes further complicated the process of establishing a cohesive national identity.
The Significance of the Map:
The map of 1776 serves as a visual representation of the nascent United States, revealing not only the geographical expanse but also the inherent challenges and opportunities that shaped its early development. It underscores the following key aspects:
-
The Importance of Communication and Transportation: The vast geographical distance between the colonies presented significant challenges in maintaining communication and transportation links. This issue became particularly relevant during the Revolutionary War, as the Continental Army relied on efficient communication and supply lines to sustain its operations.
-
The Challenges of Unity and Governance: The diverse interests, cultural backgrounds, and political ideologies of the colonies created a complex and often contentious landscape for establishing a unified government. The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, attempted to address these challenges by establishing a weak central government with limited powers, leaving most authority to the individual states.
-
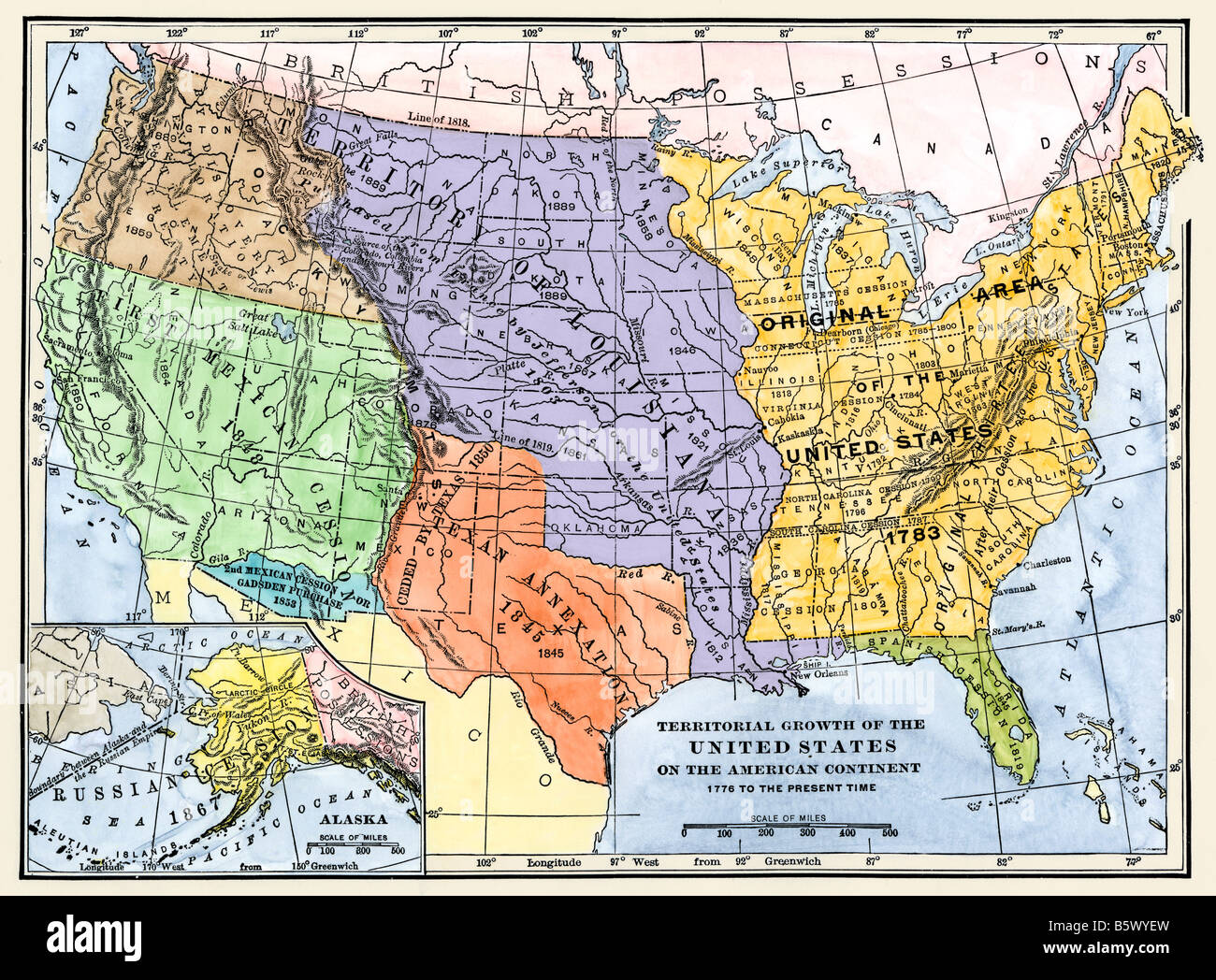
The Potential for Expansion: The map of 1776 also reveals the vast expanse of territory beyond the established colonies, representing a potential source of growth and wealth for the newly formed nation. However, this westward expansion also posed significant challenges, including conflicts with Native American tribes and territorial disputes with European powers.
FAQs
Q: Why is the map of 1776 important?
A: The map of 1776 provides a visual representation of the newly declared United States, highlighting its geographical diversity, the challenges of uniting such a disparate territory, and the potential for expansion. It serves as a crucial tool for understanding the complexities and opportunities faced by the nascent nation.
Q: What were the main challenges faced by the United States in 1776?
A: The United States in 1776 faced numerous challenges, including establishing a unified government, maintaining communication and transportation links across a vast territory, resolving territorial disputes with European powers, and managing relations with Native American tribes.
Q: How did the geography of the colonies shape their development?
A: The geography of the colonies significantly influenced their development, contributing to the emergence of distinct cultures, economies, and political ideologies. For example, the rocky coastlines and forests of New England fostered a maritime culture, while the fertile land of the Middle Colonies supported agriculture and a more diverse population.
Q: What were the key differences between the Northern, Middle, and Southern Colonies?
A: The Northern Colonies were characterized by their maritime culture, Puritan religious influence, and reliance on fishing and shipbuilding. The Middle Colonies were known for their diverse population, fertile land, and agricultural economy. The Southern Colonies were defined by their vast plantations, reliance on slave labor, and the cultivation of cash crops like tobacco and rice.
Tips
-
Visualize the Map: When studying the map of 1776, it is helpful to visualize the geographical features, such as the Appalachian Mountains, the Atlantic coastline, and the rivers that flowed through the colonies. This visualization can help you understand the challenges of transportation and communication, as well as the potential for expansion.
-
Consider the Political Landscape: The map of 1776 is not just a geographical representation but also a reflection of the political realities of the time. Consider the different forms of government in each colony, the debates surrounding independence, and the challenges of establishing a unified nation.
-
Connect the Map to Historical Events: The map of 1776 provides context for understanding key historical events, such as the Revolutionary War, the westward expansion, and the development of the United States Constitution.
Conclusion
The map of 1776 serves as a powerful reminder of the complex and challenging journey undertaken by the fledgling United States. It encapsulates the geographical diversity, the political divisions, and the potential for expansion that characterized the nation’s early years. By understanding the landscape of the thirteen colonies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the struggles, triumphs, and transformations that shaped the United States into the nation it is today.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Nation in the Making: The United States Map in 1776. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!