A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Climate Map: Understanding the Land of Extremes
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Climate Map: Understanding the Land of Extremes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Climate Map: Understanding the Land of Extremes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Climate Map: Understanding the Land of Extremes
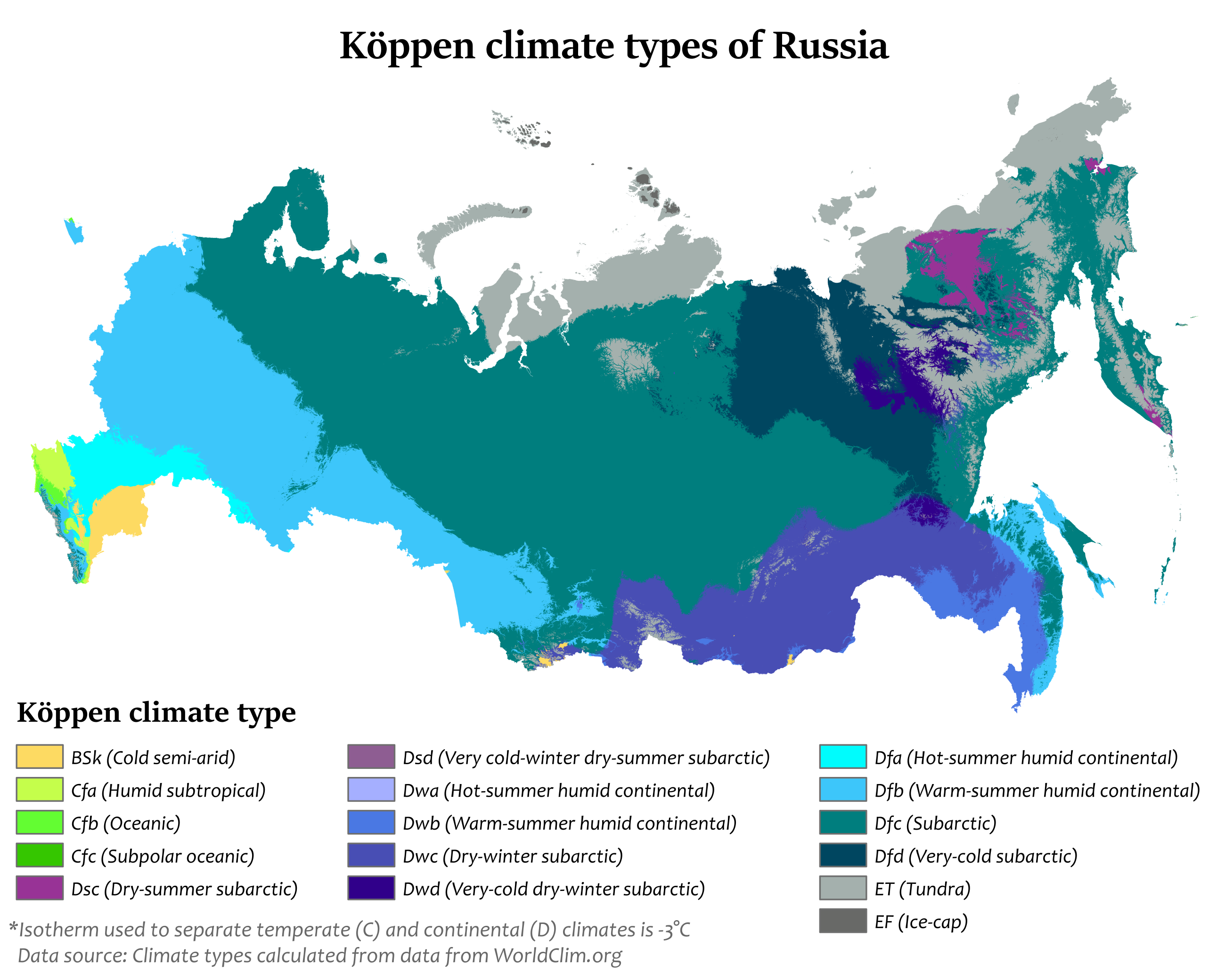
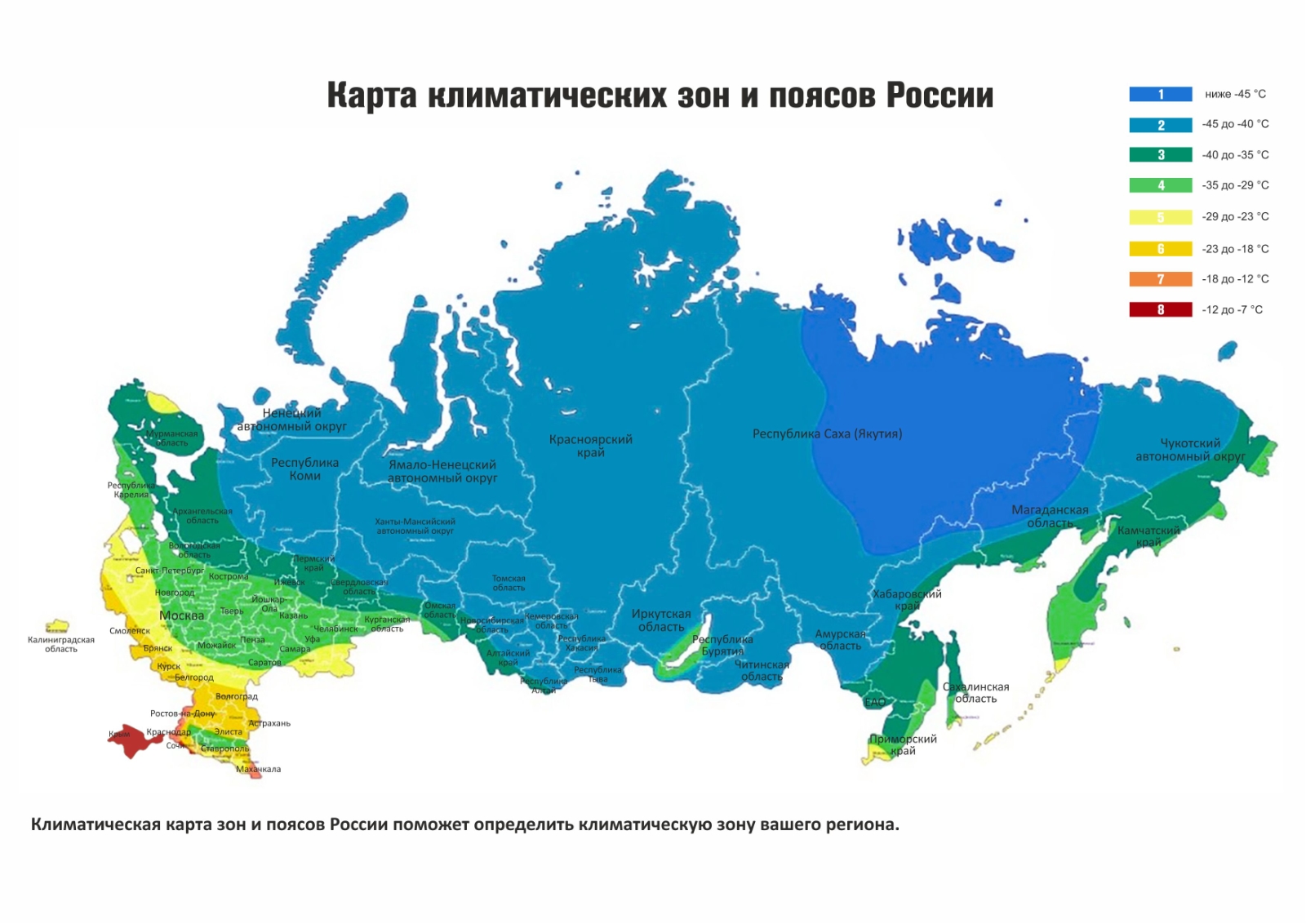
Russia, a vast expanse spanning eleven time zones and encompassing a diverse array of landscapes, is characterized by its extreme climate. Understanding this climate diversity is crucial for comprehending the country’s geography, its natural resources, its agricultural potential, and its challenges in a changing world.
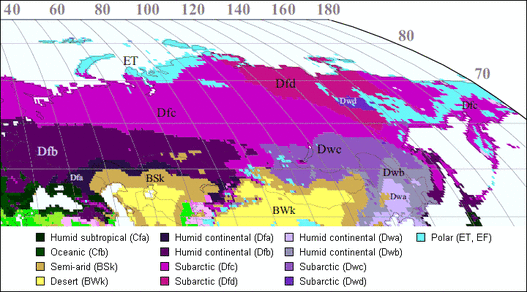
Climate Zones and Their Defining Characteristics
Russia’s climate map is a complex tapestry woven from various climate zones, each with distinct characteristics:
-
Arctic Climate: Dominating the northernmost regions, the Arctic climate features extremely cold temperatures, persistent snow cover, and limited precipitation. Summers are short and cool, with temperatures rarely exceeding freezing. This zone is home to permafrost, a permanently frozen layer of soil, which significantly impacts infrastructure and ecological processes.
-
Subarctic Climate: Located south of the Arctic, the subarctic climate experiences long, cold winters with average temperatures well below freezing. Summers are short and cool, but with longer daylight hours. This zone is characterized by extensive forests, including the vast Siberian taiga, and is home to diverse wildlife adapted to harsh conditions.
-
Humid Continental Climate: Occupying the central and western regions of Russia, the humid continental climate features distinct seasonal variations. Winters are long and cold, with temperatures frequently dipping below freezing, while summers are warm and humid. This zone experiences significant precipitation throughout the year, supporting a variety of ecosystems, including deciduous forests and mixed forests.
-
Steppe Climate: Found in the southern regions of Russia, the steppe climate is characterized by dry, hot summers and cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is limited, resulting in dry grasslands and semi-arid landscapes. This zone is prone to droughts and is often utilized for agriculture, particularly grain production.
-
Monsoon Climate: A smaller region in the Russian Far East, the monsoon climate features distinct wet and dry seasons. Summers are warm and humid, with heavy rainfall, while winters are dry and cold. This zone supports a variety of vegetation, including deciduous forests and mixed forests.
Factors Shaping Russia’s Climate
The diverse climate of Russia is shaped by a complex interplay of factors:
-
Latitude: Russia’s vast expanse stretches across a wide range of latitudes, influencing the amount of solar radiation received and the length of daylight hours. Higher latitudes receive less solar energy, resulting in colder temperatures.
-
Continental Position: Russia’s continental position, far from moderating ocean influences, leads to extreme temperature variations between seasons. Winters are particularly harsh, with temperatures dropping significantly below freezing.
-
Mountain Ranges: Mountain ranges, such as the Ural Mountains and the Caucasus Mountains, act as barriers to moisture-laden winds, creating rain shadows on their leeward sides. This effect contributes to the dryness of the steppe climate.
-
Ocean Currents: Warm ocean currents, such as the North Atlantic Current, exert a moderating influence on the climate of western Russia, while cold currents, such as the Labrador Current, contribute to the harsh conditions of the Arctic.
-
Human Activity: Human activities, including deforestation, urbanization, and industrial emissions, are altering the climate of Russia. These activities contribute to rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events.
The Importance of Understanding Russia’s Climate
A comprehensive understanding of Russia’s climate is essential for various reasons:
-
Resource Management: Climate plays a crucial role in the availability and management of natural resources, including water, forests, and minerals. Understanding climate patterns is vital for sustainable resource utilization and conservation.
-
Agriculture and Food Security: Russia’s agricultural sector is significantly influenced by climate conditions. Understanding climate patterns is crucial for optimizing crop selection, managing irrigation, and ensuring food security.
-
Infrastructure Development: Extreme temperatures and variable precipitation pose challenges for infrastructure development in Russia. Understanding climate patterns is essential for designing resilient infrastructure that can withstand harsh conditions.
-
Human Health: Climate influences human health, affecting the spread of diseases, heat stress, and cold-related injuries. Understanding climate patterns is crucial for public health planning and mitigation strategies.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Russia is experiencing the impacts of climate change, including rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events. Understanding climate patterns is crucial for adapting to and mitigating these impacts.
FAQs
Q: How does climate change affect Russia’s climate?
A: Climate change is causing significant shifts in Russia’s climate, leading to rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events. These changes have widespread implications for the country’s ecosystems, agriculture, infrastructure, and human health.
Q: What are the main challenges posed by Russia’s climate?
A: Russia’s climate poses several challenges, including:
- Harsh winters: Extreme cold temperatures and persistent snow cover can disrupt transportation, infrastructure, and daily life.
- Limited growing season: The short growing season in many regions limits agricultural productivity and crop diversity.
- Permafrost: The thawing of permafrost, due to rising temperatures, poses significant risks to infrastructure and ecosystems.
- Extreme weather events: More frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, and floods, are increasing vulnerability and posing challenges to adaptation.
Q: How is Russia adapting to climate change?
A: Russia is taking steps to adapt to climate change, including:
- Developing climate-resilient infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture: Implementing practices that minimize the impacts of climate change on agriculture, such as drought-resistant crops and efficient irrigation systems.
- Protecting natural resources: Conserving forests, wetlands, and other natural ecosystems to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts.
- Investing in research and development: Supporting research into climate change impacts, adaptation strategies, and mitigation technologies.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Climate
- Consult climate maps: Use climate maps to visualize the distribution of different climate zones and their key characteristics.
- Explore climate data: Access climate data from reputable sources, such as the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the Russian Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring (Roshydromet).
- Read about climate change impacts: Stay informed about the latest scientific research on climate change impacts in Russia.
- Engage with local communities: Learn about local adaptation strategies and challenges related to climate change.
- Support sustainable practices: Promote and support initiatives that mitigate climate change and promote climate resilience.
Conclusion
Russia’s climate map is a testament to the country’s vastness and its unique geographical position. Understanding the complex interplay of factors shaping Russia’s climate is crucial for managing its resources, adapting to climate change, and ensuring the well-being of its people. As the country continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, a comprehensive understanding of its climate will be essential for navigating a future marked by uncertainty and change.
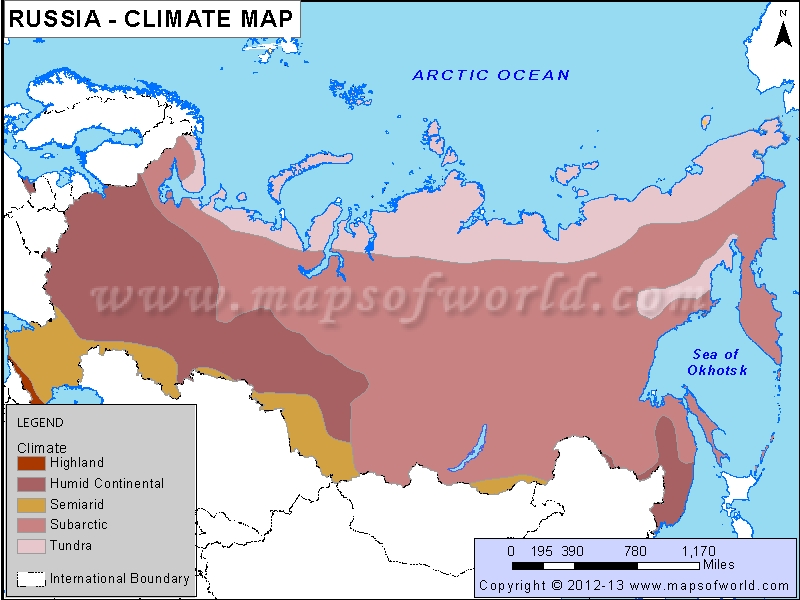
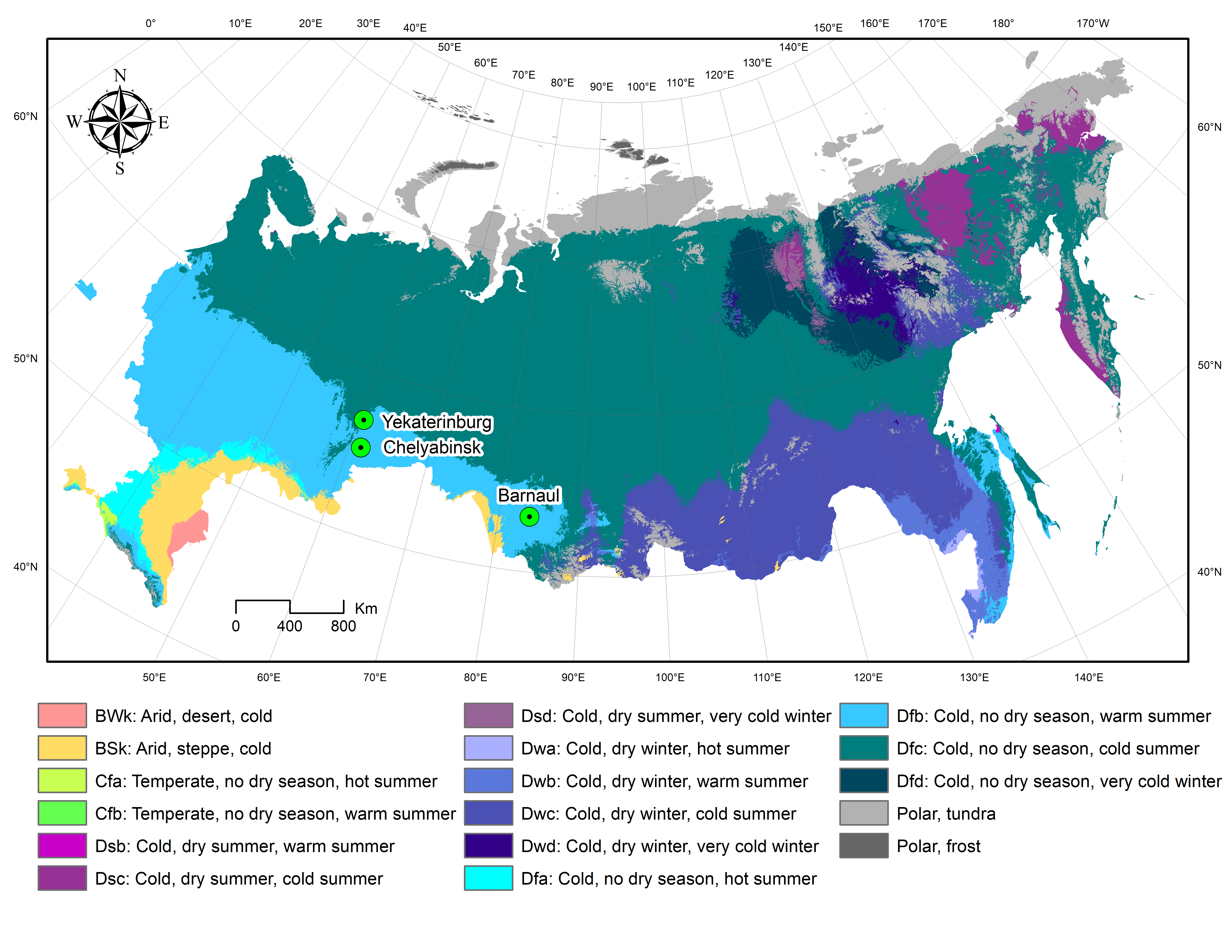
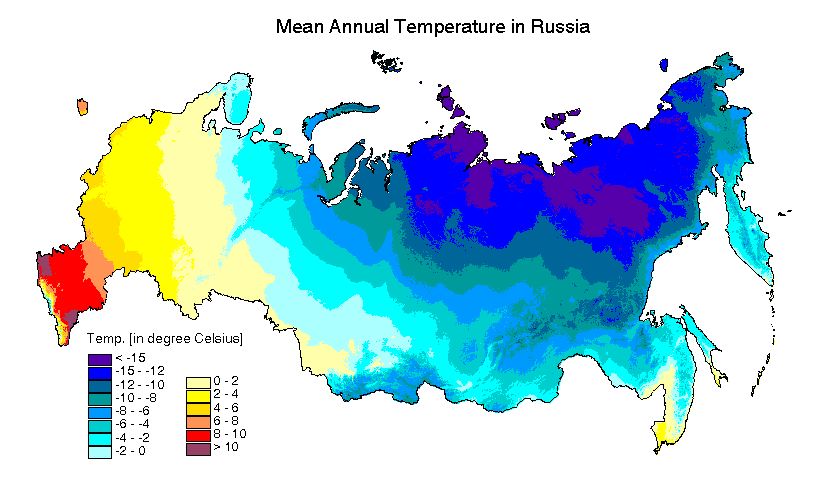



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Russia’s Climate Map: Understanding the Land of Extremes. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!