A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps
- 3.1 Defining Desert Biomes and Their Significance
- 3.2 Unveiling the World’s Deserts: The Importance of Desert Biome Maps
- 3.3 Exploring the Features of Desert Biome Maps
- 3.4 Applications of Desert Biome Maps: From Conservation to Sustainable Development
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Desert Biome Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Utilizing Desert Biome Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Importance of Visualizing Aridity
- 4 Closure
A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps

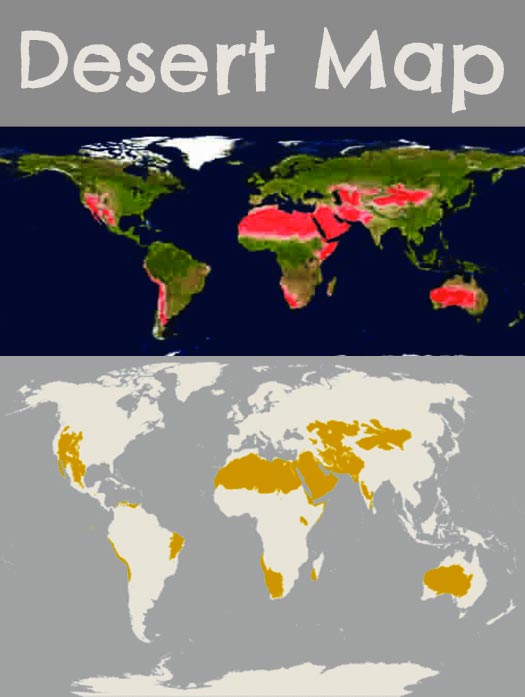
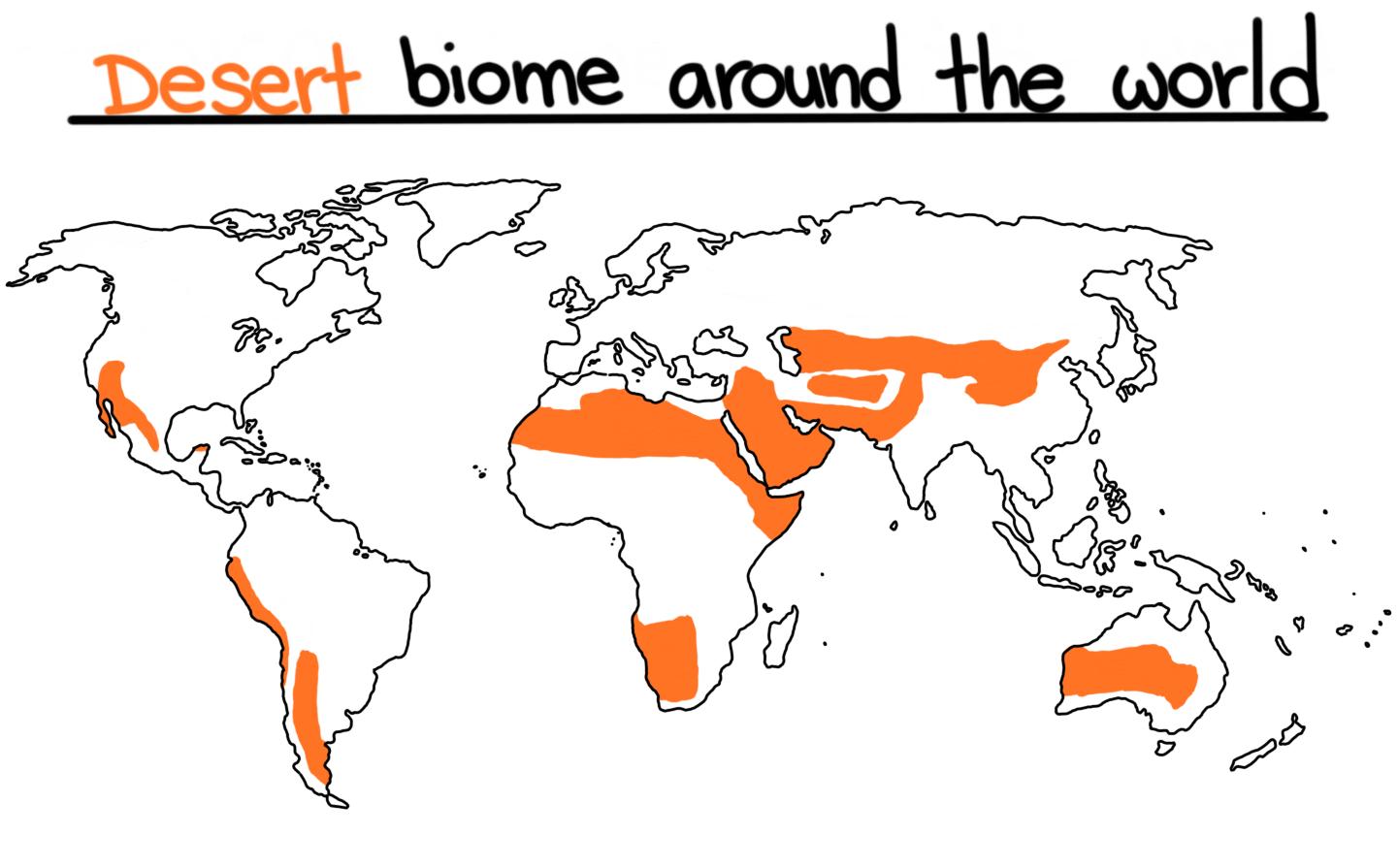
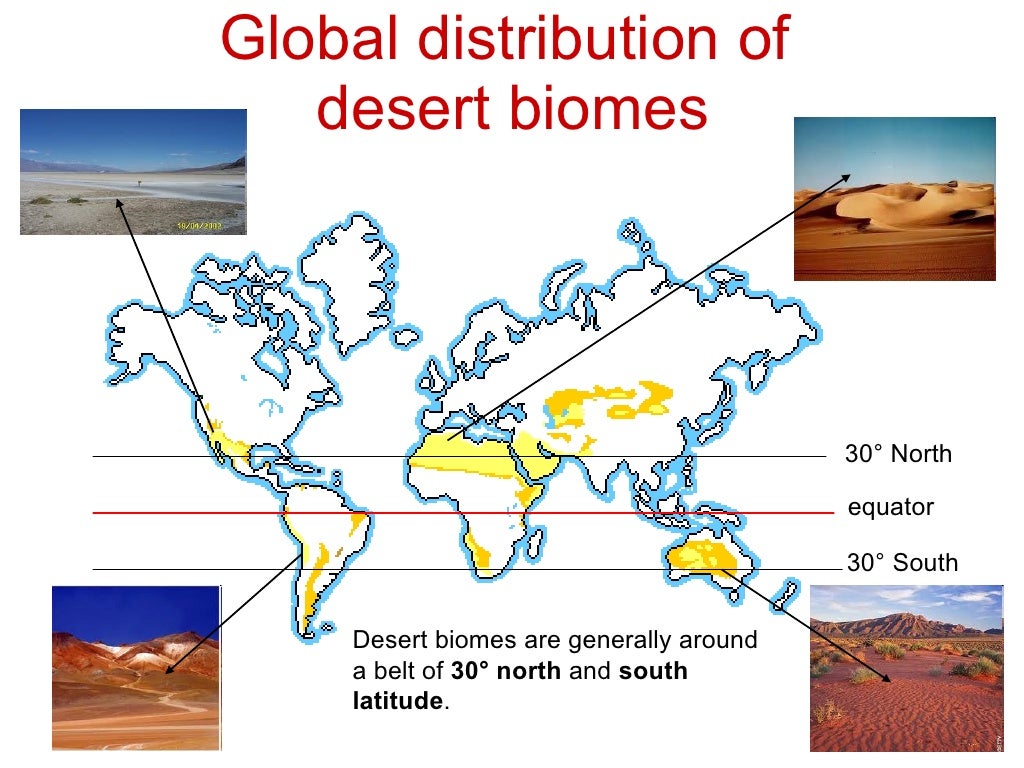
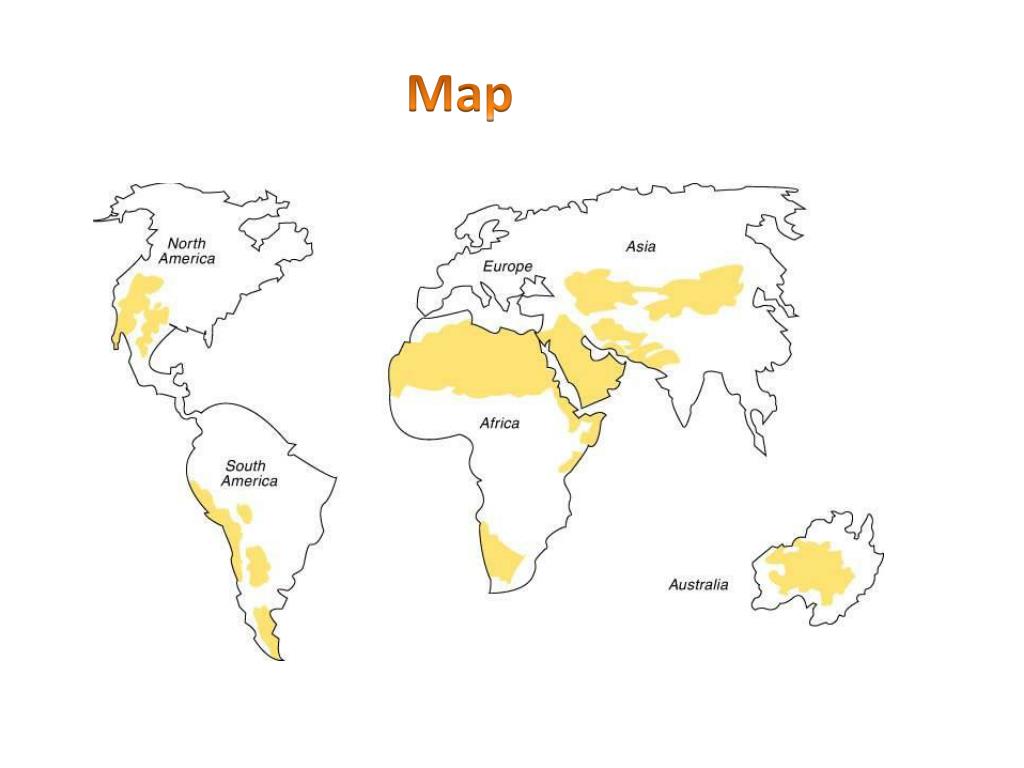
The Earth’s diverse landscapes are characterized by distinct biomes, each with its unique set of environmental conditions and adapted life forms. Among these, deserts stand out as regions of extreme aridity, encompassing vast stretches of land where water scarcity is a defining factor. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these arid ecosystems is crucial for conservation efforts, sustainable resource management, and comprehending the global climate system. Desert biome maps serve as essential tools for achieving these objectives, providing a visual representation of the world’s deserts and their key features.
Defining Desert Biomes and Their Significance
Desert biomes are defined by their low precipitation levels, typically receiving less than 10 inches of rainfall annually. This aridity shapes the environment, leading to a range of characteristic features, including:
- Sparse Vegetation: Due to water scarcity, plant life in deserts is limited and adapted to survive with minimal water. Cacti, succulents, and drought-tolerant shrubs are common examples.
- Extreme Temperatures: Deserts experience wide temperature fluctuations, often with scorching hot days and frigid nights.
- Sandy or Rocky Landscapes: The lack of vegetation exposes the underlying soil, creating vast expanses of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and barren plains.
- Unique Animal Adaptations: Desert animals have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive the harsh conditions, such as nocturnal habits, efficient water conservation mechanisms, and specialized diets.
Desert biomes are not merely isolated pockets of aridity; they play a crucial role in the global ecosystem. They:
- Influence Climate Patterns: Deserts contribute to atmospheric circulation, influencing rainfall patterns and temperature distribution across the globe.
- Support Biodiversity: Despite their harsh conditions, deserts are home to a diverse array of life forms, many of which are endemic and found nowhere else.
- Provide Resources: Deserts contain valuable natural resources, such as minerals, oil, and geothermal energy, which contribute to human economies.
- Offer Cultural and Historical Significance: Many deserts hold cultural and historical importance for indigenous communities and have served as migration routes and trade centers throughout history.
Unveiling the World’s Deserts: The Importance of Desert Biome Maps
Desert biome maps are essential tools for visualizing and understanding the distribution, characteristics, and significance of these arid ecosystems. They offer a comprehensive overview, revealing:
- Geographical Boundaries: Desert biome maps clearly delineate the geographical extent of various desert regions around the world, highlighting their location and size.
- Types of Deserts: Maps can differentiate between various desert types, such as hot deserts, cold deserts, coastal deserts, and interior deserts, based on their climate, vegetation, and geographical features.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Maps can pinpoint areas within deserts that are particularly rich in biodiversity, highlighting regions with high concentrations of endemic species and unique ecosystems.
- Resource Distribution: Desert biome maps can illustrate the distribution of natural resources within deserts, such as water sources, mineral deposits, and potential energy resources.
- Human Impacts: Maps can depict areas of human activity within deserts, including settlements, infrastructure, and agricultural practices, helping to assess the impact of human activities on these fragile ecosystems.
Exploring the Features of Desert Biome Maps
Desert biome maps can be constructed using various data sources and visualization techniques. Some key features commonly included in these maps are:
- Legend: A legend provides a key to the map’s symbols and colors, clarifying the meaning of different features depicted on the map.
- Scale: The map’s scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world, providing a sense of the map’s spatial resolution.
- Projection: The map’s projection refers to the method used to represent the curved Earth’s surface on a flat map, influencing the accuracy of distances and shapes.
- Data Sources: The map’s data sources can include satellite imagery, climate data, vegetation surveys, and ecological studies, providing a basis for the information depicted on the map.
- Spatial Analysis Tools: Advanced mapping software can be used to perform spatial analysis on desert biome maps, allowing researchers to analyze patterns, identify relationships, and generate insights into the distribution and characteristics of deserts.
Applications of Desert Biome Maps: From Conservation to Sustainable Development
Desert biome maps have numerous applications, contributing to a wide range of endeavors:
- Conservation Planning: Maps help identify priority areas for conservation efforts, focusing resources on regions with high biodiversity, unique ecosystems, or threatened species.
- Resource Management: Maps assist in managing natural resources within deserts, ensuring sustainable utilization of water, minerals, and energy resources.
- Climate Change Research: Maps provide valuable data for climate change research, helping to understand the impact of climate change on desert ecosystems and predict future changes.
- Environmental Monitoring: Maps can be used to monitor changes in desert ecosystems over time, detecting signs of degradation, desertification, or land-use changes.
- Sustainable Development: Maps contribute to sustainable development initiatives in desert regions, guiding infrastructure development, agricultural practices, and tourism activities to minimize environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions about Desert Biome Maps
Q: What are the different types of desert biomes depicted on maps?
A: Desert biome maps often distinguish between different types of deserts, including:
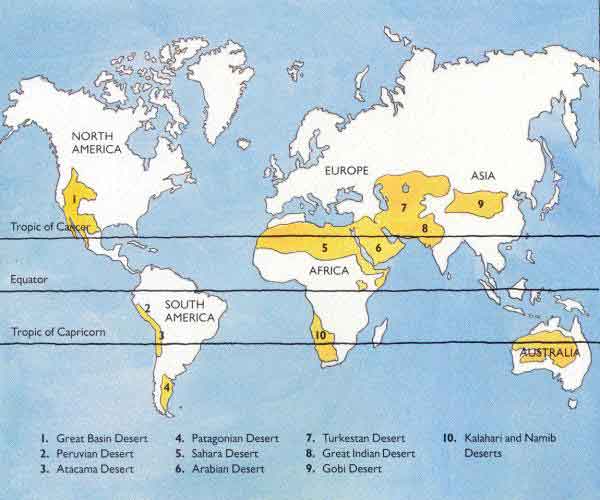
- Hot Deserts: Characterized by high temperatures, low rainfall, and sparse vegetation, examples include the Sahara Desert and the Arabian Desert.
- Cold Deserts: Experience cold temperatures, low rainfall, and limited vegetation, with examples being the Gobi Desert and the Atacama Desert.
- Coastal Deserts: Located along coastlines, these deserts receive low rainfall due to cold ocean currents, such as the Namib Desert and the Atacama Desert.
- Interior Deserts: Located far from the coast, these deserts receive low rainfall due to their location in the rain shadow of mountain ranges, such as the Great Basin Desert and the Mojave Desert.
Q: How are desert biome maps created?
A: Desert biome maps are created using a combination of data sources and mapping techniques. These include:
- Satellite Imagery: Remote sensing data from satellites provides detailed information on vegetation cover, land surface features, and climate patterns.
- Climate Data: Precipitation records, temperature data, and wind patterns provide insights into the aridity of different regions.
- Vegetation Surveys: Field surveys of plant communities provide information on species composition, distribution, and adaptation to desert conditions.
- Ecological Studies: Research on desert ecosystems provides insights into the interactions between organisms and the environment, helping to define the boundaries and characteristics of desert biomes.
Q: How can I access desert biome maps?
A: Desert biome maps are available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: Organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), and the European Space Agency (ESA) provide access to maps and data related to desert ecosystems.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research centers often publish maps and data related to their research on desert biomes.
- Environmental Organizations: Non-profit organizations focused on conservation and environmental protection often develop and disseminate desert biome maps to support their initiatives.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Websites like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and ArcGIS Online offer access to various maps, including some depicting desert biomes.
Q: What are the limitations of desert biome maps?
A: Desert biome maps, while valuable tools, have certain limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of maps can vary, influencing the level of detail and accuracy of information depicted.
- Data Availability: Data availability can be limited in certain regions, especially in remote or understudied areas.
- Dynamic Nature: Desert ecosystems are dynamic and constantly changing, making it challenging to capture the full extent of their variability.
- Interpretation Bias: The interpretation of map data can be influenced by the perspectives and assumptions of the mapmakers.
Q: How can desert biome maps contribute to sustainable development?
A: Desert biome maps can contribute to sustainable development by:
- Guiding Infrastructure Development: Maps can help identify suitable locations for infrastructure projects, minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring responsible resource utilization.
- Optimizing Agricultural Practices: Maps can aid in developing sustainable agricultural practices adapted to desert conditions, reducing water consumption and soil degradation.
- Promoting Sustainable Tourism: Maps can help promote responsible tourism practices, minimizing disturbance to sensitive ecosystems and maximizing benefits for local communities.
- Facilitating Resource Management: Maps can assist in managing water resources, ensuring equitable access and preventing overuse, while also supporting sustainable extraction of other resources.
Tips for Utilizing Desert Biome Maps Effectively
- Consider the Map’s Purpose: Before using a desert biome map, clearly define the purpose of the analysis, whether it’s for conservation planning, resource management, or climate change research.
- Evaluate Data Sources: Assess the reliability and accuracy of the data used to create the map, considering the source, date of collection, and methods used.
- Understand Map Projections: Be aware of the map’s projection, as it can affect the accuracy of distances and shapes depicted.
- Utilize Spatial Analysis Tools: Employ spatial analysis tools to extract meaningful insights from the map, such as identifying patterns, calculating distances, and comparing different data layers.
- Collaborate with Experts: Consult with experts in desert ecology, conservation, or resource management to ensure proper interpretation and application of the map’s information.
Conclusion: The Importance of Visualizing Aridity
Desert biome maps provide a powerful tool for understanding, visualizing, and managing the Earth’s arid ecosystems. By revealing the distribution, characteristics, and significance of deserts, these maps contribute to conservation efforts, resource management, and sustainable development. As human activities continue to impact desert environments, the use of desert biome maps becomes increasingly crucial for ensuring the preservation of these unique and valuable ecosystems for future generations.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Desert Biome Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!