A Comprehensive Exploration of the French Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Map of France
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of the French Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Map of France
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of the French Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Map of France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of the French Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Map of France
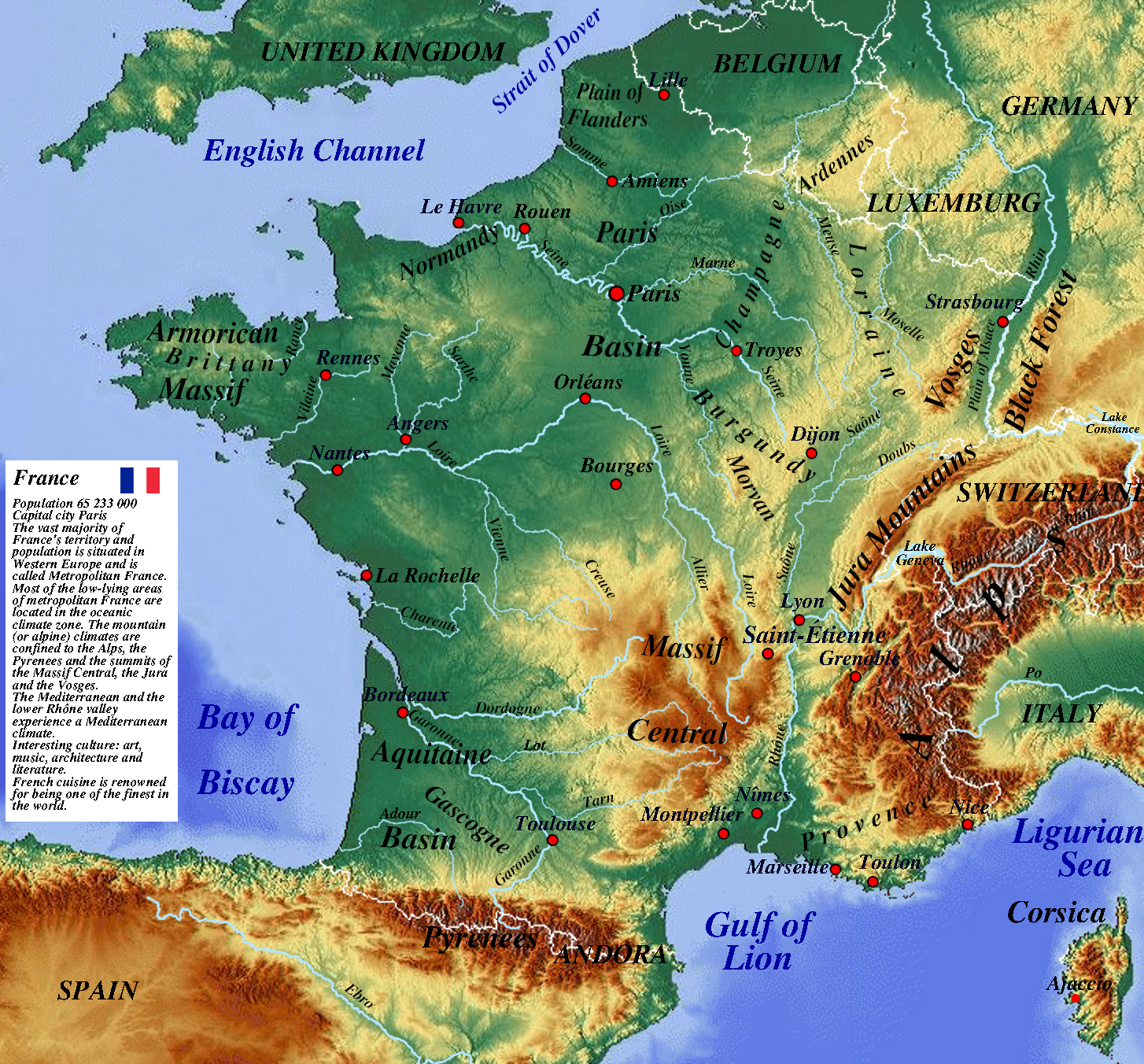
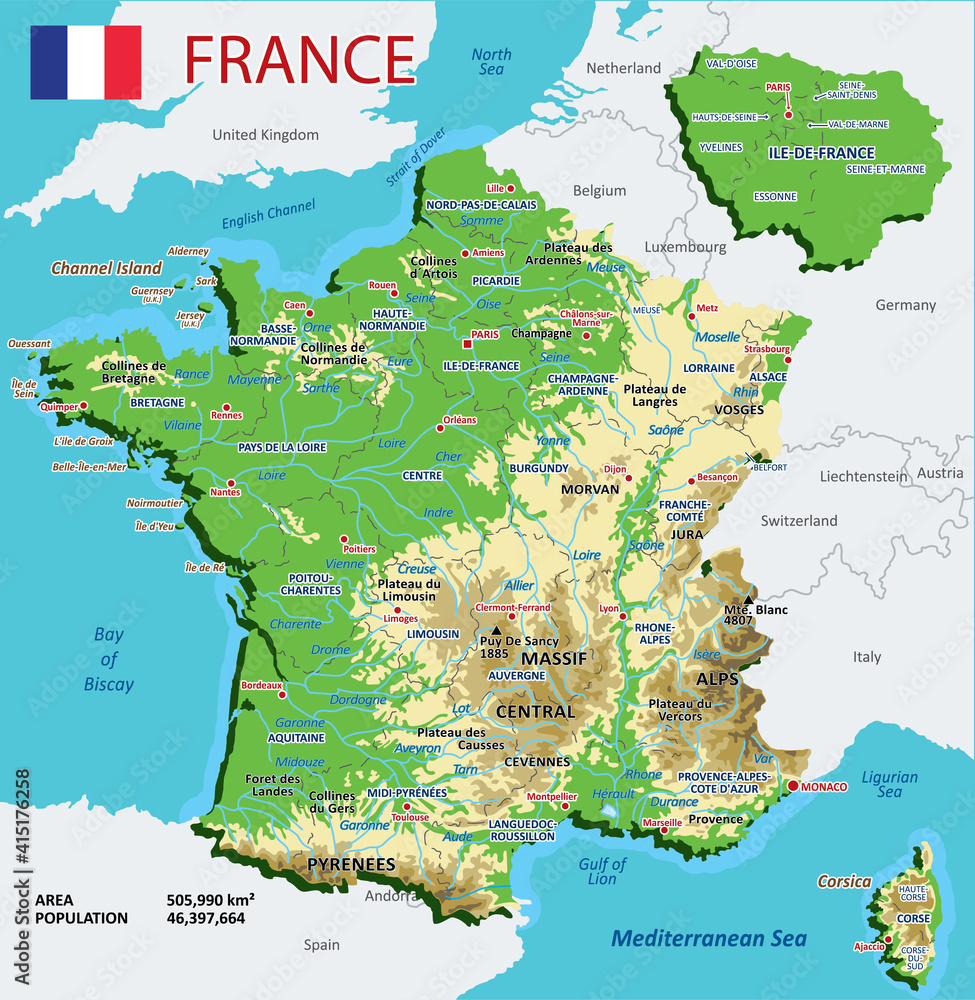
France, a nation renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and captivating landscapes, boasts a diverse and captivating physical geography. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its physical map offers a deeper appreciation for its unique characteristics, shaping its history, economy, and cultural identity.
Delving into the Topography: Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines
The French landscape is a captivating blend of dramatic mountain ranges, fertile plains, and picturesque coastlines, each contributing to the nation’s distinctive character.
-
The Majestic Alps: The towering Alps, forming a natural barrier between France and its neighbors, dominate the southeastern portion of the country. The highest peak, Mont Blanc, at 4,808.73 meters, is a testament to the region’s raw power and scenic grandeur. The Alps are a haven for outdoor enthusiasts, offering opportunities for skiing, hiking, and mountaineering.
-
The Rugged Pyrenees: Separating France from Spain, the Pyrenees are a range of rugged mountains, known for their challenging terrain and breathtaking vistas. The Pyrenees offer a unique ecosystem, home to a diverse array of flora and fauna.
-
The Rolling Hills of the Massif Central: Located in the center of France, the Massif Central is a vast plateau characterized by rolling hills, volcanic peaks, and deep gorges. The region is known for its rich agricultural land and picturesque villages.
-
The Fertile Plains: The northern and western regions of France are dominated by vast, fertile plains, ideal for agriculture. The fertile soil of the Paris Basin, for instance, has historically supported extensive farming and contributed to the growth of major cities like Paris.
-
The Varied Coastlines: France’s coastline stretches over 3,427 kilometers, encompassing both the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. From the dramatic cliffs of Brittany to the sandy beaches of the French Riviera, the coastline offers a diverse array of landscapes, attracting tourists and shaping the nation’s maritime history.
The Influence of Rivers and Waterways
France’s network of rivers and waterways plays a crucial role in its physical geography and economic development. The Loire, the longest river in France, flows through the heart of the country, providing fertile land for agriculture and facilitating transportation. The Rhone, originating in the Alps, is another vital waterway, connecting the Mediterranean coast to the interior.
The Seine, flowing through Paris, has been a key factor in the city’s growth and development. The intricate network of canals, connecting rivers and cities, has historically facilitated trade and transport, contributing to France’s economic prosperity.
Geological History: Shaping the Landscape
The physical map of France is a testament to the country’s complex geological history. The formation of the Alps and Pyrenees, through tectonic plate collisions, resulted in the dramatic mountain ranges that define the southeastern and southwestern regions.
The Massif Central, with its volcanic peaks and deep gorges, is a result of volcanic activity that shaped the central landscape. The fertile plains, formed by sedimentary deposits over millions of years, provide the foundation for France’s agricultural success.
Climate Variations: From Oceanic to Mediterranean
France experiences a diverse range of climates, influenced by its location, topography, and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
-
Oceanic Climate: The northern and western regions of France experience an oceanic climate, characterized by mild temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. This climate is conducive to agriculture and supports lush vegetation.
-
Continental Climate: The eastern region of France experiences a continental climate, with colder winters and warmer summers. The temperature range is more significant compared to the oceanic climate.
-
Mediterranean Climate: The southeastern region of France enjoys a Mediterranean climate, characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This climate is ideal for growing fruits, vegetables, and grapes, contributing to the region’s renowned wine production.
The Significance of the Physical Map
The physical map of France holds immense significance, shaping its historical development, cultural identity, and economic prosperity.
-
Historical Influence: The natural barriers created by the Alps and Pyrenees influenced the country’s historical development, providing protection and shaping its interactions with neighboring countries. The fertile plains have supported agriculture, driving economic growth and population density.
-
Cultural Diversity: The diverse landscapes and climates have contributed to the rich tapestry of French culture. From the vibrant coastal cities to the charming villages nestled in the mountains, each region has developed its own unique traditions and customs.
-
Economic Impact: The physical map influences France’s economic activities. The fertile plains support agriculture, while the mountainous regions provide opportunities for tourism and forestry. The rivers and canals have historically facilitated trade and transportation, contributing to the country’s economic prosperity.
FAQs on the Physical Map of France
Q: What is the highest mountain in France?
A: Mont Blanc, located in the Alps, is the highest mountain in France, reaching a height of 4,808.73 meters.
Q: What are the major rivers in France?
A: The major rivers in France include the Loire, Rhone, Seine, Garonne, and Meuse.
Q: What are the main types of climates found in France?
A: France experiences oceanic, continental, and Mediterranean climates.
Q: How does the physical map of France influence its economy?
A: The physical map influences agriculture, tourism, forestry, and transportation, contributing to France’s economic diversity.
Tips for Exploring the Physical Map of France
-
Embark on a Road Trip: Explore the diverse landscapes of France by car, allowing you to experience the scenic beauty of the mountains, plains, and coastlines.
-
Hike the Trails: Discover the natural wonders of France by hiking through the Alps, Pyrenees, and Massif Central, enjoying stunning views and diverse ecosystems.
-
Cruise the Waterways: Experience the charm of France’s canals and rivers, navigating through picturesque towns and villages, enjoying the tranquility of the waterways.
Conclusion: A Nation Shaped by its Landscape
The physical map of France is a testament to the country’s diverse and captivating landscapes, shaping its history, culture, and economy. From the majestic Alps to the fertile plains, from the rugged Pyrenees to the picturesque coastlines, France offers a rich tapestry of geographical wonders, inviting exploration and appreciation. Understanding the intricacies of its physical map allows for a deeper understanding of the nation’s unique character and the enduring influence of its landscape.
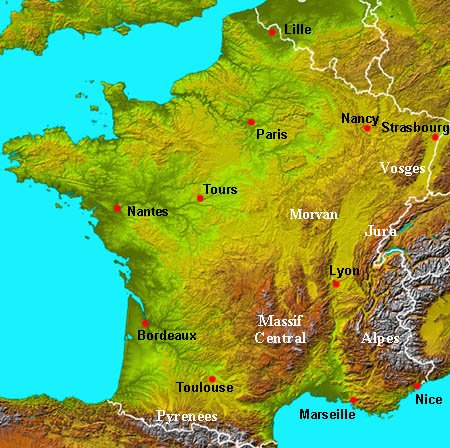

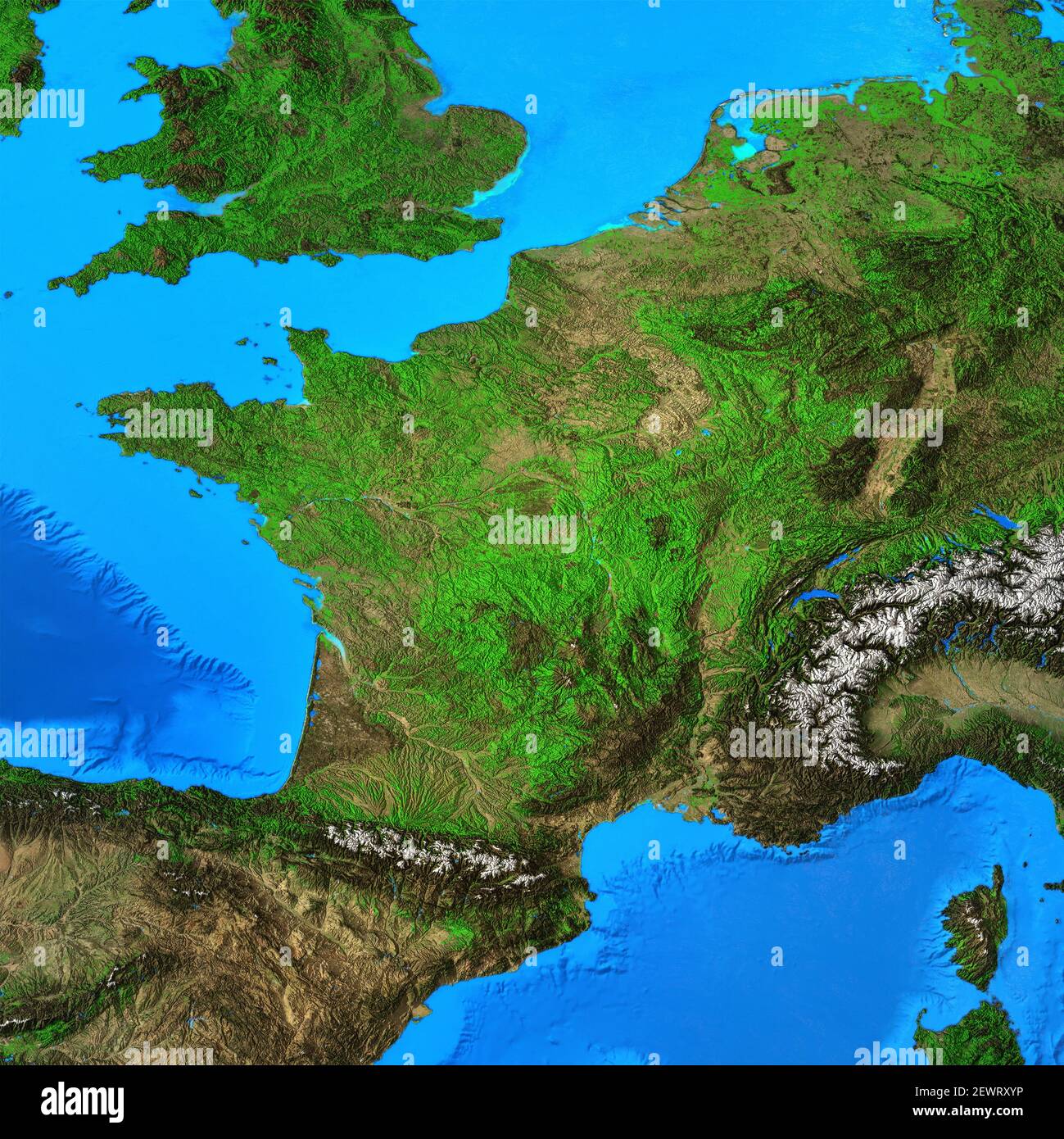
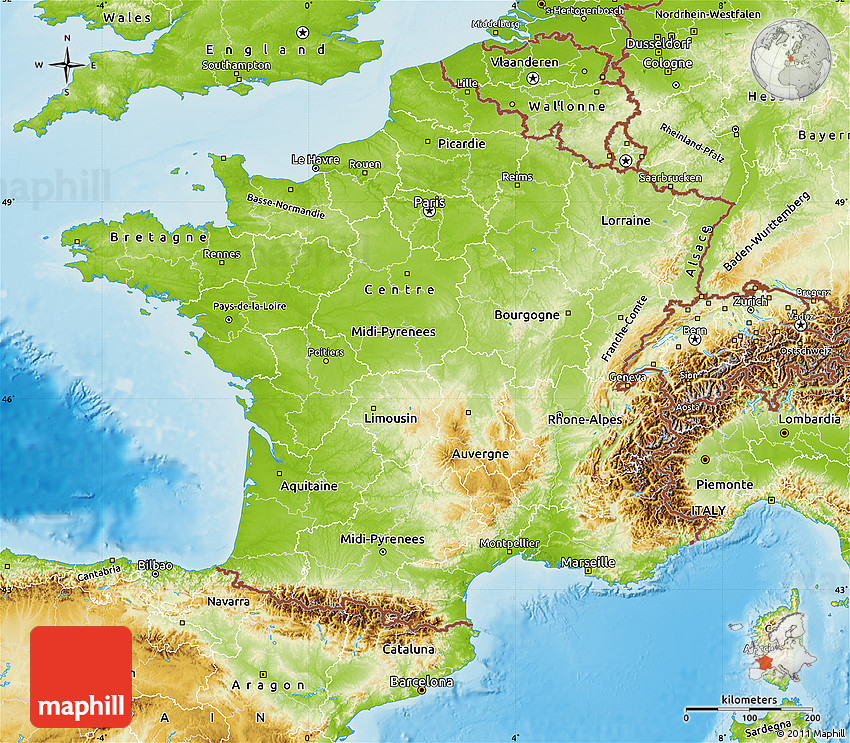



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of the French Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Map of France. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!